Practice Free NetSec-Generalist Exam Online Questions
Which step is necessary to ensure an organization is using the inline cloud analysis features in its Advanced Threat Prevention subscription?
- A . Configure Advanced Threat Prevention profiles with default settings and only focus on high-risk traffic to avoid affecting network performance.
- B . Enable SSL decryption in Security policies to inspect and analyze encrypted traffic for threats.
- C . Update or create a new anti-spyware security profile and enable the appropriate local deep – learning models.
- D . Disable anti-spyware to avoid performance impacts and rely solely on external threat intelligence.
B
Explanation:
The inline cloud analysis feature in the Advanced Threat Prevention subscription enables real-time threat detection using machine learning (ML) and deep-learning models. However, for it to be effective, the firewall must decrypt encrypted traffic to analyze potential threats hidden within TLS/SSL connections.
Why SSL Decryption is Necessary?
Threat actors often hide malware and exploits in encrypted traffic.
Without SSL decryption, inline cloud analysis cannot inspect encrypted threats.
Decryption allows full visibility into traffic for inline deep-learning threat detection.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect?
Which two components of a Security policy, when configured, allow third-party contractors access to internal applications outside business hours? (Choose two.)
- A . User-ID
- B . Schedule
- C . Service
- D . App-ID
AB
Explanation:
To allow third-party contractors access to internal applications outside business hours, the Security Policy must include:
User-ID C
Identifies specific users (e.g., third-party contractors) and applies access rules accordingly. Ensures that only authenticated users from the contractor group receive access. Schedule C
Specifies the allowed access time frame (e.g., outside business hours: 6 PM – 6 AM).
Ensures that contractors can only access applications during designated off-hours.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect?
C. Service ❌
Incorrect, because Service defines ports and protocols, not user identity or time-based access control.
D. App-ID ❌
Incorrect, because App-ID identifies and classifies applications, but does not restrict access based on user identity or time.
Reference to Firewall Deployment and Security Features:
Firewall Deployment C Ensures contractors access internal applications securely via User-ID and Schedule.
Security Policies C Implements granular time-based and identity-based access control.
VPN Configurations C Third-party contractors may access applications through GlobalProtect VPN.
Threat Prevention C Reduces attack risks by limiting access windows for third-party users.
WildFire Integration C Ensures downloaded contractor files are scanned for threats.
Zero Trust Architectures C Supports least-privilege access based on user identity and time restrictions.
Thus, the correct answers are:
✅ A. User-ID
✅ B. Schedule
A company currently uses Prisma Access for its mobile users. A use case is discovered in which mobile users will need to access an internal site, but there is no existing network communication between the mobile users and the internal site.
Which Prisma Access functionality needs to be deployed to enable routing between the mobile users and the internal site?
- A . Interconnect license
- B . Service connection
- C . Autonomous Digital Experience Manager (ADEM)
- D . Security processing node
B
Explanation:
Prisma Access provides secure remote access for mobile users, but by default, mobile users cannot access internal sites unless explicitly configured.
How Service Connection Enables Routing Between Mobile Users and Internal Sites:
Service Connection establishes a secure tunnel between Prisma Access and the internal network.
Allows direct routing between mobile users and internal applications.
Enables access without requiring additional VPN connections.
Ensures that Prisma Access can securely route traffic between mobile users and the internal site.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect?
All branch sites in an organization have NGFWs running in production, and the organization wants to centralize its logs with Strata Logging Service.
Which type of certificate is required to ensure connectivity from the NGFWs to Strata Logging Service?
- A . Device
- B . Server
- C . Root
- D . Intermediate CA
C
Explanation:
To centralize logs from NGFWs to the Strata Logging Service, a Root Certificate Authority (Root CA) certificate is required to ensure secure connectivity between firewalls and Palo Alto Networks’ cloud-based Strata Logging Service.
Why a Root Certificate is Required?
Authenticates Firewall Connections C Ensures NGFWs trust the Strata Logging Service.
Enables Encrypted Communication C Protects log integrity and confidentiality.
Prevents Man-in-the-Middle Attacks C Ensures secure TLS encryption for log transmission.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect?
All branch sites in an organization have NGFWs running in production, and the organization wants to centralize its logs with Strata Logging Service.
Which type of certificate is required to ensure connectivity from the NGFWs to Strata Logging Service?
- A . Device
- B . Server
- C . Root
- D . Intermediate CA
C
Explanation:
To centralize logs from NGFWs to the Strata Logging Service, a Root Certificate Authority (Root CA) certificate is required to ensure secure connectivity between firewalls and Palo Alto Networks’ cloud-based Strata Logging Service.
Why a Root Certificate is Required?
Authenticates Firewall Connections C Ensures NGFWs trust the Strata Logging Service.
Enables Encrypted Communication C Protects log integrity and confidentiality.
Prevents Man-in-the-Middle Attacks C Ensures secure TLS encryption for log transmission.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect?
Which two configurations are required when creating deployment profiles to migrate a perpetual VM-Series firewall to a flexible VM? (Choose two.)
- A . Choose "Fixed vCPU Models" for configuration type.
- B . Allocate the same number of vCPUs as the perpetual VM.
- C . Deploy virtual Panorama for management.
- D . Allow only the same security services as the perpetual VM.
AC
Explanation:
Migrating a perpetual VM-Series firewall license to a flexible VM-Series license involves specific configurations to ensure a seamless transition. The process requires careful planning and execution to align with Palo Alto Networks’ licensing models and deployment strategies.
A company has an ongoing initiative to monitor and control IT-sanctioned SaaS applications. To be successful, it will require configuration of decryption policies, along with data filtering and URL Filtering Profiles used in Security policies.
Based on the need to decrypt SaaS applications, which two steps are appropriate to ensure success? (Choose two.)
- A . Validate which certificates will be used to establish trust.
- B . Configure SSL Forward Proxy.
- C . Create new self-signed certificates to use for decryption.
- D . Configure SSL Inbound Inspection.
AB
Explanation:
To successfully monitor and control IT-sanctioned SaaS applications, decryption policies must be configured, along with Data Filtering and URL Filtering Profiles in Security Policies.
Why These Two Steps Are Necessary?
Validate which certificates will be used to establish trust ( ✔️ Correct)
When configuring SSL decryption, the firewall must establish trust between endpoints and the proxy certificate.
This involves deploying a trusted root certificate to internal user devices to avoid SSL/TLS warnings. Configure SSL Forward Proxy ( ✔️ Correct)
SSL Forward Proxy is required for decrypting outbound HTTPS traffic to SaaS applications.
It allows policy enforcement on SaaS-bound traffic, including URL filtering, data filtering, and application control.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect?
C. Create new self-signed certificates to use for decryption. ❌
Incorrect, because self-signed certificates are not recommended for large-scale deployments.
Enterprise deployments should use an internal CA or a trusted third-party CA.
D. Configure SSL Inbound Inspection. ❌
Incorrect, because SSL Inbound Inspection is used for decrypting traffic destined for internal servers, not SaaS application traffic.
SaaS applications are external services, so SSL Forward Proxy is required instead.
Reference to Firewall Deployment and Security Features:
Firewall Deployment C Enforces SSL decryption policies on SaaS traffic.
Security Policies C Applies URL filtering, threat prevention, and data filtering on decrypted traffic.
VPN Configurations C Ensures GlobalProtect users’ traffic is inspected securely.
Threat Prevention C Detects malware, credential theft, and unauthorized data exfiltration in SaaS traffic.
WildFire Integration C Analyzes decrypted files for malware threats.
Panorama C Provides centralized management of SaaS decryption policies.
Zero Trust Architectures C Ensures only approved SaaS applications are accessed securely.
Thus, the correct answers are:
✅ A. Validate which certificates will be used to establish trust.
✅ B. Configure SSL Forward Proxy.
An IT security administrator is maintaining connectivity and security between on-premises infrastructure, private cloud, and public cloud environments in Strata Cloud Manager (SCM).
Which set of practices must be implemented to effectively manage certificates and ensure secure communication across these segmented environments?
- A . Use a centralized certificate management solution. Regularly renew and update certificates.
Employ strong encryption protocols. - B . Use self-signed certificates for all environments. Renew certificates manually once a year.
Avoid automating certificate management to maintain control. - C . Rely on the cloud provider’s default certificates.
Avoid renewing certificates to reduce overhead and complexity. Manage certificate deployment manually. - D . Implement different certificate authorities (CAs) for each environment. Use default certificate settings.
Renew certificates only when they expire to reduce overhead and complexity.
A
Explanation:
When managing connectivity and security between on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud environments in Strata Cloud Manager (SCM), proper certificate management is essential to:
Ensure encrypted communication across segmented environments Prevent expired or weak certificates from becoming security vulnerabilities Simplify management across multiple cloud and on-premise networks.
Why is Centralized Certificate Management the Correct Choice?
A centralized solution automates certificate deployment, renewal, and monitoring.
Regular renewal prevents security gaps caused by expired certificates.
Strong encryption ensures secure communication between environments.
Other Answer Choices Analysis
(B) Use self-signed certificates, renew manually, and avoid automation C
High security risk: Self-signed certificates are not trusted across hybrid environments.
Manual renewal is error-prone and can lead to outages.
(C) Rely on cloud provider’s default certificates, avoid renewal C Cloud provider certificates do not cover on-premises security.
Avoiding renewal increases the risk of certificate expiration and security breaches.
(D) Use different CAs for each environment, renew only when expired C
Managing multiple CAs increases complexity and does not provide unified security.
Delaying renewal can result in expired certificates causing outages.
Reference and Justification:
Firewall Deployment & Security Policies C Secure communication requires valid, trusted certificates.
Zero Trust Architectures C Consistent certificate management enforces encrypted, trusted communication.
Thus, A centralized certificate management solution (A) is the correct answer, as it ensures secure, automated, and regularly updated encryption across on-prem, private, and public cloud environments.
Based on the image below, which source IP address will be seen in the data filtering logs of the Cloud NGFW for AWS with the default rulestack settings?
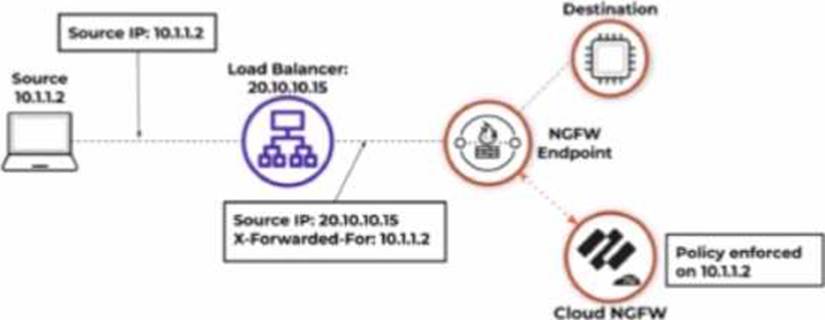
- A . 10.1.1.3
- B . 20.10.10.16
- C . 20.10.10.15
- D . 10.1.1.2
C
Explanation:
Based on the image and default rulestack settings of the Cloud NGFW for AWS, the source IP address seen in the data filtering logs will be 20.10.10.15, which is the IP address of the load balancer.
Default Rulestack Behavior: By default, the rulestack settings do not inspect or preserve the original client IP (e.g., 10.1.1.2) in the "X-Forwarded-For" header. Instead, the load balancer’s IP (20.10.10.15) is recorded as the source IP.
Logging Mechanism: Unless explicitly configured to parse the "X-Forwarded-For" header, the firewall’s logs will reflect the IP address of the device directly sending the traffic to the NGFW (the load balancer in this case).
Reference: Cloud NGFW for AWS Documentation
Data Filtering Logs and Source IP Behavior
