Practice Free N10-009 Exam Online Questions
Which of the following appliances provides users with an extended footprint that allows connections from multiple devices within a designated WLAN?
- A . Router
- B . Switch
- C . Access point
- D . Firewall
C
Explanation:
An access point (AP) provides users with an extended footprint that allows connections from multiple devices within a designated Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN).
Router: Typically used to connect different networks, not specifically for extending wireless coverage.
Switch: Used to connect devices within a wired network, not for providing wireless access.
Access Point (AP): Extends wireless network coverage, allowing multiple wireless devices to connect to the network.
Firewall: Primarily used for network security, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules, not for providing wireless connectivity. Network
Reference: CompTIA Network+ N10-007 Official Certification Guide: Explains the roles and functions of network appliances, including access points.
Cisco Networking Academy: Provides training on deploying and managing wireless networks with access points.
Network+ Certification All-in-One Exam Guide: Covers network devices and their roles in creating and managing networks.
Which of the following would be violated if an employee accidentally deleted a customer’s data?
- A . Integrity
- B . Confidentiality
- C . Vulnerability
- D . Availability
D
Explanation:
Availability refers to ensuring that data is accessible when needed. If a customer’s data is accidentally deleted, it impacts availability, as the data can no longer be accessed.
After installing a series of Cat 8 keystones, a data center architect notices higher than normal interference during tests.
Which of the following steps should the architect take to troubleshoot the issue?
- A . Check to see if the end connections were wrapped in copper tape before terminating.
- B . Use passthrough modular crimping plugs instead of traditional crimping plugs.
- C . Connect the RX/TX wires to different pins.
- D . Run a speed test on a device that can only achieve 100Mbps speeds.
A
Explanation:
Importance of Proper Termination:
Cat 8 cabling requires precise termination practices to ensure signal integrity and reduce interference. One common requirement is to wrap the end connections in copper tape to maintain shielding and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Interference Troubleshooting:
Interference in high-frequency cables like Cat 8 can be caused by improper shielding or grounding.
Checking the end connections for proper wrapping in copper tape is a crucial step.
Why Other Options are Less Likely:
Passthrough modular crimping plugs: Not specifically related to interference issues and are typically used for ease of cable assembly.
Connecting RX/TX wires to different pins: Would likely result in no connection or incorrect data transmission rather than interference.
Running a speed test on a device that can only achieve 100Mbps speeds: This would not diagnose interference and would not provide relevant information for Cat 8 cabling rated for higher speeds. Corrective Actions:
Verify that all end connections are properly wrapped with copper tape before termination.
Ensure that the shielding is continuous and properly grounded throughout the installation.
Retest the cabling for interference after making corrections.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials and structured cabling installation guides.
A security engineer is trying to connect cameras to a 12-port PoE switch, but only eight cameras turn on.
Which of the following should the engineer check first?
- A . Ethernet cable type
- B . Voltage
- C . Transceiver compatibility
- D . DHCP addressing
B
Explanation:
Power over Ethernet (PoE) allows devices such as cameras, access points, and VoIP phones to receive both power and data over the same Ethernet cable. If only eight out of twelve cameras turn on, the most likely issue is that the PoE switch has exceeded its power budget (total wattage capacity).
PoE Budget Limitation: PoE switches have a maximum power output, which can limit the number of devices they support simultaneously.
Voltage Check: Different PoE standards exist:
SIMULATION
A network technician replaced an access layer switch and needs to reconfigure it to allow the
connected devices to connect to the correct networks.
INSTRUCTIONS
Click on the appropriate port(s) on Switch 1 and Switch 3 to verify or reconfigure the correct settings:
・ Ensure each device accesses only its correctly associated network.
・ Disable all unused switchports.
. Require fault-tolerant connections between the switches.
. Only make necessary changes to complete the above requirements.
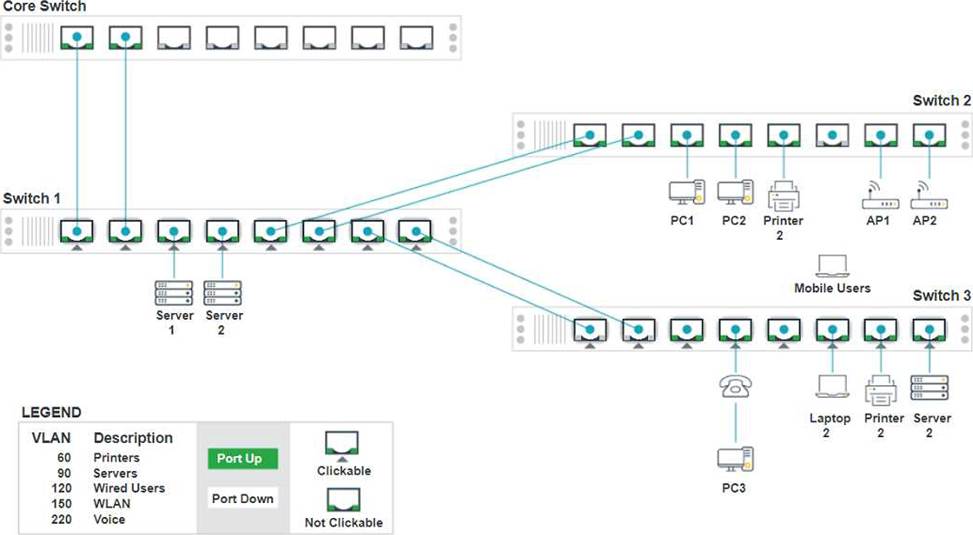
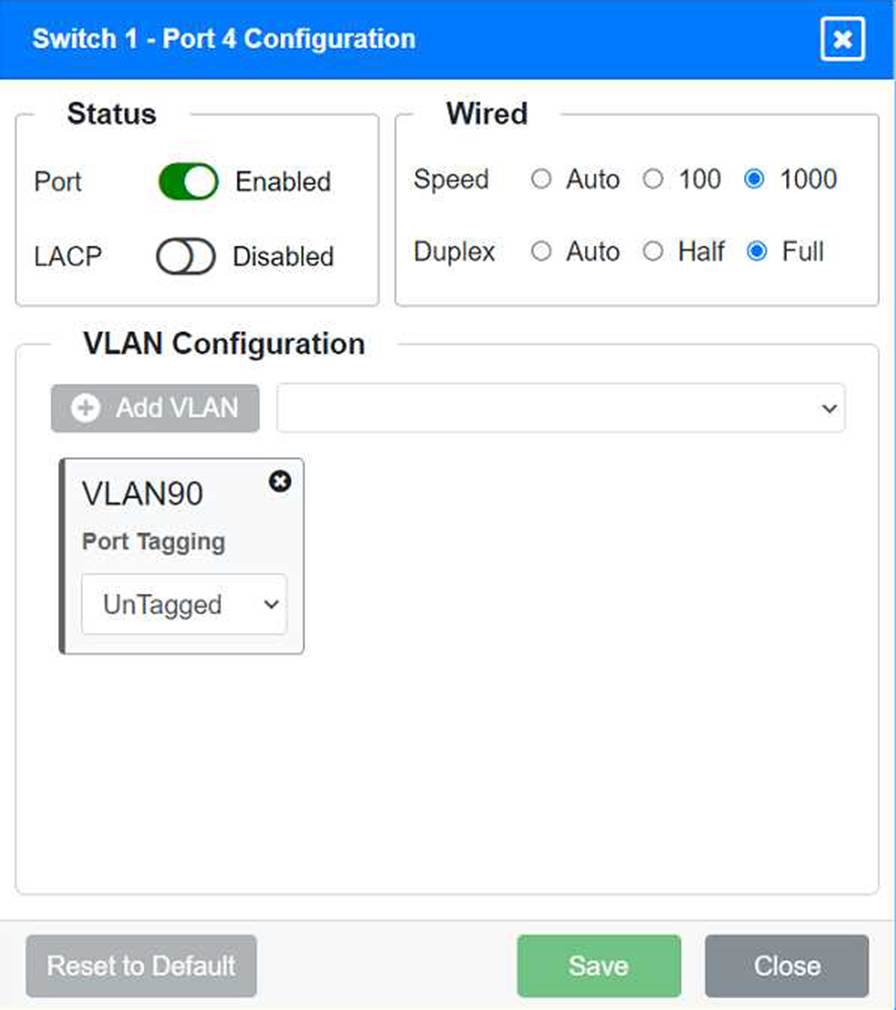
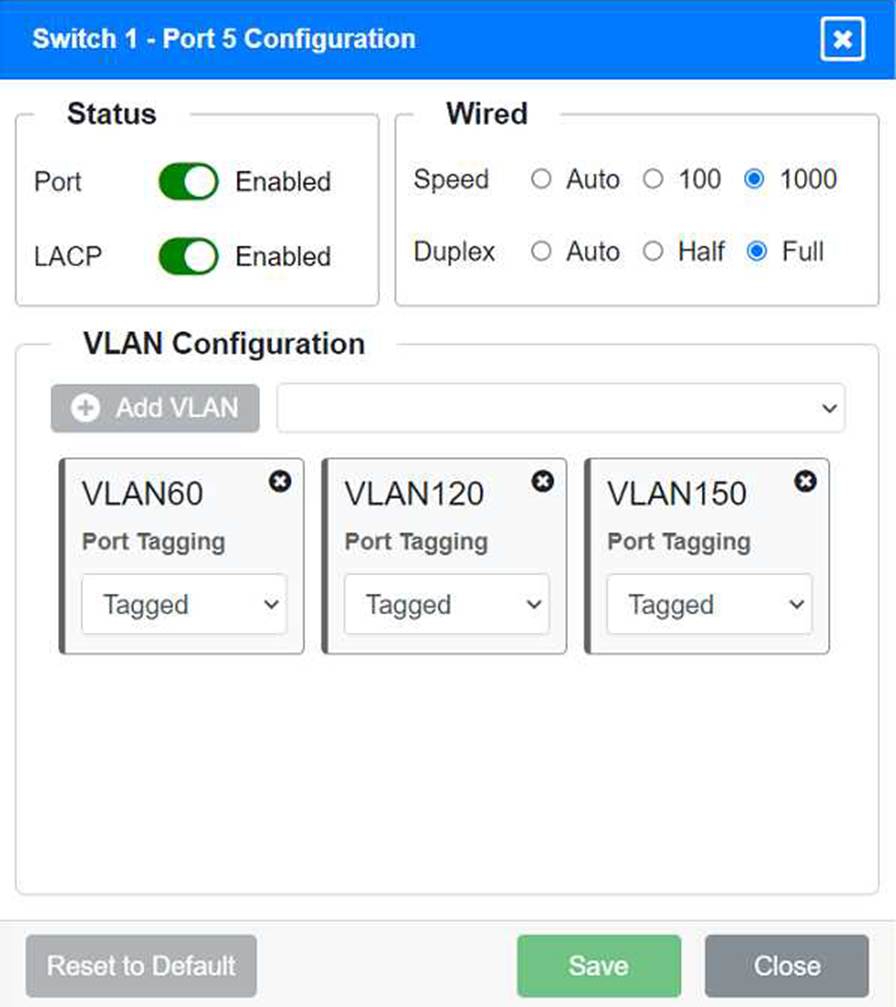
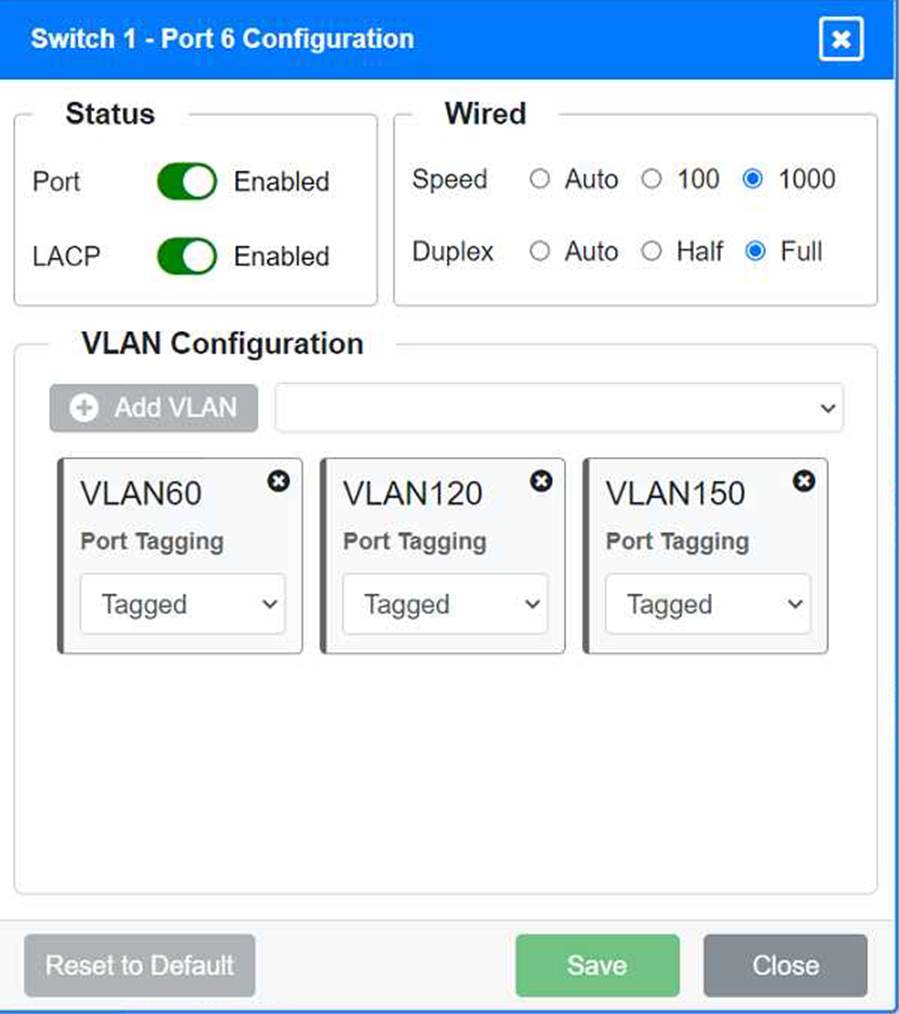
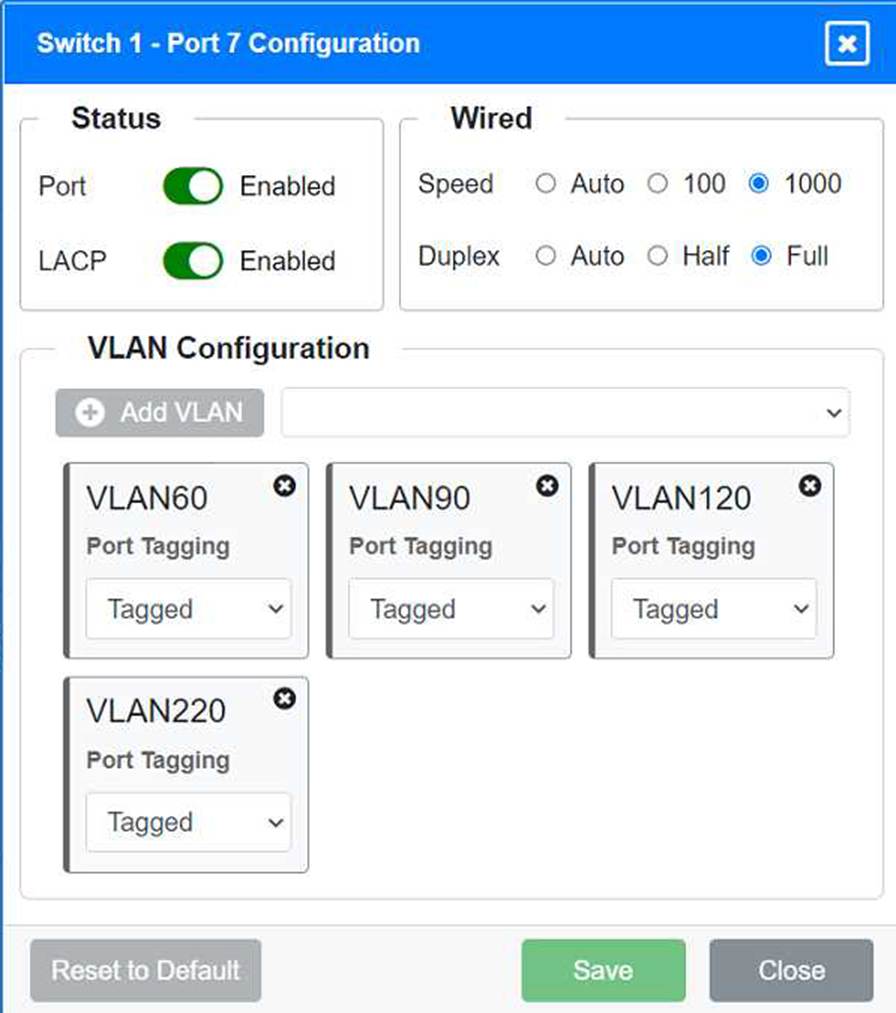
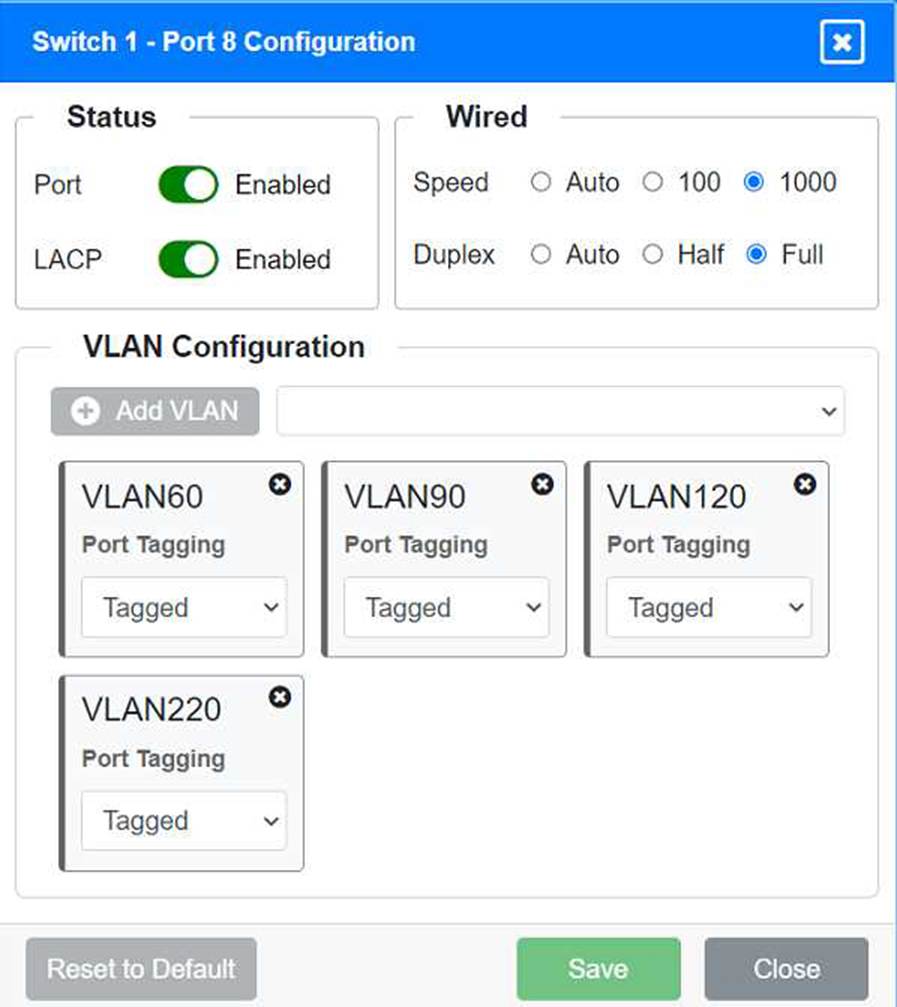
Identify the correct VLANs for each device and port.
Enable necessary ports and disable unused ports.
Configure fault-tolerant connections between the switches.
Configuration Details
Switch 1
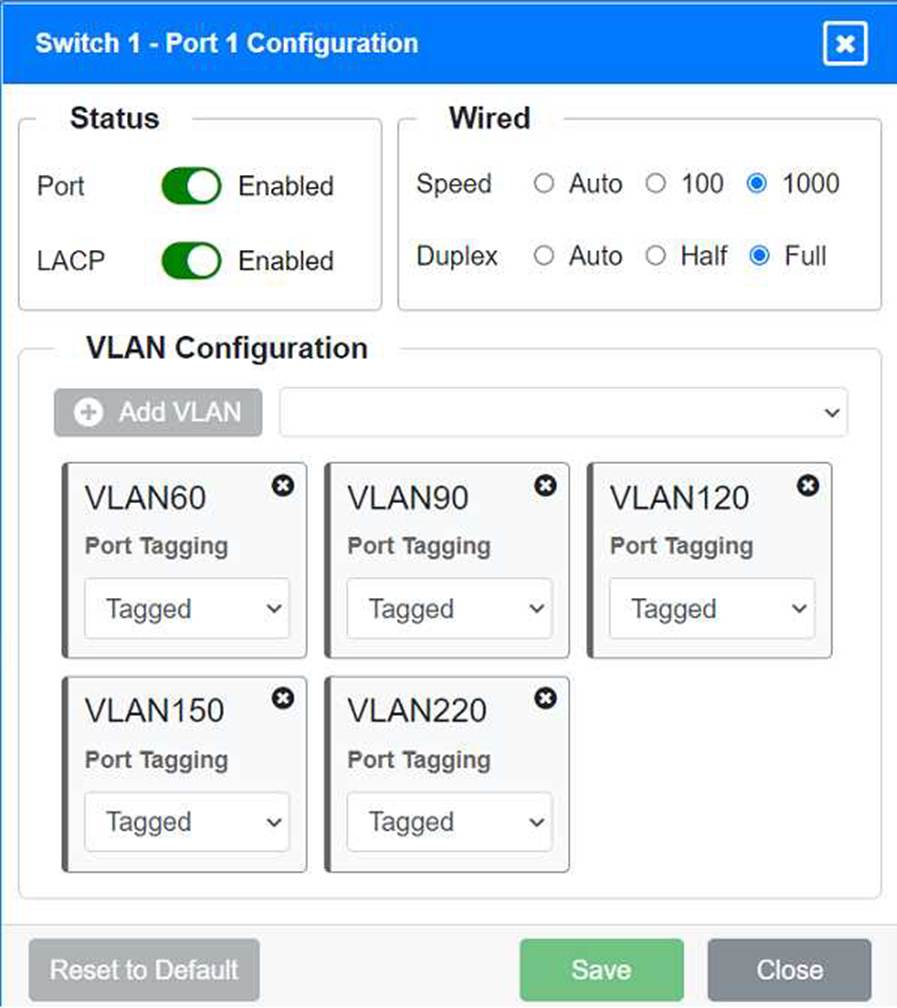
Port 1 Configuration (Uplink to Core Switch)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
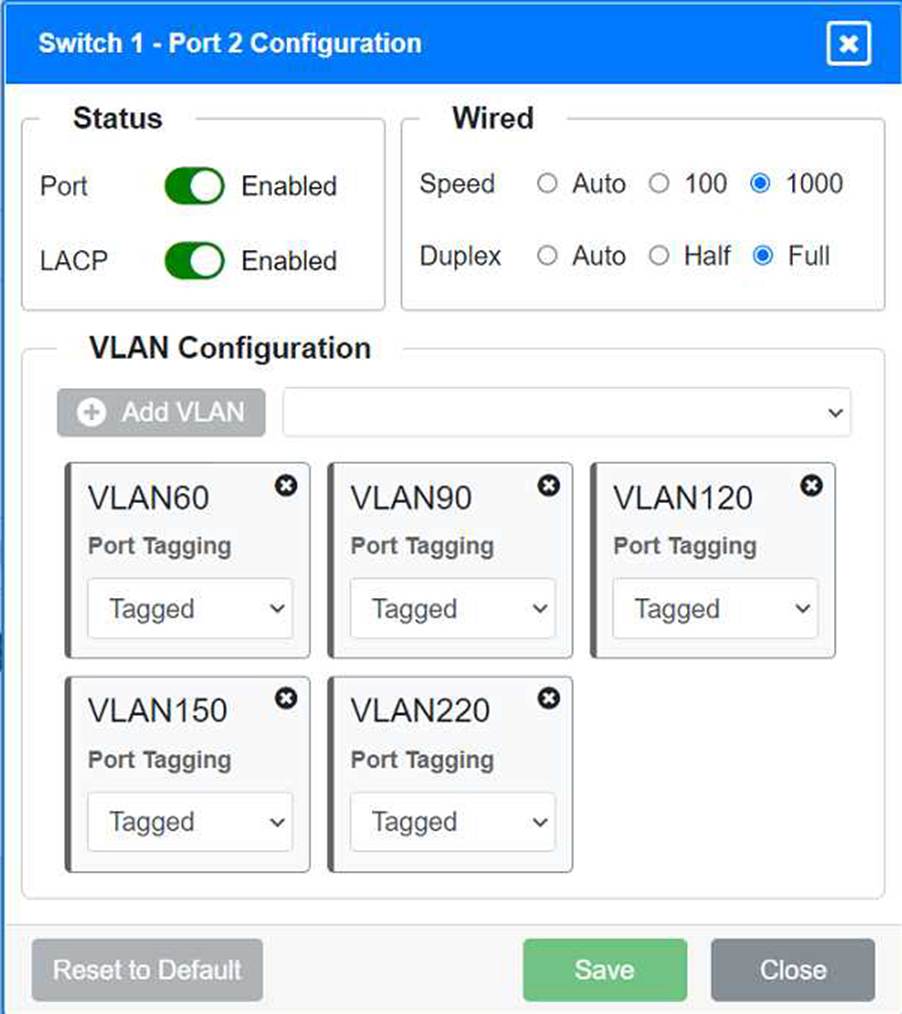
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN150, VLAN220 Port 2 Configuration (Uplink to Core Switch) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
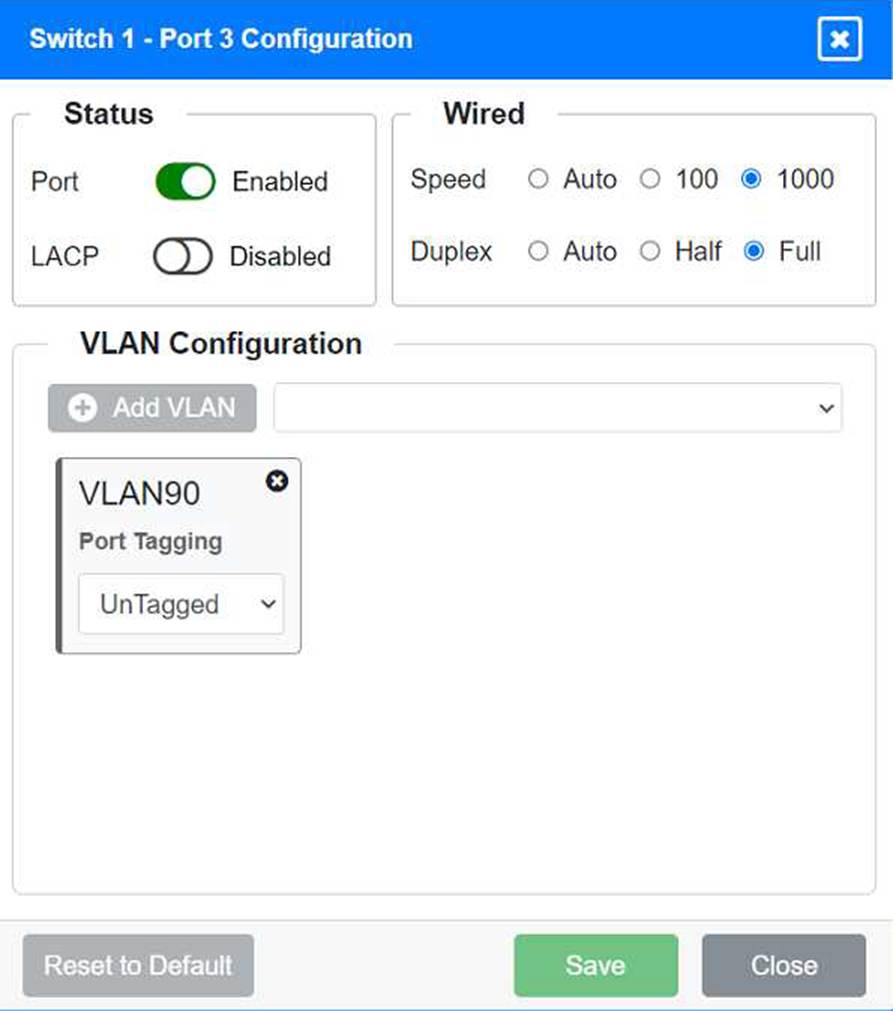
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN150, VLAN220 Port 3 Configuration (Server Connection) Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN90 (Servers)
Port 4 Configuration (Server Connection)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN90 (Servers)
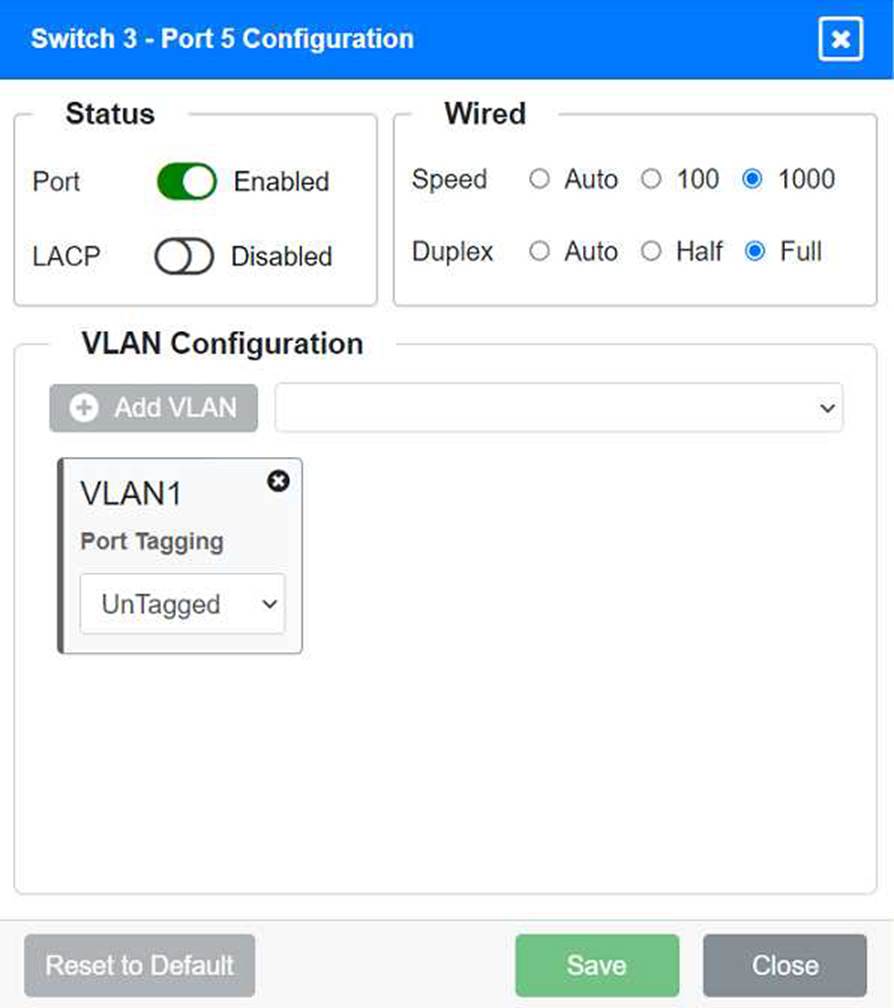
Port 5 Configuration (Wired Users and WLAN)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN120, VLAN150 Port 6 Configuration (Wired Users and WLAN) Status: Enabled
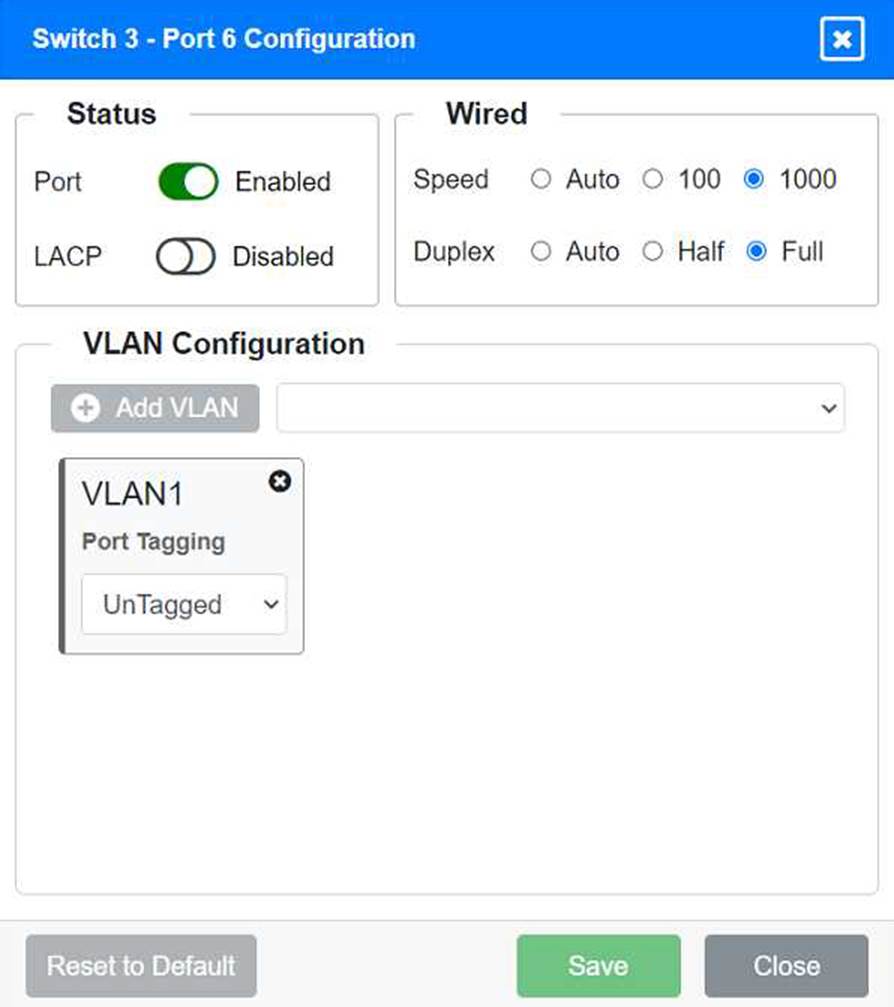
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
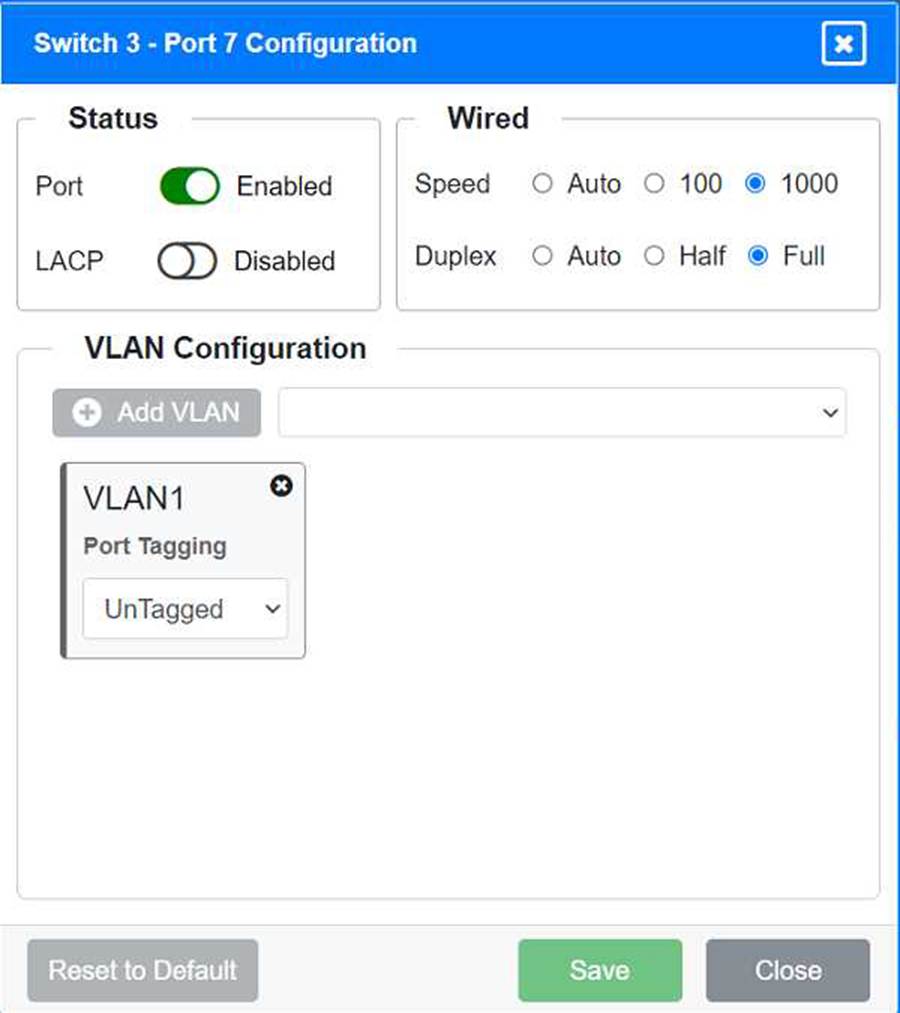
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN120, VLAN150 Port 7 Configuration (Voice and Wired Users) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
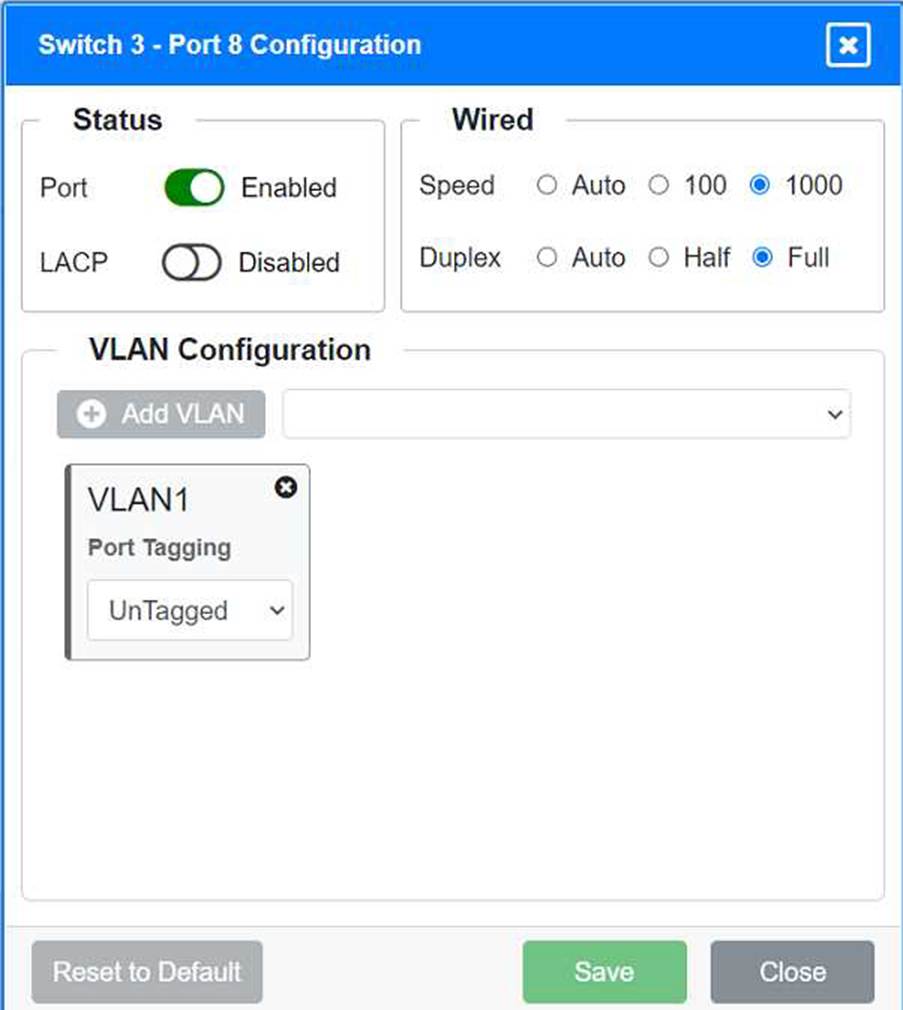
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN220 Port 8 Configuration (Voice, Printers, and Wired Users) Status: Enabled
LACP: Enabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Tagged for VLAN60, VLAN90, VLAN120, VLAN220 Switch 3
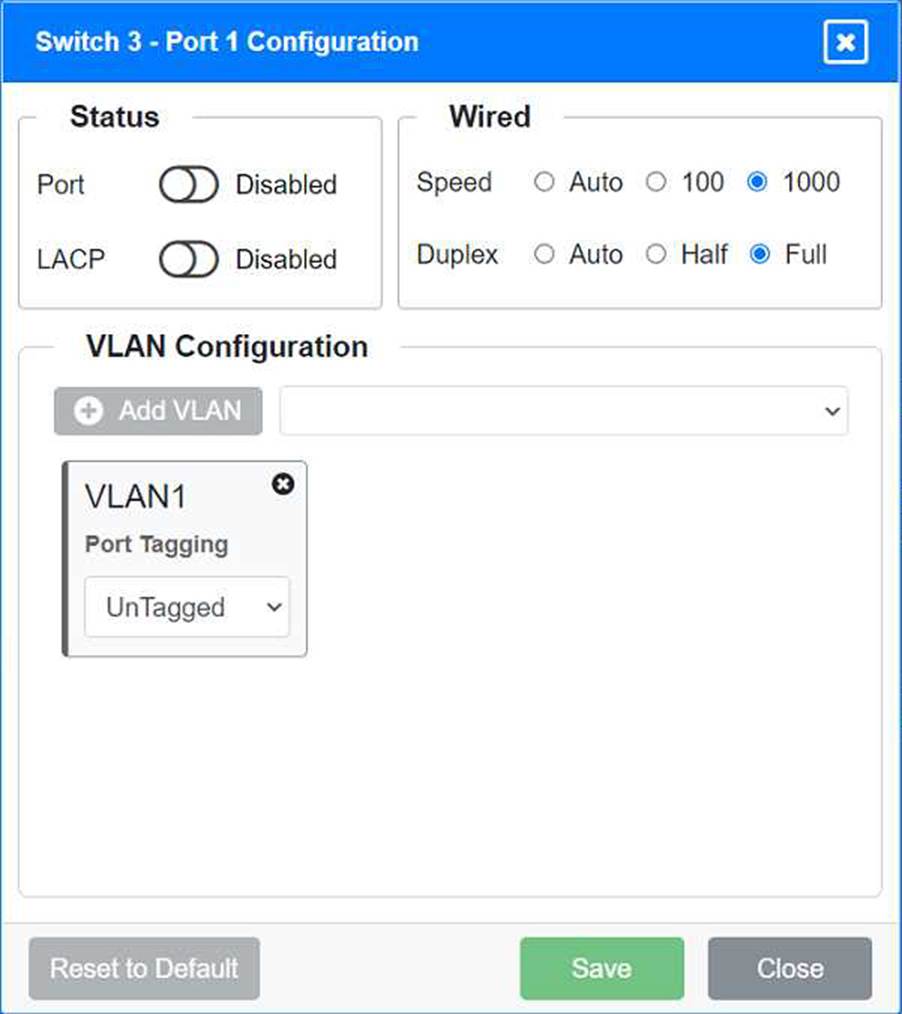
Port 1 Configuration (Unused)
Status: Disabled
LACP: Disabled
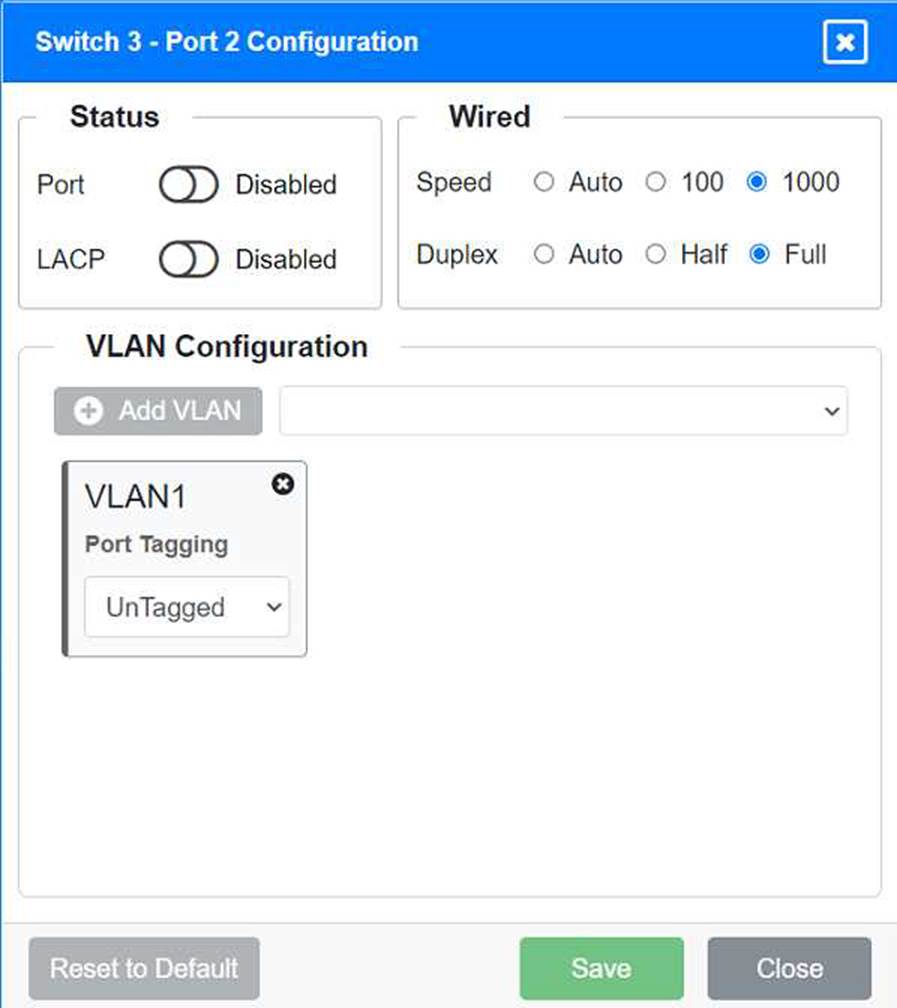
Port 2 Configuration (Unused)
Status: Disabled
LACP: Disabled
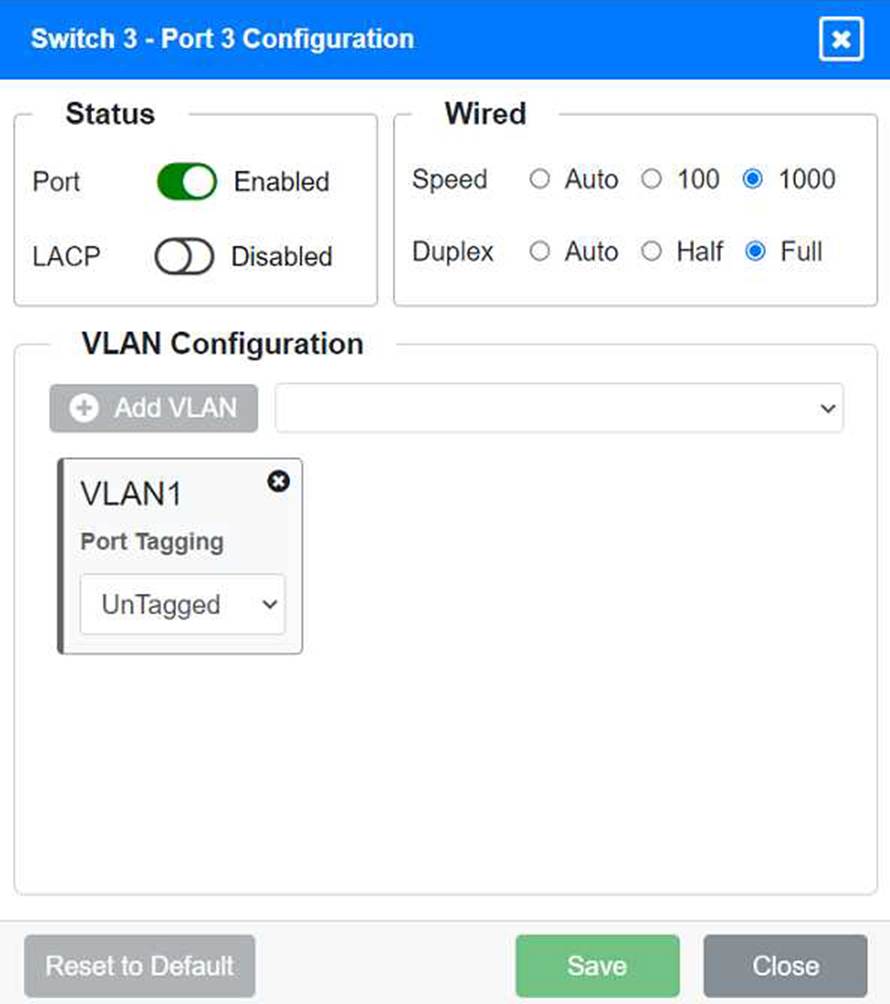
Port 3 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
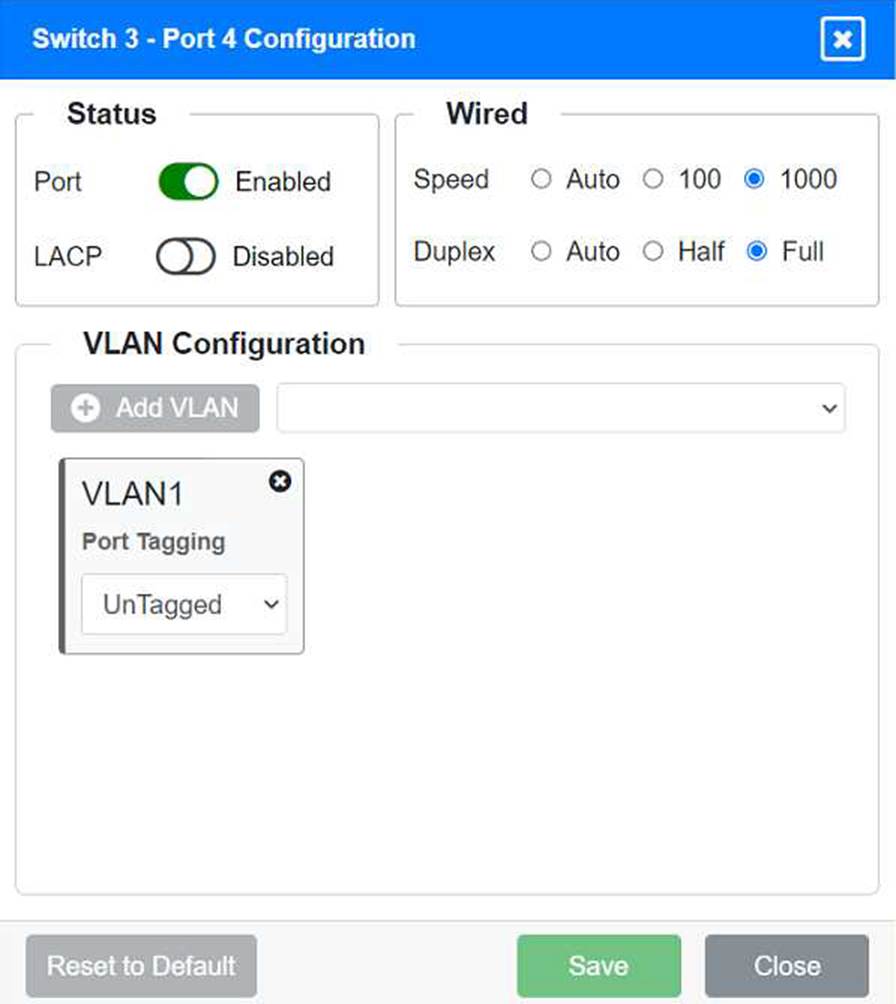
Port 4 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
Port 5 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
Port 6 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
Port 7 Configuration (Connection to Device)
Status: Enabled
LACP: Disabled
Speed: 1000
Duplex: Full
VLAN Configuration: Untagged for VLAN1 (Default)
Summary of Configurations
Ports 1 and 2 on Switch 1 are configured as trunk ports with VLAN tagging enabled for all necessary VLANs.
Ports 3 and 4 on Switch 1 are configured for server connections with VLAN 90 untagged.
Ports 5, 6, 7, and 8 on Switch 1 are configured for devices needing access to multiple VLANs.
Unused ports on Switch 3 are disabled.
Ports 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 on Switch 3 are enabled for default VLAN1. Ensure All Switches and Ports are Configured as per the Requirements: Core Switch Ports should be configured as needed for uplinks to Switch 1. Ensure LACP is enabled for redundancy on trunk ports between switches.
By following these configurations, each device will access only its correctly associated network, unused switch ports will be disabled, and fault-tolerant connections will be established between the switches.
SIMULATION
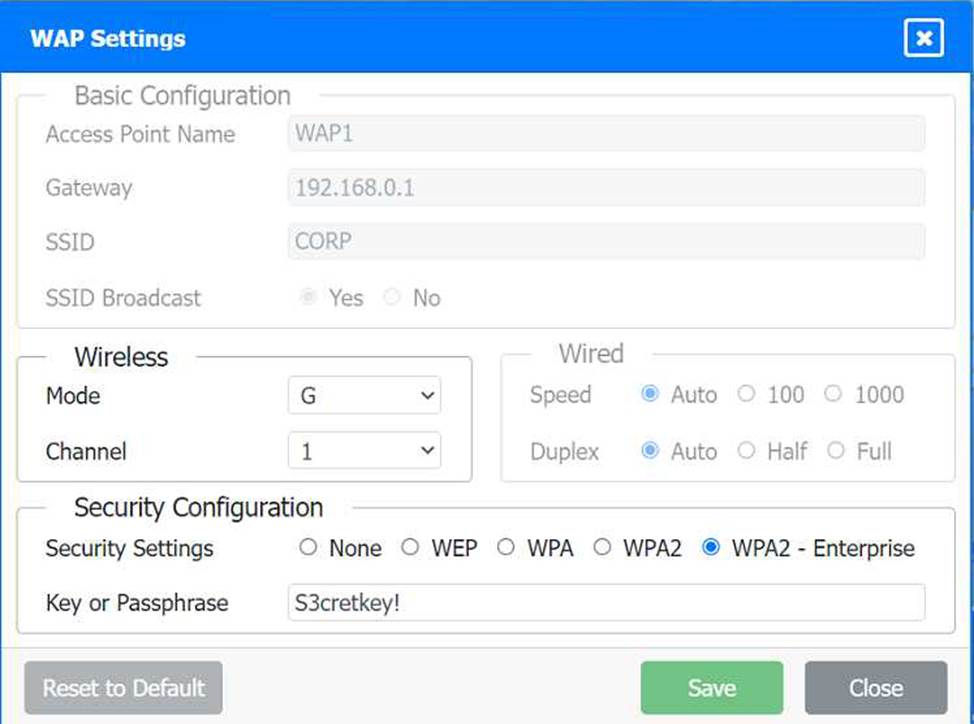
A network administrator has been tasked with configuring a network for a new corporate office. The office consists of two buildings, separated by 50 feet with no physical connectivity.
The configuration must meet the following requirements:
. Devices in both buildings should be able to access the Internet.
. Security insists that all Internet traffic be inspected before entering the network.
. Desktops should not see traffic destined for other devices.
INSTRUCTIONS
Select the appropriate network device for each location. If applicable, click on the magnifying glass next to any device which may require configuration updates and make any necessary changes.
Not all devices will be used, but all locations should be filled.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
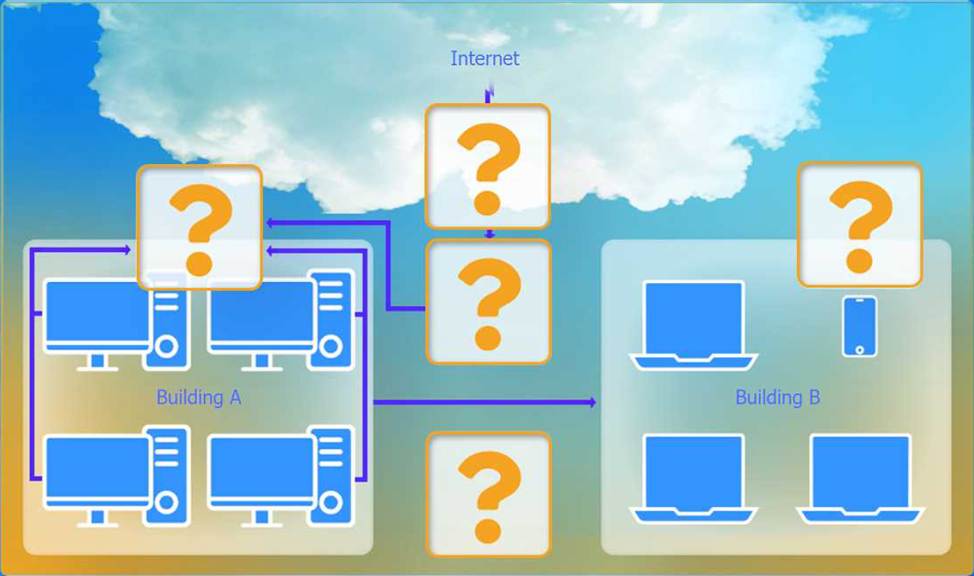

Security insists that all Internet traffic be inspected before entering the network.
Desktops should not see traffic destined for other devices.
Here is the corrected layout with explanation:
Building A:
Switch: Correctly placed to connect all desktops.
Firewall: Correctly placed to inspect all incoming and outgoing traffic.
Building B:
Switch: Not needed. Instead, place a Wireless Access Point (WAP) to provide wireless connectivity for laptops and mobile devices.
Between Buildings:
Wireless Range Extender: Correctly placed to provide connectivity between the buildings wirelessly.
Connection to the Internet:
Router: Correctly placed to connect to the Internet and route traffic between the buildings and the Internet.
Firewall: The firewall should be placed between the router and the internal network to inspect all traffic before it enters the network.
Corrected Setup:
Top-left (Building A): Switch
Bottom-left (Building A): Firewall (inspect traffic before it enters the network)
Top-middle (Internet connection): Router
Bottom-middle (between buildings): Wireless Range Extender
Top-right (Building B): Wireless Access Point (WAP)
In this corrected setup, the WAP in Building B will connect wirelessly to the Wireless Range Extender, which is connected to the Router. The Router is connected to the Firewall to ensure all traffic is inspected before it enters the network.
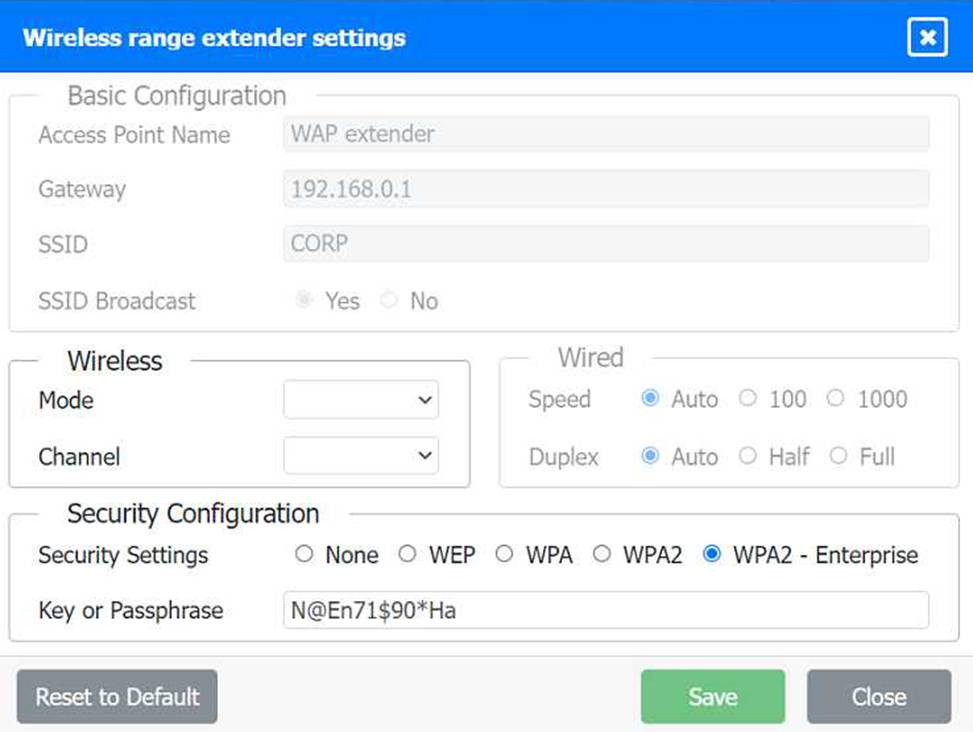
Configuration for Wireless Range Extender:
SSID: CORP
Security Settings: WPA2 or WPA2 – Enterprise
Key or Passphrase: [Enter a strong passphrase]
Mode: [Set based on your network plan]
Channel: [Set based on your network plan]
Speed: Auto
Duplex: Auto
With these settings, both buildings will have secure access to the Internet, and all traffic will be inspected by the firewall before entering the network. Desktops and other devices will not see traffic intended for others, maintaining the required security and privacy.
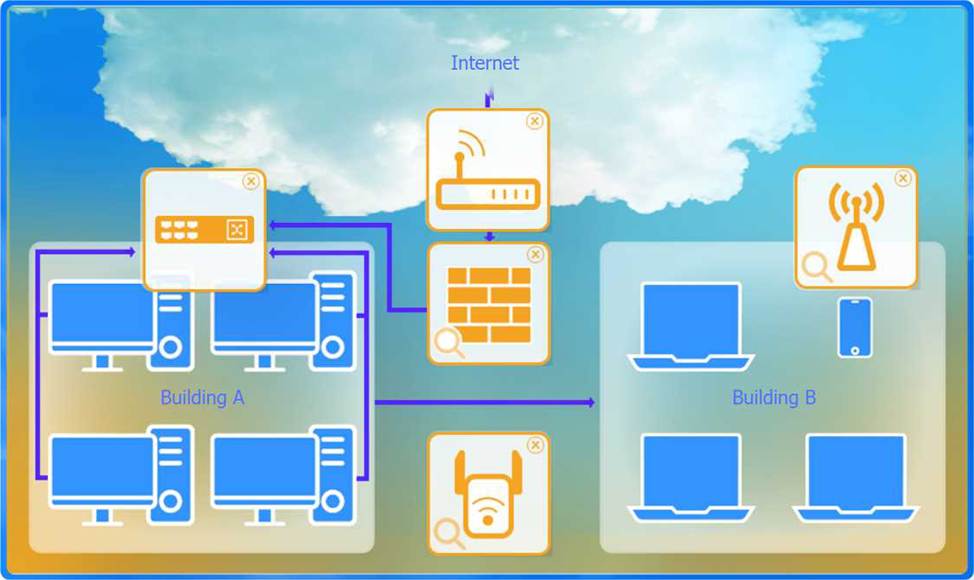
To configure the wireless range extender for security, follow these steps:
SSID (Service Set Identifier):
Ensure the SSID is set to "CORP" as shown in the exhibit.
Security Settings:
WPA2 or WPA2 – Enterprise: Choose one of these options for stronger security. WPA2-Enterprise provides more robust security with centralized authentication, which is ideal for a corporate environment.
Key or Passphrase:
If you select WPA2, enter a strong passphrase in the "Key or Passphrase" field.
If you select WPA2 – Enterprise, you will need to configure additional settings for authentication servers, such as RADIUS, which is not shown in the exhibit.
Wireless Mode and Channel:
Set the appropriate mode and channel based on your network design and the environment to avoid
interference. These settings are not specified in the exhibit, so set them according to your network plan.
Wired Speed and Duplex:
Set the speed to "Auto" unless you have specific requirements for 100 or 1000 Mbps.
Set the duplex to "Auto" unless you need to specify half or full duplex based on your network equipment.
Save Configuration:
After making the necessary changes, click the "Save" button to apply the settings.
Here is how the configuration should look after adjustments:
SSID: CORP
Security Settings: WPA2 or WPA2 – Enterprise
Key or Passphrase: [Enter a strong passphrase]
Mode: [Set based on your network plan]
Channel: [Set based on your network plan]
Speed: Auto
Duplex: Auto
Once these settings are configured, your wireless range extender will provide secure connectivity for devices in both buildings.
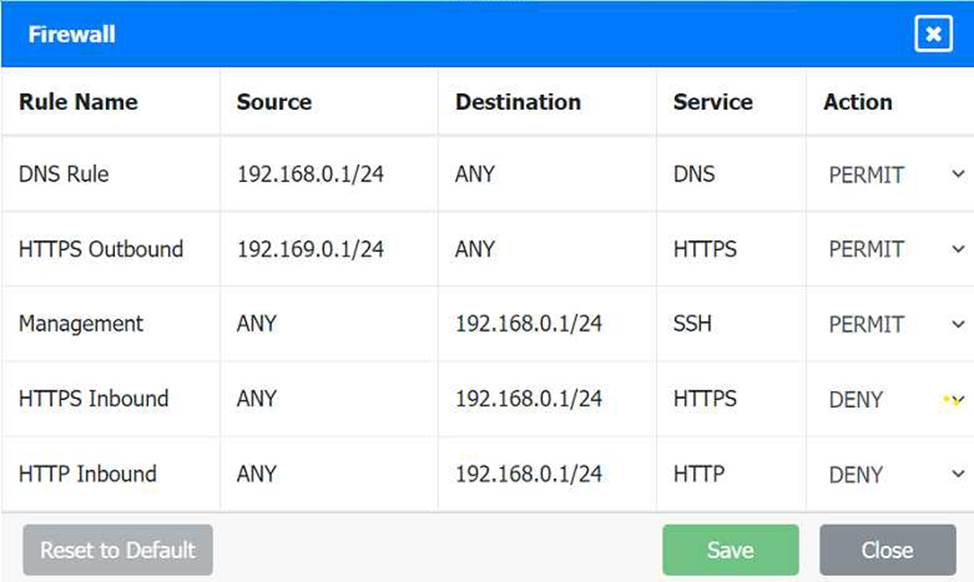
Firewall setting to to ensure complete compliance with the requirements and best security practices, consider the following adjustments and additions:
DNS Rule: This rule allows DNS traffic from the internal network to any destination, which is fine.
HTTPS Outbound: This rule allows HTTPS traffic from the internal network (assuming 192.169.0.1/24 is a typo and should be 192.168.0.1/24) to any destination, which is also good for secure web browsing.
Management: This rule allows SSH access to the firewall for management purposes, which is necessary for administrative tasks.
HTTPS Inbound: This rule denies inbound HTTPS traffic to the internal network, which is good unless you have a web server that needs to be accessible from the internet.
HTTP Inbound: This rule denies inbound HTTP traffic to the internal network, which is correct for security purposes.
Suggested Additional Settings:
Permit General Outbound Traffic: Allow general outbound traffic for web access, email, etc.
Block All Other Traffic: Ensure that all other traffic is blocked to prevent unauthorized access.
Firewall Configuration Adjustments:
Correct the Network Typo:
Ensure that the subnet 192.169.0.1/24 is corrected to 192.168.0.1/24.
Permit General Outbound Traffic:
Rule Name: General Outbound
Source: 192.168.0.1/24
Destination: ANY
Service: ANY
Action: PERMIT
Deny All Other Traffic:
Rule Name: Block All
Source: ANY
Destination: ANY
Service: ANY
Action: DENY
Here is how your updated firewall settings should look:
Rule Name Source Destination Service Action
DNS Rule 192.168.0.1/24 ANY DNS PERMIT
HTTPS Outbound 192.168.0.1/24 ANY HTTPS PERMIT
Management ANY 192.168.0.1/24 SSH PERMIT
HTTPS Inbound ANY 192.168.0.1/24 HTTPS DENY
HTTP Inbound ANY 192.168.0.1/24 HTTP DENY
General Outbound 192.168.0.1/24 ANY ANY PERMIT
Block All ANY ANY ANY DENY
These settings ensure that:
Internal devices can access DNS and HTTPS services externally.
Management access via SSH is permitted.
Inbound HTTP and HTTPS traffic is denied unless otherwise specified.
General outbound traffic is allowed.
All other traffic is blocked by default, ensuring a secure environment.
Make sure to save the settings after making these adjustments.
A network engineer is now in charge of all SNMP management in the organization. The engineer must use a SNMP version that does not utilize plaintext data.
Which of the following is the minimum version of SNMP that supports this requirement?
- A . v1
- B . v2c
- C . v2u
- D . v3
D
Explanation:
SNMPv3 is the version of the Simple Network Management Protocol that introduces security enhancements, including message integrity, authentication, and encryption. Unlike previous versions (v1 and v2c), SNMPv3 supports encrypted communication, ensuring that data is not transmitted in plaintext. This provides confidentiality and protects against eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials.
Three access points have Ethernet that runs through the ceiling. One of the access points cannot reach the internet.
Which of the following tools can help identify the issue?
- A . Network tap
- B . Cable tester
- C . Visual fault locator
- D . Toner and probe
B
Explanation:
A cable tester is a tool that can help identify issues with the physical cabling, such as breaks or improper terminations, which may prevent the access point from reaching the internet.
To reduce costs and increase mobility, a Chief Technology Officer (CTO) wants to adopt cloud services for the organization and its affiliates. To reduce the impact for users, the CTO wants key services to run from the on-site data center and enterprise services to run in the cloud.
Which of the following deployment models is the best choice for the organization?
- A . Public
- B . Hybrid
- C . SaaS
- D . Private
B
Explanation:
A hybrid cloud deployment model is the best choice for the CTO’s requirements. It allows the organization to run key services from the on-site data center while leveraging the cloud for enterprise services. This approach provides flexibility, scalability, and cost savings, while also minimizing disruptions to users by keeping critical services local. The hybrid model integrates both private and public cloud environments, offering the benefits of both.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials and cloud computing principles.
A network administrator needs to fail over services to an off-site environment. This process will take four weeks to become fully operational.
Which of the following DR (Disaster Recovery) concepts does this describe?
- A . Hot site
- B . Warm site
- C . Cold site
- D . Active-active approach
C
Explanation:
A cold site is a backup facility that provides infrastructure (such as power, cooling, and space) but does not have active IT resources installed. When a disaster occurs, IT teams must bring in and configure all necessary hardware and software before services can resume. This process can take weeks or longer―which matches the scenario described.
• Why not the other options?
• Hot site (A) C A hot site is a fully operational backup facility with up-to-date data and pre-configured hardware, allowing almost instant failover (minutes to hours).
• Warm site (B) C A warm site has pre-installed hardware and some software/configurations, but it requires some setup before becoming fully operational (hours to a few days).
• Active-active approach (D) C This means that multiple sites run simultaneously with load balancing,
ensuring no downtime in case of a failure.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) Official Guide C Chapter 15: Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
