Practice Free NSK200 Exam Online Questions
You want to provision users and groups to a Netskope tenant. You have Microsoft Active Directory servers hosted in two different forests.
Which statement is true about this scenario?
- A . You can use the Netskope Adapter Tool for user provisioning.
- B . You can use the Netskope virtual appliance for user provisioning
- C . You cannot provision users until you migrate to Azure AD or Okta.
- D . You can use SCIM version 2 for user provisioning.
D
Explanation:
You can use SCIM version 2 for user provisioning in this scenario. SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management) is a standard protocol for exchanging identity information across different cloud applications. Netskope supports SCIM version 2 and can integrate with identity providers (IdPs) that follow the same standard, such as Microsoft Azure AD, Okta, OneLogin, and Ping Identity. You can use SCIM to provision users and groups from multiple Active Directory forests to a Netskope tenant. The other options are not valid for this scenario. The Netskope Adapter Tool and the Netskope virtual appliance are used for user identification, not provisioning. They can only connect to one Active Directory forest at a time. You do not need to migrate to Azure AD or Okta to provision users, as Netskope supports other IdPs that use SCIM as well.
Reference: Provisioning Users for Netskope Client1, SCIM Integration2
To which three event types does Netskope’s REST API v2 provide access? (Choose three.)
- A . application
- B . alert
- C . client
- D . infrastructure
- E . user
ABD
Explanation:
Netskope’s REST API v2 provides access to various event types via URI paths. The event types include application, alert, infrastructure, audit, incident, network, and page. These event types can be used to retrieve data from Netskope’s cloud security platform. The event types client and user are not supported by the REST API v2.
Reference: REST API v2 Overview, Cribl Netskope Events and Alerts Integration, REST API Events and Alerts Response Descriptions
You are having issues with fetching user and group Information periodically from the domain controller and posting that information to your tenant instance in the Netskope cloud.
To begin the troubleshooting process, what would you Investigate first in this situation?
- A . On-Premises Log Parser
- B . Directory Importer
- C . DNS Connector
- D . AD Connector
B
Explanation:
The Directory Importer is a component of the Netskope Adapters that connects to the domain controller and periodically fetches user and group information to post that info to your tenant instance in the Netskope cloud1. If you are having issues with this process, the first thing you should investigate is the Directory Importer itself. You can check the status of the Directory Importer service, the configuration file, the logs, and the connectivity to the domain controller and the Netskope cloud2. Therefore, option B is correct and the other options are incorrect.
Reference: Configure Directory Importer – Netskope Knowledge Portal, Troubleshooting Directory Importer – Netskope Knowledge Portal
The risk team at your company has determined that traffic from the sales team to a custom Web application should not be inspected by Netskope. All other traffic to the Web application should continue to be inspected.
In this scenario, how would you accomplish this task?
- A . Create a Do Not Decrypt Policy using User Group and Domain in the policy page.
- B . Create a Do Not Decrypt Policy using Application in the policy page and a Steering Exception for Group
- C . Create a Do Not Decrypt Policy using Destination IP and Application in the policy page.
- D . Create a Do Not Decrypt Policy using Source IP and Application in the policy page.
A
Explanation:
To prevent traffic from the sales team to a custom Web application from being inspected by Netskope, you need to create a Do Not Decrypt Policy using User Group and Domain in the policy page. A Do Not Decrypt Policy allows you to specify the traffic you want to leave encrypted and not further analyzed by Netskope via the Real-time Protection policies3. You can use the User Group criteria to match the sales team members and the Domain criteria to match the custom Web application. This way, only the traffic from the sales team to the custom Web application will be exempted from decryption, while all other traffic to the Web application will continue to be inspected.
Your company has many users that are remote and travel often. You want to provide the greatest visibility into their activities, even while traveling.
Using Netskope, which deployment method would be used in this scenario?
- A . Use a Netskope client.
- B . Use an IPsec tunnel.
- C . Use a GRE tunnel.
- D . Use proxy chaining.
A
Explanation:
Deploying the Netskope client on remote and traveling users’ devices provides the highest level of visibility into their activities regardless of their location. The Netskope client can steer traffic securely to the Netskope Security Cloud, offering consistent monitoring and protection.
Your customer implements Netskope Secure Web Gateway to secure all Web traffic. While they have created policies to block certain categories, there are many new sites available dally that are not yet categorized. The customer’s users need quick access and cannot wait to put in a request to gain access requiring a policy change or have the site’s category changed.
To solve this problem, which Netskope feature would provide quick, safe access to these types of sites?
- A . Netskope Cloud Firewall (CFW)
- B . Netskope Remote Browser Isolation (RBI)
- C . Netskope Continuous Security Assessment (CSA)
- D . Netskope SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM)
B
Explanation:
To solve the problem of providing quick, safe access to uncategorized and risky websites, the Netskope feature that the customer should use is Netskope Remote Browser Isolation (RBI). Netskope RBI is a part of the Netskope Secure Web Gateway offering that intercepts a user’s browsing session to a website, acting as a proxy that fetches the content for that user and renders the content in an isolated browsing instance. The rendered content is delivered to the user’s browser as a safe stream of pixels. This safely silos the end user’s device and the enterprise network and systems, separating it from their browsing activity and restricting the ability of an attacker to establish control and / or breach other systems and exfiltrate data1. Netskope RBI can be easily invoked with an ‘isolate’ policy action within the Netskope Security Cloud for any website category or domain2. Therefore, option B is correct and the other options are incorrect.
Reference: Remote Browser Isolation – Netskope Knowledge Portal, Netskope Remote Browser Isolation – Netskope
Which object would be selected when creating a Malware Detection profile?
- A . DLP profile
- B . File profile
- C . Domain profile
- D . User profile
B
Explanation:
A file profile is an object that contains a list of file hashes that can be used to create a malware detection profile. A file profile can be configured as an allowlist or a blocklist, depending on whether the files are known to be benign or malicious. A file profile can be created in the Settings > File Profile page1. A malware detection profile is a set of rules that define how Netskope handles malware incidents. A malware detection profile can be created in the Policies > Threat Protection > Malware Detection Profiles page2. To create a malware detection profile, one needs to select a file profile as an allowlist or a blocklist, along with the Netskope malware scan option. The other options are not objects that can be selected when creating a malware detection profile.
Your company wants to deploy Netskope using a tunnel because you have a mixture of device operating systems. You also do not want to enable encryption because you want to maximize bandwidth.
- A . explicit proxy
- B . IPsec
- C . proxy chaining
- D . GRE
D
Explanation:
GRE tunnels are the optimal choice in this scenario. GRE is a commonly used, non-encrypted tunneling protocol that supports a variety of device operating systems, and it offers efficient bandwidth usage without encryption overhead, which aligns with the company’s requirements.
An engineering firm is using Netskope DLP to identify and block sensitive documents, including schematics and drawings. Lately, they have identified that when these documents are blocked, certain employees may be taking screenshots and uploading them. They want to block any screenshots from being uploaded.
Which feature would you use to satisfy this requirement?
- A . exact data match (EDM)
- B . document fingerprinting
- C . ML image classifier
- D . optical character recognition (OCR)
C
Explanation:
To block any screenshots from being uploaded, the engineering firm should use the ML image classifier feature of Netskope DLP. This feature uses machine learning to detect sensitive information within images, such as screenshots, whiteboards, passports, driver’s licenses, etc. The firm can create a DLP policy that blocks any image upload that matches the screenshot classifier. This will prevent employees from circumventing the DLP controls by taking screenshots of sensitive documents.
Reference: Improved DLP Image Classifiers, Netskope Data Loss Prevention, The Importance of a Machine Learning-Based Source Code Classifier
Review the exhibit.
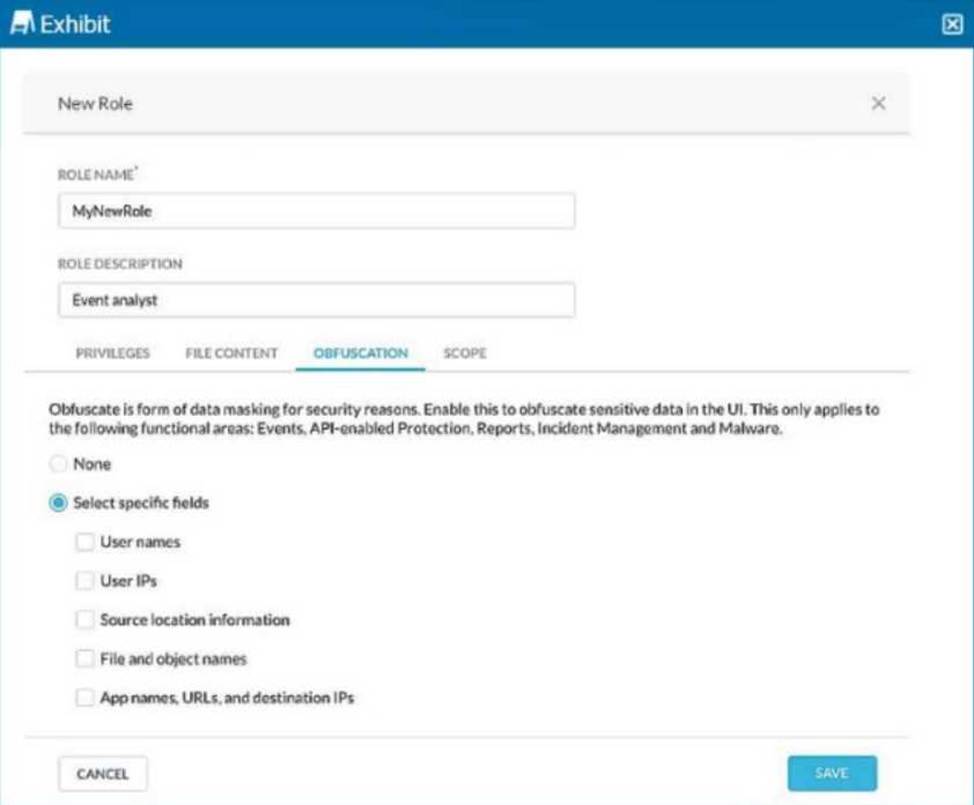
You are asked to create a new role that allows analysts to view Events and Reports while providing user privacy. You need to avoid directly exposing identities and user location information.
Which three fields must you obfuscate in this scenario? (Choose three.)
- A . User IPs
- B . User names
- C . App names, URLs, and destination IPs
- D . File and object names
- E . Source location information
ABE
Explanation:
To ensure user privacy in the Events and Reports view, obfuscate sensitive information like User IPs, User names, and Source location information. This helps protect identities and prevent location tracking of users while allowing visibility into activity details.
