Practice Free NSE7_PBC-7.2 Exam Online Questions
You are configuring the failover settings on a FortiGate active-passive SDN connector solution in Microsoft Azure.
Which two mandatory settings are required after the initial deployment? (Choose two)
- A . Subscription-id
- B . FortiGate license file
- C . Active FortiGate serial number
- D . Resource group name
A, D
Explanation:
For configuring the failover settings on a FortiGate active-passive SDN connector solution in Microsoft Azure, the two mandatory settings required after the initial deployment are:
Refer to the exhibit.
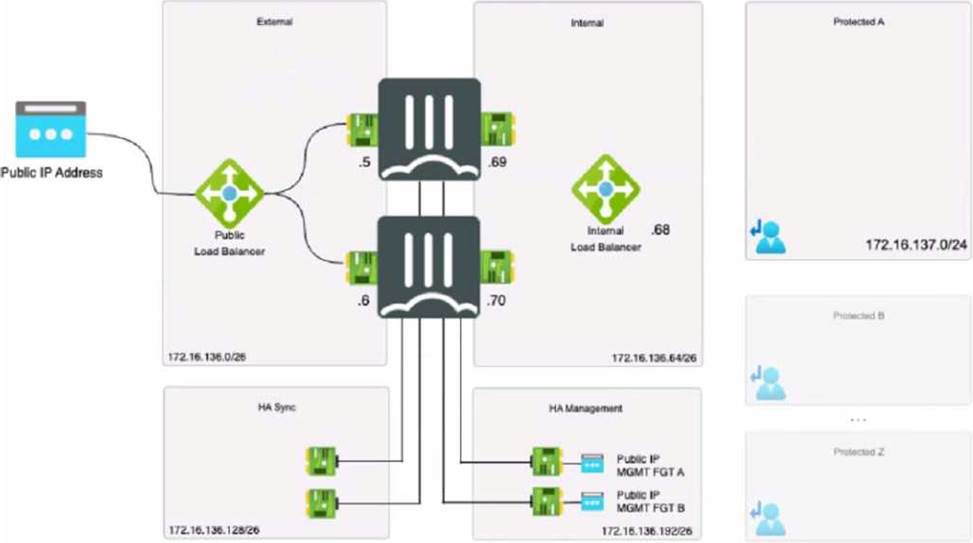
The exhibit shows an active-passive high availability FortiGate pair with external and internal Azure load balancers. There is no SDN connector used in this solution.
Which configuration should the administrator implement?
- A . Lambda IP address with one static route.
- B . Probe IP address with two static routes
- C . Probe IP address with one BGP route
- D . Public load balancer IP address with two BGP routes.
B
Explanation:
Based on the provided exhibit showing an active-passive FortiGate High Availability (HA) pair with external and internal Azure load balancers and without the use of an SDN connector, the administrator should implement a Probe IP address with two static routes (Option B).
Probe IP Address: Azure load balancers use a health probe to determine the health of the instances in the backend pool. The health probe ensures that the load balancer only directs traffic to the active (primary) FortiGate in an HA pair.
Two Static Routes: Given that this is an active-passive setup, static routing should be used to ensure deterministic traffic flow. Two static routes would be configured to ensure that traffic can flow to the active unit and be correctly routed to the protected subnets in failover scenarios.
Reference: The recommendation for using a Probe IP address with static routes is based on Azure’s best practices for load balancer configuration, particularly for HA scenarios, as well as on Fortinet’s HA documentation for cloud deployments. This setup ensures high availability while allowing proper traffic distribution based on the health probe’s findings.
An administrator would like to keep track of sensitive data files located in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 bucket and protect it from malware.
Which Fortinet product or feature should the administrator use?
- A . FortiCNP application control policies
- B . FortiCNP web sensitive polices
- C . FortiCNP DLP policies
- D . FortiCNP compliance scanning policies
C
Explanation:
To keep track of sensitive data files located in AWS S3 buckets and protect them from malware, the
administrator should use:
C. FortiCNP DLP policies.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP policies are designed to detect and prevent unauthorized access or sharing of sensitive data. In the context of AWS S3, DLP policies can be used to scan for sensitive information stored in S3 objects and enforce protective measures to prevent data exfiltration or compromise.
FortiCNP Integration: FortiCNP is Fortinet’s cloud-native protection platform that offers security and compliance solutions across cloud environments. By applying DLP policies within FortiCNP, the administrator can ensure sensitive data within S3 is monitored and protected consistently.
Reference: Fortinet’s FortiCNP documentation provides information on implementing DLP policies within cloud environments, highlighting the capabilities for protecting sensitive data within cloud storage services like AWS S3.
Refer to the exhibit
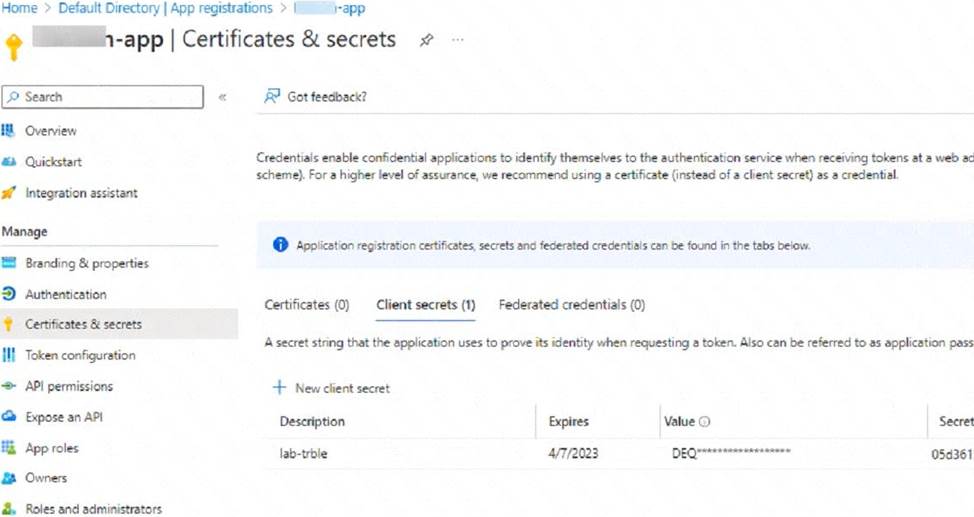
An administrator is trying to deploy a FortiGate VM in Microsoft Azure using Terraform However, during the configuration, the Azure client secret is no longer visible in the Azure portal.
How would the administrator obtain the Azure client secret to configure on Terratorm?
- A . The administrator must create a new Azure account
- B . Log in to the Azure CLI with power user to obtain the client secret
- C . The administrator can create a new client secret
- D . The administrator must obtain the client secret through Azure Cloud Shell.
C
Explanation:
The Azure client secret is a one-time value that is only visible when it is created. If the administrator loses or forgets the client secret, they cannot retrieve it from the Azure portal. However, they can create a new client secret and use it to configure Terraform. To create a new client secret, they need to follow these steps12:
Sign in to the Azure portal and navigate to the Azure Active Directory service.
Select the application name under the App Registrations.
Select Certificates & Secrets > New client secret to create a new client secret. Add a description and an expiration date for the client secret and select Add. Copy the value of the new client secret immediately as it will not be shown again.
Reference: Generate new Client Secret and link to key-vault | Microsoft Learn
Azure Quickstart – Set and retrieve a secret from Key Vault using Azure portal | Microsoft Learn
Refer to the exhibit
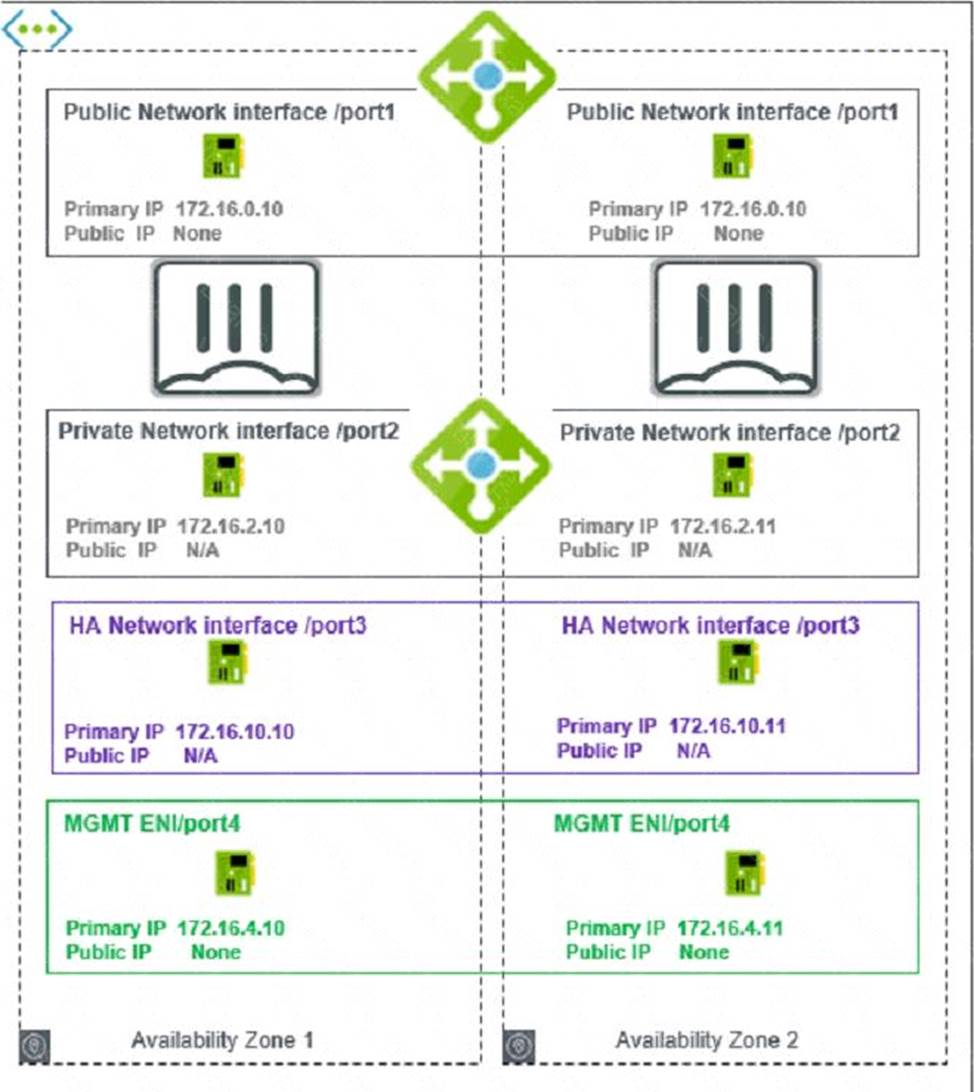
You are deploying two FortiGate VMS in HA active-passive mode with load balancers in Microsoft Azure
Which two statements are true in this load balancing scenario? (Choose two.)
- A . The FortiGate public IP is the next-hop for all the traffic.
- B . An internal load balancer listener is the next-hop for outgoing traffic.
- C . You must add a route to the Microsoft VIP used for the health check.
- D . A dedicated management interface can be used for load balancing.
BD
Explanation:
A is incorrect because the FortiGate public IP is not the next-hop for all the traffic. The FortiGate public IP is only used for incoming traffic from the internet. The Azure load balancer distributes the incoming traffic to the active FortiGate VM based on a health probe123. The FortiGate public IP is not used for outgoing traffic or internal traffic.
B is correct because an internal load balancer listener is the next-hop for outgoing traffic. The internal load balancer listener is configured with a floating IP address that is assigned to the active FortiGate VM. The internal load balancer listener also has a health probe to monitor the status of the FortiGate VMs123. The internal load balancer listener forwards the outgoing traffic to the internet through the public load balancer.
C is incorrect because you do not need to add a route to the Microsoft VIP used for the health check. The Microsoft VIP is an internal IP address that is used by the Azure load balancer to send health probes to the FortiGate VMs123. The Microsoft VIP is not reachable from outside the Azure network and does not require any routing configuration on the FortiGate VMs.
D is correct because a dedicated management interface can be used for load balancing. In this deployment, port4 is used as a dedicated management interface that connects to the management network3. The dedicated management interface can be used to access the FortiGate VMs for configuration and monitoring purposes. The dedicated management interface can also be used to synchronize the configuration and session information between the primary and secondary devices in an HA cluster2.
Which two attachments are necessary to connect a transit gateway to an existing VPC with BGP? (Choose two)
- A . A transport attachment
- B . A BGP attachment
- C . A connect attachment
- D . A GRE attachment
AC
Explanation:
The correct answer is A and C. A transport attachment and a connect attachment are necessary to connect a transit gateway to an existing VPC with BGP.
According to the AWS documentation for Transit Gateway, a transit gateway is a network transit hub that connects VPCs and on-premises networks. To connect a transit gateway to an existing VPC with BGP, you need to do the following steps:
Create a transport attachment. A transport attachment is a resource that connects a VPC or VPN to a transit gateway. You can specify the BGP options for the transport attachment, such as the autonomous system number (ASN) and the BGP peer IP address.
Create a connect attachment. A connect attachment is a resource that enables you to use your own appliance to provide network services for traffic that flows through the transit gateway. You can use a connect attachment to route traffic between the transport attachment and your appliance using GRE tunnels and BGP.
The other options are incorrect because:
A BGP attachment is not a valid type of attachment for a transit gateway. BGP is a protocol that enables dynamic routing between the transit gateway and the VPC or VPN.
A GRE attachment is not a valid type of attachment for a transit gateway. GRE is a protocol that encapsulates packets for tunneling purposes. GRE tunnels are established between the connect attachment and your appliance.
: [Transit Gateways – Amazon Virtual Private Cloud] : [Transit Gateway Connect – Amazon Virtual Private Cloud]
Refer to the exhibit

An administrator deployed an HA active-active load balance sandwich in Microsoft Azure. The setup requires configuration synchronization between devices-
What are two outcomes from the configured settings? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate-VM instances are scaled out automatically according to predefined workload levels.
- B . FortiGate A and FortiGate B are two independent devices.
- C . By default, FortiGate uses FGCP
- D . It does not synchronize the FortiGate hostname
BD
Explanation:
B) FortiGate A and FortiGate B are two independent devices. This means that they are not part of a cluster or a high availability group, and they do not share the same configuration or state information. They are configured as standalone FortiGates with standalone configuration synchronization enabled1. This feature allows them to synchronize most of their configuration settings with each other, except for some settings that identify the FortiGate to the network, such as the hostname1.
D. It does not synchronize the FortiGate hostname. This is one of the settings that are excluded from the standalone configuration synchronization, as mentioned above. The hostname is a unique identifier for each FortiGate device, and it should not be changed by the synchronization process1.
The other options are incorrect because:
FortiGate-VM instances are not scaled out automatically according to predefined workload levels. This is a feature of the auto scaling solution for FortiGate-VM on Azure, which requires a different deployment and configuration than the one shown in the exhibit2. The exhibit shows a static deployment of two FortiGate-VM instances behind an Azure load balancer, which does not support auto scaling.
By default, FortiGate does not use FGCP. FGCP stands for FortiGate Clustering Protocol, which is used to synchronize configuration and state information between FortiGate devices in a cluster or a high availability group3. However, the exhibit shows that the FortiGates are not in a cluster or a high availability group, and they use standalone configuration synchronization instead of FGCP.
A customer would like to use FortiGate fabric integration With FortiCNP
When configuring a FortiGate VM to add to FortiCNP, which three mandatory configuration steps must you follow on FortiGate? (Choose three.)
- A . Enable send logs-
- B . Create and IPS sensor and a firewall policy
- C . Create an IPsec tunnel.
- D . Create an SSL]SSH inspection profile.
- E . Enable two-factor authentication.
ABD
Explanation:
To configure a FortiGate VM to add to FortiCNP, you need to perform three steps on FortiGate:
Enable send logs in FortiGate to allow FortiCNP to receive the IPS logs from FortiGate.
Create an SSL/SSH inspection profile on FortiGate to inspect the encrypted traffic and apply IPS protection.
Create an IPS sensor and a firewall policy on FortiGate to enable IPS detection and prevention for the
traffic.
Reference: FortiCNP 22.4.a Administration Guide, page 22-24
FortiGate IPS Administration Guide, page 9-10
Refer to the exhibit
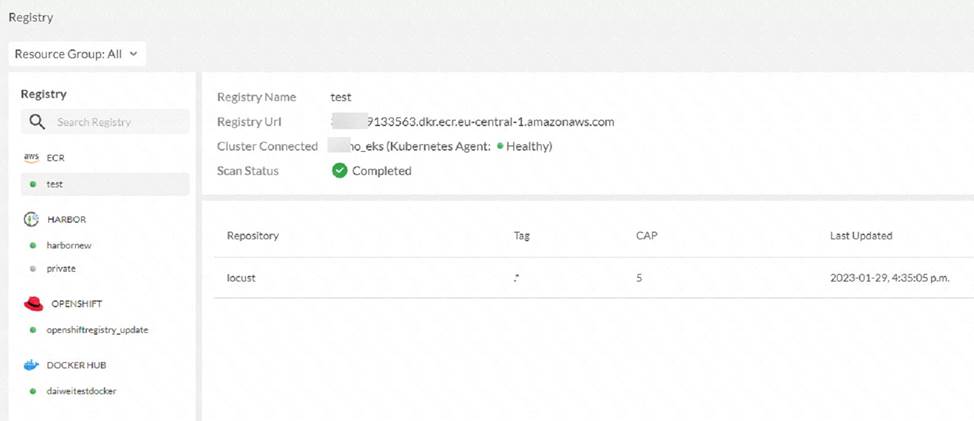
The exhibit shows the results of a FortiCNP registry scan
Which two statements are correct? (Choose two)
- A . When adding a repository, you can leave the Tag section blank to scan all images-
- B . The registry scan is part of the FortiCNP cloud protection.
- C . The registry scan is part of the FortiCNP container protection.
- D . When adding a repository, you can add a minimum number of images to be imported through the CAP section.
AC
Explanation:
The exhibit shows the results of a FortiCNP registry scan, which is part of the FortiCNP container protection. FortiCNP’s Container Protection provides deep visibility into the security posture of container registries and images1. The registry scan utilizes Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) index regularly updated by NVD to detect underlying vulnerabilities, security flaws, and provides security best practices2. The registry scan is performed at the registry level, and it can scan all images in a repository if the Tag section is left blank when adding a repository2. The CAP section stands for Container Assurance Policy, which defines the minimum number of images to be scanned per repository3. Therefore, the correct statements are A andC.
Reference: Container Image Scan | FortiCNP 22.3.a, FortiCNP, Cloud Native Application Protection Platform | FortiCNP
What are two main features in Amazon Web Services (AWS) network access control lists (ACLs)? (Choose two.)
- A . You cannot use Network ACL and Security Group at the same time.
- B . The default network ACL is configured to allow all traffic
- C . Network ACLs are stateless, and inbound and outbound rules are used for traffic filtering
- D . Network ACLs are tied to an instance
BC
Explanation:
B) The default network ACL is configured to allow all traffic. This means that when you create a VPC, AWS automatically creates a default network ACL for that VPC, and associates it with all the subnets in the VPC1. By default, the default network ACL allows all inbound and outbound IPv4 traffic and, if applicable, IPv6 traffic1. You can modify the default network ACL, but you cannot delete it1. C. Network ACLs are stateless, and inbound and outbound rules are used for traffic filtering. This means that network ACLs do not keep track of the traffic that they allow or deny, and they evaluate each packet separately1. Therefore, you need to create both inbound and outbound rules for each type of traffic that you want to allow or deny1. For example, if you want to allow SSH traffic from a specific IP address to your subnet, you need to create an inbound rule to allow TCP port 22 from that IP address, and an outbound rule to allow TCP port 1024-65535 (the ephemeral ports) to that IP address2.
The other options are incorrect because:
You can use network ACL and security group at the same time. Network ACL and security group are two different types of security layers for your VPC that can work together to control traffic3. Network ACL acts as a firewall for your subnets, while security group acts as a firewall for your instances3. You can use both of them to create a more granular and effective security policy for your VPC.
Network ACLs are not tied to an instance. Network ACLs are associated with subnets, not instances1. This means that network ACLs apply to all the instances in the subnets that they are associated with1. You cannot associate a network ACL with a specific instance. However, you can associate a security group with a specific instance or multiple instances3.
