Practice Free MuleSoft Integration Architect I Exam Online Questions
An insurance provider is implementing Anypoint platform to manage its application infrastructure and is using the customer hosted runtime for its business due to certain financial requirements it must meet. It has built a number of synchronous API’s and is currently hosting these on a mule runtime on one server These applications make use of a number of components including heavy use of object stores and VM queues.
Business has grown rapidly in the last year and the insurance provider is starting to receive reports of reliability issues from its applications.
The DevOps team indicates that the API’s are currently handling too many requests and this is over loading the server. The team has also mentioned that there is a significant downtime when the server is down for maintenance.
As an integration architect, which option would you suggest to mitigate these issues?
- A . Add a load balancer and add additional servers in a server group configuration
- B . Add a load balancer and add additional servers in a cluster configuration
- C . Increase physical specifications of server CPU memory and network
- D . Change applications by use an event-driven model
What is a defining characteristic of an integration-Platform-as-a-Service (iPaaS)?
- A . A Cloud-based
- B . No-code
- C . Code-first
- D . On-premises
An organization’s security requirements mandate centralized control at all times over authentication and authorization of external applications when invoking web APIs managed on Anypoint Platform.
What Anypoint Platform feature is most idiomatic (used for its intended purpose), straightforward, and maintainable to use to meet this requirement?
- A . Client management configured in access management
- B . Identity management configured in access management
- C . Enterprise Security module coded in Mule applications
- D . External access configured in API Manager
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://blogs.mulesoft.com/dev-guides/api-security-ways-to-authenticate-and-authorize/
An API implementation is being designed that must invoke an Order API which is known to repeatedly experience downtime. For this reason a fallback API is to be called when the Order API is unavailable.
What approach to designing invocation of the fallback API provides the best resilience?
- A . Redirect client requests through an HTTP 303 temporary redirect status code to the fallback API whenever the Order API is unavailable
- B . Set an option in the HTTP Requester component that invokes the order API to instead invoke a fallback API whenever an HTTP 4XX or 5XX response status code is received from Order API
- C . Create a separate entry for the order API in API manager and then invoke this API as a fallback API if the primary Order API is unavailable
- D . Search Anypoint Exchange for a suitable existing fallback API and them implement invocations to their fallback API in addition to the Order API
A
Explanation:
* Resilience testing is a type of software testing that observes how applications act under stress. It’s meant to ensure the product’s ability to perform in chaotic conditions without a loss of core functions or data; it ensures a quick recovery after unforeseen, uncontrollable events.
* In case an API invocation fails ― even after a certain number of retries ― it might be adequate to invoke a different API as a fallback. A fallback API, by definition, will never be ideal for the purpose of the API client, otherwise it would be the primary API.
* Here are some examples for fallback APIs:
– An old, deprecated version of the same API.
– An alternative endpoint of the same API and version (e.g. API in another CloudHub region).
– An API doing more than required, and therefore not as performant as the primary API.
– An API doing less than required and therefore forcing the API Client to offer a degraded service, which is still better than no service at all.
* API clients implemented as Mule applications offer the ‘Until Successful Scope and Exception’ strategies at their disposal, which together allow configuring fallback actions such as a fallback API invocation.
* All HTTP response status codes within the 3xx category are considered redirection messages. These codes indicate to the user agent (i.e. your web browser) that an additional action is required in order to complete the request and access the desired resource
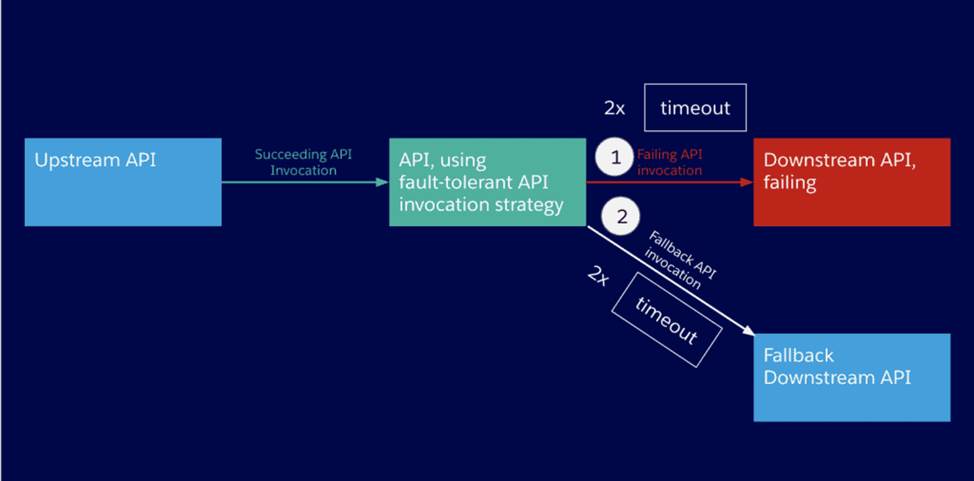
Hence correct answer is Redirect client requests through an HTTP 303 temporary redirect status code to the fallback API whenever the Order API is unavailable
As part of a growth strategy, a supplier signs a trading agreement with a large customer. The customer sends purchase orders to the supplier according to the ANSI X12 EDI standard, and the supplier creates the orders in its ERP system using the information in the EDI document.
The agreement also requires that the supplier provide a new RESTful API to process request from the customer for current product inventory level from the supplier’ s ERP system.
Which two fundamental integration use cases does the supplier need to deliver to provide an end-to-end solution for this business scenario? (Choose two.)
- A . Synchronized data transfer
- B . Sharing data with external partners
- C . User interface integration
- D . Streaming data ingestion
- E . Data mashups
A Mule application is built to support a local transaction for a series of operations on a single database. The Mule application has a Scatter-Gather that participates in the local transaction.
What is the behavior of the Scatter-Gather when running within this local transaction?
- A . Execution of each route within the Scatter-Gather occurs sequentially
Any error that occurs inside the Scatter-Gather will result in a rollback of all the database operations - B . Execution of all routes within the Scatter-Gather occurs in parallel
Any error that occurs inside the Scatter-Gather will result in a rollback of all the database operations - C . Execution of each route within the Scatter-Gather occurs sequentially
Any error that occurs inside the Scatter-Gather will NOT result in a rollback of any of the database operations - D . Execution of each route within the Scatter-Gather occurs in parallel
Any error that occurs inside the Scatter-Gather will NOT result in a rollback of any of the database operations
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.4/transaction-management
An organization is designing the following two Mule applications that must share data via a common persistent object store instance:
– Mule application P will be deployed within their on-premises datacenter.
– Mule application C will run on CloudHub in an Anypoint VPC.
The object store implementation used by CloudHub is the Anypoint Object Store v2 (OSv2).
What type of object store(s) should be used, and what design gives both Mule applications access to the same object store instance?
- A . Application P uses the Object Store connector to access a persistent object store Application C accesses this persistent object store via the Object Store REST API through an IPsec tunnel
- B . Application C and P both use the Object Store connector to access the Anypoint Object Store v2
- C . Application C uses the Object Store connector to access a persistent object Application P accesses the persistent object store via the Object Store REST API
- D . Application C and P both use the Object Store connector to access a persistent object store
C
Explanation:
Correct answer is Application A accesses the persistent object store via the Object Store REST API Application B uses the Object Store connector to access a persistent object * Object Store v2 lets CloudHub applications store data and states across batch processes, Mule components and applications, from within an application or by using the Object Store REST API. * On-premise Mule applications cannot use Object Store v2. * You can select Object Store v2 as the implementation for Mule 3 and Mule 4 in CloudHub by checking the Object Store V2 checkbox in Runtime Manager at deployment time.
* CloudHub Mule applications can use Object Store connector to write to the object store
* The only way on-premises Mule applications can access Object Store v2 is via the Object Store REST API.
* You can configure a Mule app to use the Object Store REST API to store and retrieve values from an object store in another Mule app.
A project team is working on an API implementation using the RAML definition as a starting point. The team has updated the definition to include new operations and has published a new version to exchange. Meanwhile another team is working on a mule application consuming the same API implementation.
During the development what has to be performed by the mule application team to take advantage of the newly added operations?
- A . Scaffold the client application with the new definition
- B . Scaffold API implementation application with the new definition
- C . Update the REST connector from exchange in the client application
- D . Update the API connector in the API implementation and publish to exchange
A company wants its users to log in to Anypoint Platform using the company’s own internal user credentials. To achieve this, the company needs to integrate an external identity provider (IdP) with the company’s Anypoint Platform master organization, but SAML 2.0 CANNOT be used.
Besides SAML 2.0, what single-sign-on standard can the company use to integrate the IdP with their Anypoint Platform master organization?
- A . SAML 1.0
- B . OAuth 2.0
- C . Basic Authentication
- D . OpenID Connect
D
Explanation:
As the Anypoint Platform organization administrator, you can configure identity management in Anypoint Platform to set up users for single sign-on (SSO).
Configure identity management using one of the following single sign-on standards:
1) OpenID Connect: End user identity verification by an authorization server including SSO
2) SAML 2.0: Web-based authorization including cross-domain SSO
Refer to the exhibit.
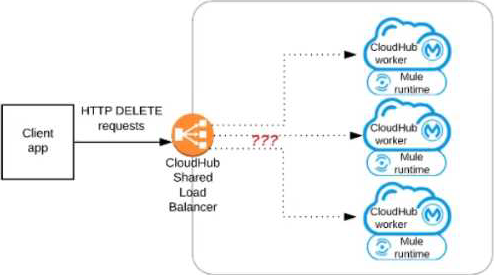
A Mule application has an HTTP Listener that accepts HTTP DELETE requests. This Mule application Is deployed to three CloudHub workers under the control of the CloudHub Shared Load Balancer. A web client makes a sequence of requests to the Mule application’s public URL.
How is this sequence of web client requests distributed among the HTTP Listeners running in the three CloudHub workers?
- A . Each request is routed to the PRIMARY CloudHub worker in the PRIMARY Availability Zone (AZ)
- B . Each request is routed to ONE ARBiTRARY CloudHub worker in the PRIMARY Availability Zone (AZ)
- C . Each request Is routed to ONE ARBiTRARY CloudHub worker out of ALL three CloudHub workers
- D . Each request is routed (scattered) to ALL three CloudHub workers at the same time
C
Explanation:
Correct behavior is Each request is routed to ONE ARBITRARY CloudHub worker out of ALL three CloudHub workers
