Practice Free N10-008 Exam Online Questions
A newly installed multifunction copier needs to be set up so scanned documents can be emailed to recipients.
Which of the following ports from the copier’s IP address should be allowed?
- A . 22
- B . 25
- C . 53
- D . 80
B
Explanation:
Port 25 is the port number that is commonly used for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), which is a protocol that allows sending and receiving email messages over a network1. Port 25 from the copier’s IP address should be allowed so that scanned documents can be emailed to recipients. Port 22 is the port number that is commonly used for Secure Shell (SSH), which is a protocol that allows secure and encrypted remote access and control of a device over a network1. Port 22 from the copier’s IP address is not necessary for emailing scanned documents.
Port 53 is the port number that is commonly used for Domain Name System (DNS), which is a protocol that allows resolving domain names to IP addresses and vice versa on a network1. Port 53 from the copier’s IP address is not necessary for emailing scanned documents.
Port 80 is the port number that is commonly used for Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which is a protocol that allows transferring web pages and other resources over a network1. Port 80 from the copier’s IP address is not necessary for emailing scanned documents.
Which of the following should be implemented to allow remote users to access network resources while only redirecting necessary traffic?
- A . Split-tunnel VPN
- B . Geofencing
- C . Client-to-site VPN
- D . Remote desktop gateway
A
Explanation:
A split-tunnel VPN is a VPN feature that allows remote users to access network resources while only redirecting necessary traffic through the VPN tunnel. A split-tunnel VPN enables users to choose which applications or websites to secure with the VPN and which to connect normally through the internet. This can improve performance, conserve bandwidth, and avoid compatibility issues with some services that depend on the user’s location. A split-tunnel VPN can also allow users to access local devices or resources that are not accessible through the VPN.
A network administrator needs to connect two routers in a point-to-point configuration and conserve IP space.
Which of the following subnets should the administrator use?
- A . /24
- B . /26
- C . /28
- D . /30
D
Explanation:
A /30 subnet is the smallest possible subnet that can be used for a point-to-point configuration between two routers. A /30 subnet has only two usable host addresses, one for each router, and a network address and a broadcast address. A /30 subnet conserves IP space by minimizing the number of wasted addresses. A /24, /26, or /28 subnet would have more usable host addresses than needed for a point-to-point configuration and would waste IP space.
Reference: Routing Technologies C N10-008 CompTIA Network+: 2.21 CompTIA Network+ Certification Exam Objectives, page 10
Which of the following routing protocols should be implemented to create a route between a local area network and an ISP?
- A . BGP
- B . EIGRP
- C . RIP
- D . OSPF
A
Explanation:
BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol, and it is a routing protocol that is used to exchange routing
information between different autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet. An AS is a network or a group of networks that are under the same administrative control and share a common routing policy. BGP is used to create routes between local area networks and Internet service providers (ISPs), as well as between different ISPs. BGP is considered an exterior gateway protocol (EGP), as opposed to an interior gateway protocol (IGP) such as EIGRP, RIP, or OSPF, which are used to create routes within an AS.
Reference: CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Cert Guide, Chapter 3, Section 3.4
An IDS was installed behind the edge firewall after a network was breached. The network was then breached again even though the IDS logged the attack.
Which of the following should be used in place of these devices to prevent future attacks?
- A . A network tap
- B . A proxy server
- C . A UTM appliance
- D . A content filter
C
Explanation:
A UTM appliance stands for Unified Threat Management appliance, which is a device that combines multiple security functions into one solution. A UTM appliance can provide firewall, IDS/IPS, antivirus, VPN, web filtering, and other security features. A network technician can use a UTM appliance in place of an edge firewall and an IDS to prevent future attacks, as a UTM appliance can block malicious traffic and detect and respond to intrusions more effectively.
Reference: https://www.comptia.org/blog/what-is-utm
Which of the following is used when a workstation sends a DHCP broadcast to a server on another LAN?
- A . Reservation
- B . Dynamic assignment
- C . Helper address
- D . DHCP offer
C
Explanation:
A helper address is an IP address that is configured on a router interface to forward DHCP broadcast messages to a DHCP server on another LAN. A DHCP broadcast message is a message that a workstation sends when it needs to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server. Since broadcast messages are not routed across different networks, a helper address is needed to relay the DHCP broadcast message to the DHCP server on another network.
Reference: https://www.comptia.org/training/books/network-n10-008-study-guide (page 199)
A customer is hosting an internal database server. None of the users are able to connect to the server, even though it appears to be working properly.
Which of the following is the best way to verify traffic to and from the server?
- A . Protocol analyzer
- B . nmap
- C . ipconfig
- D . Speed test
A
Explanation:
A protocol analyzer is the best way to verify traffic to and from the server. A protocol analyzer, also known as a packet sniffer or network analyzer, is a tool that captures and analyzes the network packets that are sent and received by a device. A protocol analyzer can show the source and destination IP addresses, ports, protocols, and payload of each packet, as well as any errors or anomalies in the network communication. A protocol analyzer can help troubleshoot network connectivity issues by identifying the root cause of the problem, such as misconfigured firewall rules, incorrect routing, or faulty network devices12.
To use a protocol analyzer to verify traffic to and from the server, the customer can follow these steps:
Install a protocol analyzer tool on a device that is connected to the same network as the server, such as Wireshark3 or Microsoft Network Monitor4.
Select the network interface that is used to communicate with the server, and start capturing the network traffic.
Filter the captured traffic by using the IP address or hostname of the server, or by using a specific port or protocol that is used by the database service.
Analyze the filtered traffic and look for any signs of successful or failed connection attempts, such as TCP SYN, ACK, or RST packets, or ICMP messages.
If there are no connection attempts to or from the server, then there may be a problem with the network configuration or device settings that prevent the traffic from reaching the server.
If there are connection attempts but they are rejected or dropped by the server, then there may be a problem with the server configuration or service settings that prevent the traffic from being accepted by the server.
The other options are not the best ways to verify traffic to and from the server. nmap is a tool that can scan a network and discover hosts and services, but it cannot capture and analyze the network packets in detail. ipconfig is a command that can display and configure the IP settings of a device, but it cannot monitor or test the network communication with another device. Speed test is a tool that can measure the bandwidth and latency of a network connection, but it cannot diagnose or troubleshoot specific network problems.
Network users reported that a recent firmware upgrade to a firewall did not resolve the issue that prompted the upgrade.
Which of the following should be performed NEXT?
- A . Reopen the service ticket, request a new maintenance window, and roll back to the anterior firmware version.
- B . Gather additional information to ensure users’ concerns are not been caused by a different issue with similar symptoms.
- C . Employ a divide-and-conquer troubleshooting methodology by engaging the firewall vendor’s support.
- D . Escalate the issue to the IT management team in order to negotiate a new SLA with the user’s manager.
B
Explanation:
Before taking any further action, it is important to verify that the problem reported by the users is the same as the one that prompted the firmware upgrade. It is possible that the firmware upgrade did resolve the original issue, but a new or different issue has arisen with similar symptoms. By gathering additional information from the users, such as error messages, screenshots, logs, or network traces, the technician can confirm or rule out this possibility and avoid wasting time and resources on unnecessary steps.
Reopening the service ticket, requesting a new maintenance window, and rolling back to the anterior firmware version (A) is a possible option if the firmware upgrade did not resolve the original issue and caused more problems. However, this should not be done without first verifying that the users’ concerns are related to the firmware upgrade and not a different issue.
Employing a divide-and-conquer troubleshooting methodology by engaging the firewall vendor’s support © is another possible option if the technician needs assistance from the vendor to diagnose or resolve the issue. However, this should also not be done without first gathering additional information from the users to narrow down the scope of the problem and provide relevant details to the vendor.
Escalating the issue to the IT management team in order to negotiate a new SLA with the user’s manager (D) is not a relevant option at this stage. An SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a contract that defines the expectations and responsibilities of both parties in terms of service quality, availability, performance, and response time. Negotiating a new SLA does not address the root cause of the issue or help to resolve it. Moreover, escalating an issue to management should only be done when all other options have been exhausted or when there is a significant impact or risk to the business.
A network administrator is reviewing the following metrics from a network management system regarding a switchport.
The administrator suspects an issue because users are calling in regards to the switchport’s performance:
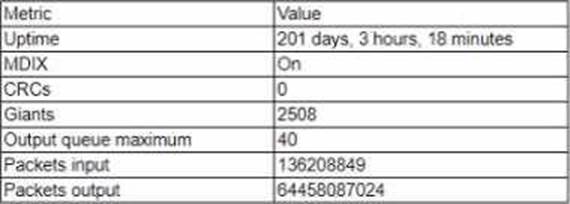
Based on the information in the chart above, which of the following fs the cause of these performance issues?
- A . The connected device is exceeding the configured MTU.
- B . The connected device is sending too many packets
- C . The switchport has been up for too long
- D . The connected device is receiving too many packets.
- E . The switchport does not have enough CRCs
A
Explanation:
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest size of a data packet that can be transmitted over a network link12. The MTU is usually configured on the network devices, such as routers and switches, to match the physical or logical characteristics of the link34.
If the connected device sends a packet that is larger than the MTU of the switchport, the packet will be either fragmented or dropped, depending on the protocol and configuration12. This can cause performance issues, such as increased latency, reduced throughput, and packet loss56.
Based on the information in the chart, the switchport has a high number of giants, which are packets that exceed the MTU of the link78. This indicates that the connected device is exceeding the configured MTU of the switchport, and thus causing the performance issues.
The other options are not supported by the information in the chart. The number of packets sent or received by the connected device does not necessarily affect the performance of the switchport, unless there is congestion or buffer overflow. The uptime of the switchport does not affect its performance, unless there is a hardware or software failure. The number of CRCs (cyclic redundancy checks) indicates the error rate of the link, and the switchport has zero CRCs, which means there are no errors detected910.
Therefore, the best answer is
A network technician is investigating an IP phone that does not register in the VoIP system Although it received an IP address, it did not receive the necessary DHCP options. The information that is needed for the registration is distributes by the OHCP scope All other IP phones are working properly.
Which of the following does the technician need to verify?
- A . VLAN mismatch
- B . Transceiver mismatch
- C . Latency
- D . DHCP exhaustion
A
Explanation:
A VLAN mismatch is the most likely reason why an IP phone does not receive the necessary DHCP options for registration. A VLAN mismatch occurs when a device is connected to a switch port that belongs to a different VLAN than the device’s intended VLAN. This can cause communication problems or prevent access to network resources. For example, if an IP phone is connected to a switch port that belongs to the data VLAN instead of the voice VLAN, it may not receive the DHCP options that contain information such as the TFTP server address, the NTP server address, or the default gateway address for the voice VLAN. These DHCP options are essential for the IP phone to register with the VoIP system and function properly.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/voice-unified-communications/unified-communications-manager-callmanager/13979-dhcp-option-150-00.html
