Practice Free N10-009 Exam Online Questions
While troubleshooting connectivity issues, a junior network administrator is given explicit instructions to test the host’s TCP/IP stack first.
Which of the following commands should the network administrator run?
- A . ping 127.0.0.1
- B . ping 169.254.1.1
- C . ping 172.16.1.1
- D . ping 192.168.1.1
A
Explanation:
The loopback address 127.0.0.1 is used to test the TCP/IP stack of the local machine. Pinging this address confirms whether the local system’s networking stack is functioning correctly.
Which of the following does a full-tunnel VPN provide?
- A . Lower bandwidth requirements
- B . The ability to reset local computer passwords
- C . Corporate Inspection of all network traffic
- D . Access to blocked sites
C
Explanation:
A full-tunnel VPN routes all of a user’s network traffic through the corporate network. This means that the organization can inspect all network traffic for security and compliance purposes, as all data is tunneled through the VPN, allowing for comprehensive monitoring and inspection.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials.
Which of the following network cables involves bounding light off of protective cladding?
- A . Twinaxial
- B . Coaxial
- C . Single-mode
- D . Multimode
D
Explanation:
Multimode fiber optic cables involve the transmission of light signals that bounce off the core’s cladding as they travel down the fiber. This characteristic differentiates it from single-mode fiber, where the light travels directly down the fiber without reflecting off the cladding.
Here are some detailed points about multimode fiber cables:
Construction: Multimode fibers have a larger core diameter, typically 50 or 62.5 microns, compared to single-mode fibers, which have a core diameter of about 9 microns.
Light Propagation: The larger core of multimode fiber allows multiple light modes to propagate. These modes travel at different angles, leading to reflections off the core-cladding boundary. Distance and Bandwidth: Due to modal dispersion, where different light modes arrive at the receiver at different times, multimode fibers are suited for shorter distance applications compared to single-mode fibers. Typical distances are up to 550 meters for 10 Gbps Ethernet using OM4 multimode fiber. Applications: Multimode fibers are commonly used in LANs (Local Area Networks), data centers, and for shorter distance data transmission due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Network
Reference: CompTIA Network+ N10-007 Official Certification Guide, which covers fiber optic technologies, including the differences between multimode and single-mode fibers.
Cisco Networking Academy: Provides training materials and reference guides on the properties of different fiber optic cables.
Fiber Optic Association (FOA): A professional society dedicated to fiber optics, offering extensive information and certification on fiber optic technologies.
Multimode fibers are specifically designed for short-range communication with higher data rates and are typically used in environments like data centers, where high bandwidth over shorter distances is crucial. The reflections off the cladding, inherent to multimode fiber, facilitate this high-capacity communication.
168.1.0/24 as their network address and need to create three subnets with 30 hosts on each subnet.
Which of the following is a valid subnet mask that will meet the requirements?
- A . 255.255.255.128
- B . 255.255.255.192
- C . 255.255.255.224
- D . 255.255.255.240
B
Explanation:
To create three subnets with at least 30 hosts each:
Subnet Calculation: Each subnet must support 32 addresses (30 usable + 2 reserved for network and broadcast).
Bits for Subnets: Subnet mask 255.255.255.192 (/26) provides 64 addresses per subnet (4 subnets total).
Valid Subnets: Each subnet provides sufficient IPs to meet the requirement.
Which of the following devices can operate in multiple layers of the OSI model?
- A . Hub
- B . Switch
- C . Transceiver
- D . Modem
B
Explanation:
Understanding Switches:
Layer 2 (Data Link Layer): Traditional switches operate primarily at Layer 2, where they use MAC addresses to forward frames within a local network.
Layer 3 (Network Layer): Layer 3 switches, also known as multilayer switches, can perform routing functions using IP addresses to forward packets between different networks. Capabilities of Multilayer Switches:
VLANs and Inter-VLAN Routing: Multilayer switches can handle VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) configurations and perform inter-VLAN routing, enabling communication between different VLANs. Routing Protocols: They can run routing protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) to manage traffic between networks. Comparison with Other Devices:
Hub: Operates only at Layer 1 (Physical Layer) and simply repeats incoming signals to all ports.
Transceiver: Also operates at Layer 1, converting electrical signals to optical signals and vice versa.
Modem: Primarily operates at Layer 1 and Layer 2, modulating and demodulating signals for transmission over different types of media.
Practical Application:
Multilayer switches are commonly used in enterprise networks to optimize performance and manage complex routing and switching requirements within a single device.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials on network devices and the OSI model.
SIMULATION
A network technician was recently onboarded to a company. A manager has
tasked the technician with documenting the network and has provided the technician With partial information from previous documentation.
Instructions:
Click on each switch to perform a network discovery by entering commands into the terminal. Fill in the missing information using drop-down menus provided.
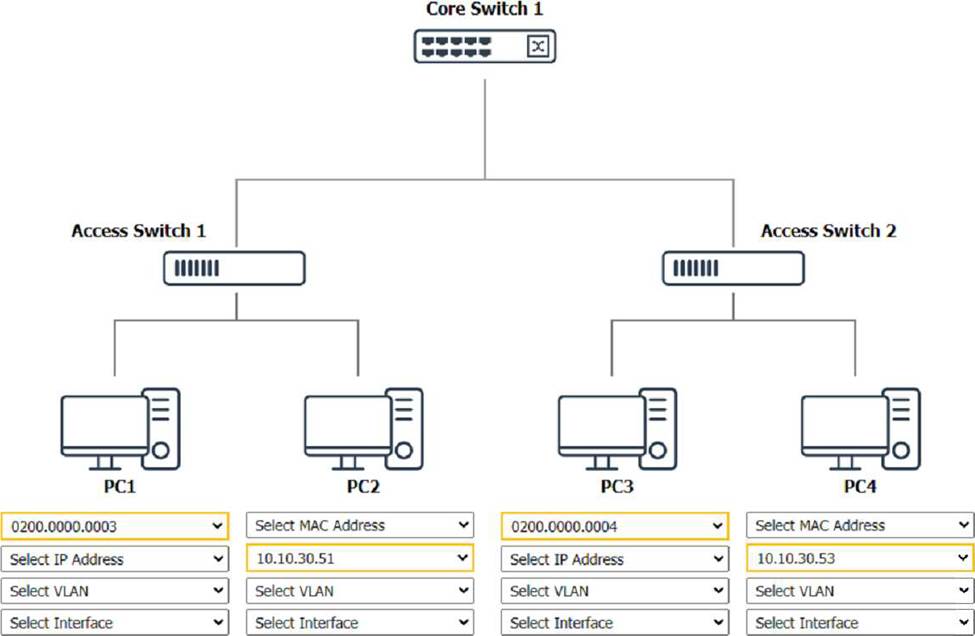
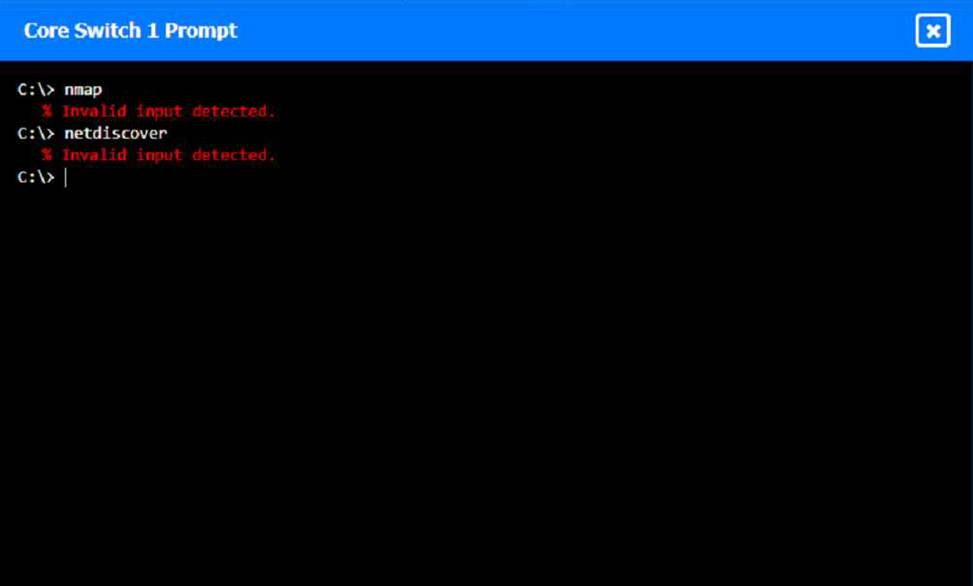
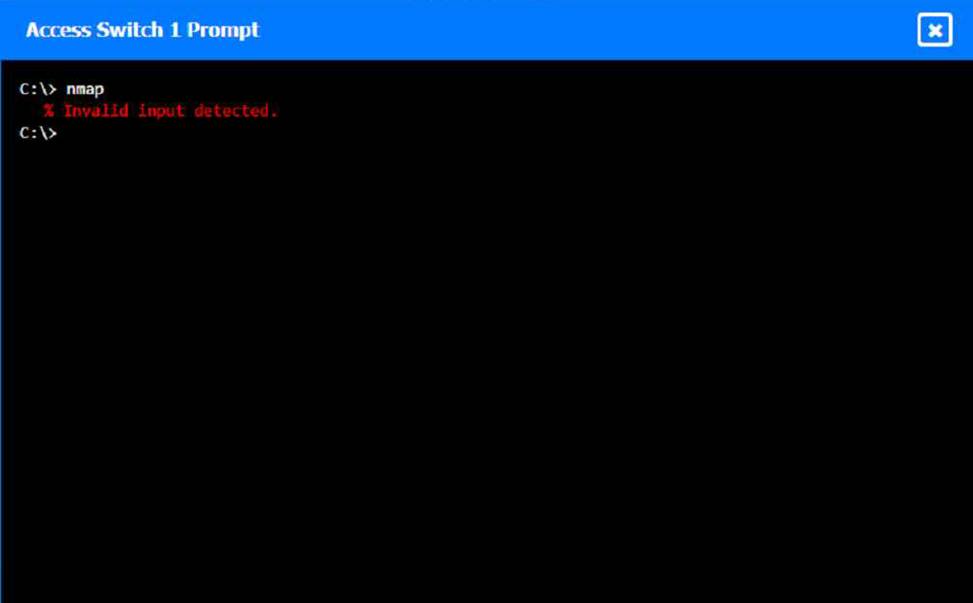
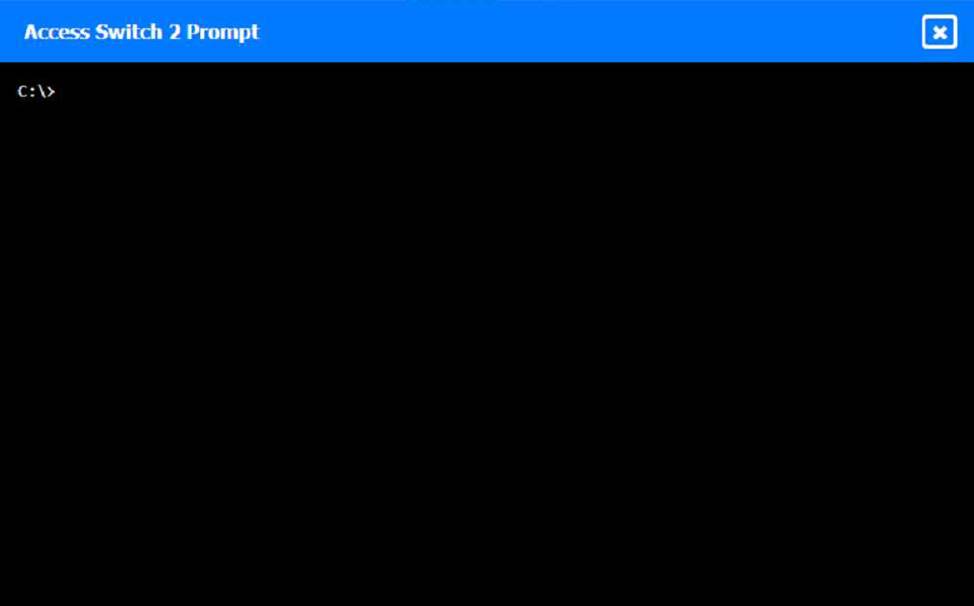
To perform a network discovery by entering commands into the terminal, you can use the following steps:
Click on each switch to open its terminal window.
Enter the command show ip interface brief to display the IP addresses and statuses of the switch interfaces.
Enter the command show vlan brief to display the VLAN configurations and assignments of the switch interfaces.
Enter the command show cdp neighbors to display the information about the neighboring devices that are connected to the switch.
Fill in the missing information in the diagram using the drop-down menus provided.
Here is an example of how to fill in the missing information for Core Switch 1:
The IP address of Core Switch 1 is 192.168.1.1.
The VLAN configuration of Core Switch 1 is VLAN 1: 192.168.1.0/24, VLAN 2: 192.168.2.0/24, VLAN 3:
SIMULATION
A network technician was recently onboarded to a company. A manager has
tasked the technician with documenting the network and has provided the technician With partial information from previous documentation.
Instructions:
Click on each switch to perform a network discovery by entering commands into the terminal. Fill in the missing information using drop-down menus provided.




To perform a network discovery by entering commands into the terminal, you can use the following steps:
Click on each switch to open its terminal window.
Enter the command show ip interface brief to display the IP addresses and statuses of the switch interfaces.
Enter the command show vlan brief to display the VLAN configurations and assignments of the switch interfaces.
Enter the command show cdp neighbors to display the information about the neighboring devices that are connected to the switch.
Fill in the missing information in the diagram using the drop-down menus provided.
Here is an example of how to fill in the missing information for Core Switch 1:
The IP address of Core Switch 1 is 192.168.1.1.
The VLAN configuration of Core Switch 1 is VLAN 1: 192.168.1.0/24, VLAN 2: 192.168.2.0/24, VLAN 3:
An organization is struggling to get effective coverage using the wireless network. The organization wants to implement a solution that will allow for continuous connectivity anywhere in the facility.
Which of the following should the network administer raptor suggest to ensure the best coverage?
- A . Implementing additional ad hoc access points
- B . Providing more Ethernet drops for user connections
- C . Deploying a mesh network in the building
- D . nl Changing the current frequency of the WI-FI
An organization is struggling to get effective coverage using the wireless network. The organization wants to implement a solution that will allow for continuous connectivity anywhere in the facility.
Which of the following should the network administer raptor suggest to ensure the best coverage?
- A . Implementing additional ad hoc access points
- B . Providing more Ethernet drops for user connections
- C . Deploying a mesh network in the building
- D . nl Changing the current frequency of the WI-FI
Which of the following steps in the troubleshooting methodology would be next after putting preventive measures in place?
- A . Implement the solution.
- B . Verify system functionality.
- C . Establish a plan of action.
- D . Test the theory to determine cause.
B
Explanation:
After implementing a solution and putting preventive measures in place, the next step is to verify that the system is functioning correctly. This ensures that the issue has been fully resolved.
