Understanding CMMC CCP and CMMC CCA Exams: Pathways to Cybersecurity Excellence
It’s a critical business function that requires dedicated professionals to ensure compliance with increasing regulations and to address rising cyber threats. Among these professionals, Certified CMMC Professionals (CCPs) and Certified CMMC Auditors (CCAs) are pivotal in strengthening organizations’ cybersecurity frameworks. If you’re considering pursuing a career in this space, understanding these certifications and their exams will be essential.
What is the CMMC Framework?
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a cybersecurity framework designed by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to protect sensitive federal contract information. It establishes a set of cybersecurity practices that contractors must follow to secure sensitive data. The CMMC is critical for companies seeking to do business with the DoD, as it ensures that these companies meet the highest cybersecurity standards.
To help organizations comply with this framework, a variety of CMMC professionals and auditors are needed to guide businesses through the certification process, assess compliance, and help with ongoing cybersecurity improvements. Among these roles, the Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) and Certified CMMC Auditor (CCA) are two of the most prominent certifications, each with distinct responsibilities and career opportunities.
The Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) Exam
The Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) certification is a key milestone for individuals looking to build their expertise in the CMMC framework. As a foundational certification, the CCP focuses on a comprehensive understanding of the CMMC and its associated practices, including the necessary steps to help an organization align with CMMC’s cybersecurity maturity levels.
Requirements and Training
To become a CCP, candidates must complete a 40-hour training course from an approved trainer. This training covers the essentials of CMMC, including its models, practices, and how to assess and implement compliance within an organization.
After completing the training, candidates must pass a proctored exam that tests their knowledge of the CMMC framework. The exam requires a deep understanding of various concepts, including but not limited to:
CMMC maturity levels
Security controls and practices
Risk management strategies
Organizational assessments for CMMC compliance
Investment and Benefits
Becoming a Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) requires a financial investment, typically costing several thousand dollars for both the training and the exam. This significant investment is reflective of the expertise and skills that a CCP gains through the certification process. While the CCP certification provides a solid foundation for a career in cybersecurity compliance, it also opens doors to various roles such as:
Cybersecurity consultants
CMMC assessors
Risk management professionals
While the pathway to becoming a CCP is relatively accessible, it requires a commitment to mastering the CMMC standards and being prepared for the challenges of enforcing cybersecurity practices within organizations.
The Certified CMMC Auditor (CCA) Exam
The Certified CMMC Auditor (CCA) is the pinnacle of CMMC certifications, representing the highest level of expertise in cybersecurity auditing within the framework. The transition from a Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) to a Certified CMMC Auditor (CCA) is a natural progression for those looking to specialize further and take on more complex and advanced roles in the CMMC ecosystem.
Advanced Training and Exam
To earn the CCA certification, candidates must complete an advanced 30-hour training program, which delves deep into auditing techniques and strategies specific to CMMC. This course builds on the knowledge gained during the CCP certification, taking it further to cover the nuances of CMMC audits, how to evaluate an organization’s maturity level, and how to provide guidance for organizations to improve their compliance.
After completing the training, candidates must pass a rigorous proctored exam designed to assess their understanding of advanced auditing procedures. The CCA exam is notably more challenging than the CCP exam, as it tests candidates’ ability to apply their knowledge in practical audit scenarios, ensuring they can effectively assess cybersecurity practices and ensure compliance with CMMC standards.
Financial Investment and Career Opportunities
As with the CCP, obtaining the CCA designation comes with a financial cost, which can be a couple of thousand dollars. However, this cost reflects the advanced knowledge and career opportunities that the CCA opens up. As a CCA, you will be qualified to work in roles such as:
Cybersecurity governance professionals
Senior risk management and compliance experts
Lead auditors for CMMC assessments
Consultants for large-scale cybersecurity audits
The CCA designation can significantly elevate your career by preparing you for high-level roles in organizations seeking to assess and improve their cybersecurity policies, especially those that deal with government contracts or sensitive data.
CCP vs. CCA: Key Differences
While both the CCP and CCA certifications are focused on the CMMC framework, the key differences lie in the depth of knowledge and roles that each certification prepares you for. Below is a quick comparison:
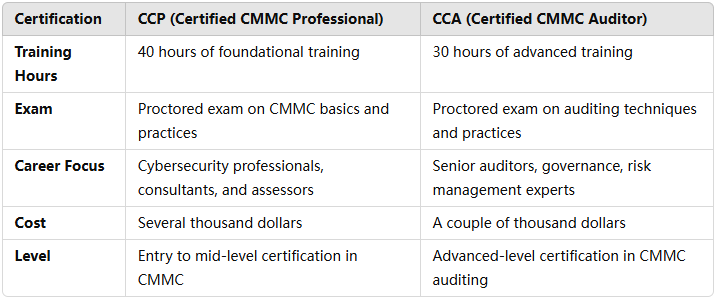
Becoming a Certified CMMC Professional (CCP) and then progressing to a Certified CMMC Auditor (CCA) is one of commitment and growth within the cybersecurity field. With cyber threats on the rise and increasing government regulations, these certifications provide professionals with the tools and knowledge needed to protect organizations and ensure compliance with CMMC standards. For those looking to further their careers in cybersecurity auditing and governance, the CCP and CCA exams offer distinct yet valuable pathways, opening doors to senior roles in cybersecurity, risk management, and compliance.
