Practice Free NCP-DB-6.5 Exam Online Questions
Where are two locations an administrator would find the size of a Source Database? (Choose two.)
- A . On the Era Dashboard Database Summary Table under Source Database.
- B . Under the Capacity widget on the Database Server VMS > List database summary page.
- C . On the Databases > Sources table.
- D . On the Profiles > Database Parameters list for the assigned DB Parameter Profile.
A, C
Explanation:
Option A: On the Era Dashboard Database Summary Table under Source Database. The dashboard provides a summary of the databases, including their sizes1.
Option B: Under the Capacity widget on the Database Server VMS > List database summary page. While this might provide information about the capacity, it does not specifically provide the size of a Source Database.
Option C: On the Databases > Sources table. This table provides detailed information about the databases, including their sizes1.
Option D: On the Profiles > Database Parameters list for the assigned DB Parameter Profile. This list provides parameters for the database but does not provide the size of a Source Database.
Where are two locations an administrator would find the size of a Source Database? (Choose two.)
- A . On the Era Dashboard Database Summary Table under Source Database.
- B . Under the Capacity widget on the Database Server VMS > List database summary page.
- C . On the Databases > Sources table.
- D . On the Profiles > Database Parameters list for the assigned DB Parameter Profile.
A, C
Explanation:
Option A: On the Era Dashboard Database Summary Table under Source Database. The dashboard provides a summary of the databases, including their sizes1.
Option B: Under the Capacity widget on the Database Server VMS > List database summary page. While this might provide information about the capacity, it does not specifically provide the size of a Source Database.
Option C: On the Databases > Sources table. This table provides detailed information about the databases, including their sizes1.
Option D: On the Profiles > Database Parameters list for the assigned DB Parameter Profile. This list provides parameters for the database but does not provide the size of a Source Database.
An administrator needs to patch a PostgreSQL database server VM from version 13.4 to 13.8.
What is the first step within the NDB patching workflow to accomplish this task?
- A . Create a new Software Profile with PostgreSQL 13.8.
- B . Create a maintenance window and add this PostgreSQL server 13.8 to the queue.
- C . Create a new Database Parameters profile for PostgreSQL server 13.8.
- D . Create a Software Profile Version with PostgreSQL 13.8.
D
Explanation:
NDB supports patching for PostgreSQL database instances. Patching for PostgreSQL is validated on VMs provisioned by NDB (greenfield deployments). To patch PostgreSQL database server VMs, you must create a software profile version by uploading the PostgreSQL update file in NDB. You can then use the PostgreSQL update to patch other database server VMs or provision a new database server VM with the updated software profile. The first step in the NDB patching workflow is to create a software profile version with the desired PostgreSQL version.
Reference: Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) Course Details, Section 4.1: NDB Patching Overview Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) Certification Details, Objective 4.1: Perform Database Patching
Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) YouTube Playlist, Video 4.1: NDB Patching Overview Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) User Guide, Section 4.4: Patch PostgreSQL Database Software
Which two statements best describe the features and functionality of Era Oracle patching? (Choose two.)
- A . Era does not require native Oracle Utility OpatchAuto to create the patch profile,
- B . Era patching can be automated using REST API/CLI for scheduled patching many Oracle servers in a fleet patching scenario,
- C . Era patching for Oracle databases has automatic rollback if any of the steps in the patching workflow fails.
- D . Era Oracle fleet patching can be rolled back if issues ere encountered after successful patching.
B, C
Explanation:
Nutanix Era provides a unified database operating model that delivers simplicity, performance, availability, and security across private and public clouds1. It standardizes your Oracle database ecosystem by mass patching the databases with one-click simplicity2. This includes the following features:
Automated Patching: Era patching can be automated using REST API/CLI for scheduled patching many Oracle servers in a fleet patching scenario1. This allows for the standardization of your Oracle database ecosystem by mass patching the databases with one-click simplicity2.
Automatic Rollback: Era patching for Oracle databases has automatic rollback if any of the steps in the patching workflow fails1. This ensures that your databases remain secure and functional even if an issue arises during the patching process1.
Refer to the exhibit.
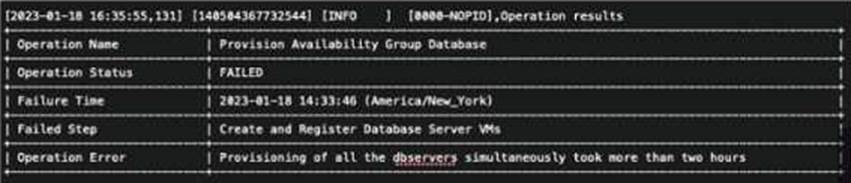
An administrator attempts to provision their first clustered database environment with NDB. The operation fails with the Operation Error shown in the exhibit.
Which database engine was being deployed during this operation?
- A . Oracle
- B . MySQL
- C . Microsoft SQL
- D . PostgreSQL
B
Explanation:
The error message in the exhibit indicates that the operation failed during the “Create and Register Database Server VMs” step because “Provisioning of all the observers simultaneously took more than two hours.” This type of error is associated with MySQL, as it involves observers which are a part of MySQL Group Replication, used for ensuring high availability1. The other options are not related to the error message, as they do not use observers or Group Replication for clustering.
Reference: 1: Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) course, Module 5: Database High Availability, Lesson 5.2: MySQL Group Replication, slide 7
How can Era be config90ured to send alert notifications to email recipients?
- A . From Administration select Era Service then go to Era service name and setup email notification,
- B . From Administration, select access control then add a user end setup email notification.
- C . From Administration, select Ere Service then go to configure notification widget and then click update to update SMTP server configuration
- D . From Administration select access control, select SMTP and then click update to update SMTP sewer configuration.
C
Explanation:
According to the Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) learning documents, to configure Era to send alert notifications to email recipients, you need to go to the Administration section, select Era Service, then go to the configure notification widget. From there, you can update the SMTP server configuration1. This allows Era to use the SMTP server to send alert notifications to the specified email recipients1.
An administrator needs to take multiple snapshots per day and retain them for one week.
How should the administrator define and schedule the SLA?
- A . • Daily snapshot retention: 7 days
• Daily snapshot at: 2 - B . • Weekly snapshot retention: 1 week
• Daily Snapshot at: 2 - C . • Weekly snapshot retention: 1 week
• Snapshots per Day: 2 - D . • Daily snapshot retention: 7 days
• Snapshots per Day: 2
D
Explanation:
The correct answer is D because it matches the requirement of taking multiple snapshots per day and retaining them for one week. Option A is incorrect because it only takes one snapshot per day, which is not enough for the administrator’s need. Option B is incorrect because it only retains the snapshots for one week, which means the older snapshots will be deleted after seven days. Option C is incorrect because it only takes two snapshots per week, which is not frequent enough for the administrator’s need.
Reference: The following sources provide more information about the SLA retention policies and how to create and modify them in NDB:
Nutanix Database Management & Automation (NDMA) course, Module 4: Protecting Databases
Using Time Machine, Lesson 4.1: Creating and Modifying SLA Retention Policies
Nutanix Certified Professional – Database Automation (NCP-DB) v6.5, Knowledge Objectives, Section 5 – Protect NDB-managed Databases Using Time Machine
Nutanix Database Service (NDB) User Guide, Chapter 6: Protecting Databases Using Time Machine,
Section 6.1: Creating and Modifying SLA Retention Policies
An administrator needs to take multiple snapshots per day and retain them for one week.
How should the administrator define and schedule the SLA?
- A . • Daily snapshot retention: 7 days
• Daily snapshot at: 2 - B . • Weekly snapshot retention: 1 week
• Daily Snapshot at: 2 - C . • Weekly snapshot retention: 1 week
• Snapshots per Day: 2 - D . • Daily snapshot retention: 7 days
• Snapshots per Day: 2
D
Explanation:
The correct answer is D because it matches the requirement of taking multiple snapshots per day and retaining them for one week. Option A is incorrect because it only takes one snapshot per day, which is not enough for the administrator’s need. Option B is incorrect because it only retains the snapshots for one week, which means the older snapshots will be deleted after seven days. Option C is incorrect because it only takes two snapshots per week, which is not frequent enough for the administrator’s need.
Reference: The following sources provide more information about the SLA retention policies and how to create and modify them in NDB:
Nutanix Database Management & Automation (NDMA) course, Module 4: Protecting Databases
Using Time Machine, Lesson 4.1: Creating and Modifying SLA Retention Policies
Nutanix Certified Professional – Database Automation (NCP-DB) v6.5, Knowledge Objectives, Section 5 – Protect NDB-managed Databases Using Time Machine
Nutanix Database Service (NDB) User Guide, Chapter 6: Protecting Databases Using Time Machine,
Section 6.1: Creating and Modifying SLA Retention Policies
An administrator needs to work with databases and time machines, but not database parameter profiles.
Which role satisfies this requirement?
- A . Database Administrator (DBA)
- B . super Administrator
- C . Database Infrastructure Administrator
- D . Infrastructure Administrator
A
Explanation:
In the Nutanix Database Automation (NCP-DB) framework, the role that allows an administrator to work with databases and time machines, but not database parameter profiles, is the Database Administrator (DBA)123. This role provides the necessary permissions to manage databases and time machines, which are essential components of the Nutanix Era solution. However, it does not grant access to database parameter profiles, which are typically managed by other roles45.
When registering SAP HANA Database and Database Server VM there are several (Linux) OS configuration requirements that must be set before registering a database Or a database server VM.
Which system file should the entry, secure_pazh be configured in?
- A . /ezc/sudores
- B . ‘etc/ profile
