Practice Free Professional Cloud Developer Exam Online Questions
You are planning to deploy your application in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. The application exposes an HTTP-based health check at /healthz. You want to use this health check endpoint to determine whether traffic should be routed to the pod by the load balancer.
Which code snippet should you include in your Pod configuration?
A)
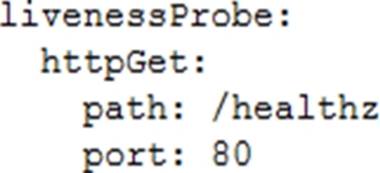
B)

C)

D)
- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
B
Explanation:
For the GKE ingress controller to use your readiness Probes as health checks, the Pods for an Ingress must exist at the time of Ingress creation. If your replicas are scaled to 0, the default health check will apply.
Your App Engine standard configuration is as follows:
service: production
instance_class: B1
You want to limit the application to 5 instances.
Which code snippet should you include in your configuration?
- A . manual_scaling:instances: 5min_pending_latency: 30ms
- B . manual_scaling:max_instances: 5idle_timeout: 10m
- C . basic_scaling:instances: 5min_pending_latency: 30ms
- D . basic_scaling:max_instances: 5idle_timeout: 10m
You are deploying a Python application to Cloud Run using Cloud Build.
The Cloud Build pipeline is shown below:

You want to optimize deployment times and avoid unnecessary steps What should you do?
- A . Remove the step that pushes the container to Artifact Registry.
- B . Add the ―cache-from argument to the Docker build step in your build config file.
- C . Store image artifacts in a Cloud Storage bucket in the same region as the Cloud Run instance.
- D . Deploy a new Docker registry in a VPC and use Cloud Build worker pools inside the VPC to run the build pipeline.
B
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/build/docs/optimize-builds/speeding-up-builds#using_a_cached_docker_image
You are writing from a Go application to a Cloud Spanner database. You want to optimize your application’s performance using Google-recommended best practices.
What should you do?
- A . Write to Cloud Spanner using Cloud Client Libraries.
- B . Write to Cloud Spanner using Google API Client Libraries
- C . Write to Cloud Spanner using a custom gRPC client library.
- D . Write to Cloud Spanner using a third-party HTTP client library.
A
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/apis/docs/cloud-client-libraries
“Cloud Client Libraries are the recommended option for accessing Cloud APIs programmatically, where available. Cloud Client Libraries use the latest client library models”
https://cloud.google.com/apis/docs/client-libraries-explained
https://cloud.google.com/go/docs/reference
You have a container deployed on Google Kubernetes Engine. The container can sometimes be slow to launch, so you have implemented a liveness probe. You notice that the liveness probe occasionally fails on launch.
What should you do?
- A . Add a startup probe.
- B . Increase the initial delay for the liveness probe.
- C . Increase the CPU limit for the container.
- D . Add a readiness probe.
B
Explanation:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-liveness-readiness-startup-probes/#configure-probes
Which service should HipLocal use to enable access to internal apps?
- A . Cloud VPN
- B . Cloud Armor
- C . Virtual Private Cloud
- D . Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/iap/docs/cloud-iap-for-on-prem-apps-overview
You have an application running in a production Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. You use Cloud Deploy to automatically deploy your application to your production GKE cluster. As part of your development process: you are planning to make frequent changes to the applications source code and need to select the tools to test the changes before pushing them to your remote source code repository.
Your toolset must meet the following requirements:
• Test frequent local changes automatically.
• Local deployment emulates production deployment.
Which tools should you use to test building and running a container on your laptop using minimal resources’?
- A . Terraform and kubeadm
- B . Docker Compose and dockerd
- C . Minikube and Skaffold
- D . kaniko and Tekton
You have an application running in a production Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster. You use Cloud Deploy to automatically deploy your application to your production GKE cluster. As part of your development process: you are planning to make frequent changes to the applications source code and need to select the tools to test the changes before pushing them to your remote source code repository.
Your toolset must meet the following requirements:
• Test frequent local changes automatically.
• Local deployment emulates production deployment.
Which tools should you use to test building and running a container on your laptop using minimal resources’?
- A . Terraform and kubeadm
- B . Docker Compose and dockerd
- C . Minikube and Skaffold
- D . kaniko and Tekton
Your operations team has asked you to create a script that lists the Cloud Bigtable, Memorystore, and Cloud SQL databases running within a project. The script should allow users to submit a filter expression to limit the results presented.
How should you retrieve the data?
- A . Use the HBase API, Redis API, and MySQL connection to retrieve database lists. Combine the results, and then apply the filter to display the results
- B . Use the HBase API, Redis API, and MySQL connection to retrieve database lists. Filter the results individually, and then combine them to display the results
- C . Run gcloud bigtable instances list, gcloud redis instances list, and gcloud sql databases list. Use a filter within the application, and then display the results
- D . Run gcloud bigtable instances list, gcloud redis instances list, and gcloud sql databases list. Use — filter flag with each command, and then display the results
D
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud/reference/topic/filters
Most gcloud commands return a list of resources on success. By default they are pretty-printed on the standard output. The –format=NAME[ATTRIBUTES](PROJECTION) and –filter=EXPRESSION flags along with projections can be used to format and change the default output to a more meaningful
result. Use the –format flag to change the default output format of a command. For details run $ gcloud topic formats.
Your team develops services that run on Google Cloud. You need to build a data processing service and will use Cloud Functions. The data to be processed by the function is sensitive. You need to ensure that invocations can only happen from authorized services and follow Google-recommended best practices for securing functions.
What should you do?
- A . Enable Identity-Aware Proxy in your project. Secure function access using its permissions.
- B . Create a service account with the Cloud Functions Viewer role. Use that service account to invoke the function.
- C . Create a service account with the Cloud Functions Invoker role. Use that service account to invoke the function.
- D . Create an OAuth 2.0 client ID for your calling service in the same project as the function you want to secure. Use those credentials to invoke the function.
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://medium.com/google-cloud/how-to-securely-invoke-a-cloud-function-from-google-kubernetes-engine-running-on-another-gcp-79797ec2b2c6
