Practice Free MD-102 Exam Online Questions
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. Active Directory is synced with a Microsoft Entra tenant.
There are 500 Active Directory domain-joined computers that run Windows 10 and are enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
You plan to implement Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard.
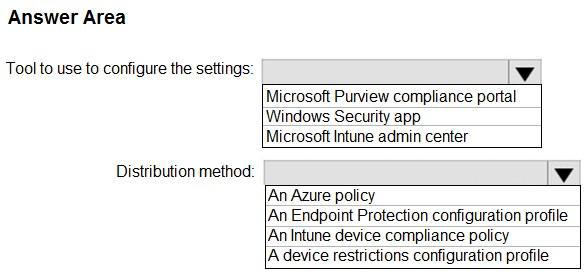
You need to create a custom Microsoft Defender Exploit Guard policy, and then distribute the policy to all the computers.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/microsoft-defender-atp/import-export-
exploit-protection-emet-xml#manage-or-deploy-a-configuration
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/endpoint-protection-windows-10
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/microsoft-defender-atp/enable-exploit-
protection
DRAG DROP
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription. The subscription contains computers that run Windows 11 and are enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
You need to create a compliance policy that meets the following requirements:
Requires BitLocker Drive Encryption (BitLocker) on each device Requires a minimum operating system version
![]()
![]()
Which setting of the compliance policy should you configure for each requirement? To answer, drag the appropriate settings to the correct requirements. Each setting may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:


Explanation:
Device Compliance settings for Windows 10/11 in Intune
As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to require BitLocker, set a minimum and maximum operating system, set a risk level using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, and more.
Box 1: Device Health
Device Health
Windows Health Attestation Service evaluation rules
Require BitLocker:
Windows BitLocker Drive Encryption encrypts all data stored on the Windows operating system volume. BitLocker uses the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to help protect the Windows operating system and user data. It also helps confirm that a computer isn’t tampered with, even if its left unattended, lost, or stolen. If the computer is equipped with a compatible TPM, BitLocker uses the TPM to lock the encryption keys that protect the data. As a result, the keys can’t be accessed until the TPM verifies the state of the computer.
Not configured (default) – This setting isn’t evaluated for compliance or non-compliance. Require – The device can protect data that’s stored on the drive from unauthorized access when the system is off, or hibernates.
Box 2: Device Properties
Requires a minimum operating system version
Device Properties
Operating System Version
To discover build versions for all Windows 10/11 Feature Updates and Cumulative Updates (to be used in some of the fields below), see Windows release information. Be sure to include the appropriate version prefix before the build numbers, like 10.0 for Windows 10 as the following examples illustrate.
Minimum OS version:
Enter the minimum allowed version in the major.minor.build.revision number format. To get the correct value, open a command prompt, and type ver.
Etc.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/compliance-policy-create-windows
DRAG DROP
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription. The subscription contains computers that run Windows 11 and are enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
You need to create a compliance policy that meets the following requirements:
Requires BitLocker Drive Encryption (BitLocker) on each device Requires a minimum operating system version
![]()
![]()
Which setting of the compliance policy should you configure for each requirement? To answer, drag the appropriate settings to the correct requirements. Each setting may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:


Explanation:
Device Compliance settings for Windows 10/11 in Intune
As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to require BitLocker, set a minimum and maximum operating system, set a risk level using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, and more.
Box 1: Device Health
Device Health
Windows Health Attestation Service evaluation rules
Require BitLocker:
Windows BitLocker Drive Encryption encrypts all data stored on the Windows operating system volume. BitLocker uses the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) to help protect the Windows operating system and user data. It also helps confirm that a computer isn’t tampered with, even if its left unattended, lost, or stolen. If the computer is equipped with a compatible TPM, BitLocker uses the TPM to lock the encryption keys that protect the data. As a result, the keys can’t be accessed until the TPM verifies the state of the computer.
Not configured (default) – This setting isn’t evaluated for compliance or non-compliance. Require – The device can protect data that’s stored on the drive from unauthorized access when the system is off, or hibernates.
Box 2: Device Properties
Requires a minimum operating system version
Device Properties
Operating System Version
To discover build versions for all Windows 10/11 Feature Updates and Cumulative Updates (to be used in some of the fields below), see Windows release information. Be sure to include the appropriate version prefix before the build numbers, like 10.0 for Windows 10 as the following examples illustrate.
Minimum OS version:
Enter the minimum allowed version in the major.minor.build.revision number format. To get the correct value, open a command prompt, and type ver.
Etc.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/compliance-policy-create-windows
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription.
You plan to enroll devices in Microsoft Intune that have the platforms and versions shown in the following table.
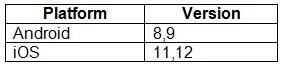
You need to configure device enrollment to meet the following requirements:
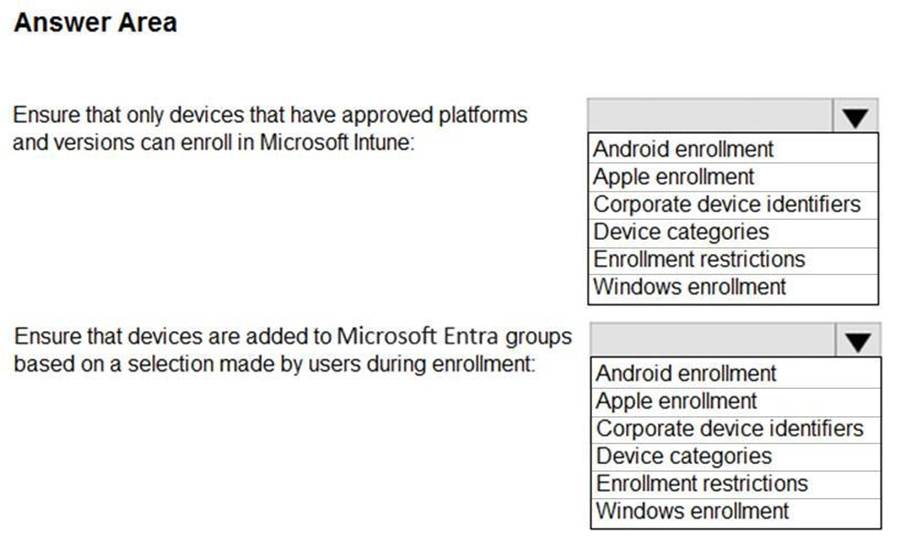
Ensure that only devices that have approved platforms and versions can enroll in Microsoft Intune. Ensure that devices are added to Microsoft Entra groups based on a selection made by users during the enrollment.
![]()
![]()
Which device enrollment setting should you configure for each requirement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Explanation:
Box 1: Enrollment restrictions
As an Intune administrator, you can create and manage enrollment restrictions that define what devices can enroll into management with Intune, including the:
Number of devices.
Operating systems and versions.
Box 2: Device categories
To make managing devices easier, you can use Microsoft Intune device categories to automatically add devices to groups based on categories that you define.
Device categories use the following workflow:
Create categories that users can choose from when they enroll their device.
When users of iOS/iPadOS and Android devices enroll a device, they must choose a category from the list of categories you configured. To assign a category to a Windows device, users must use the Company Portal website.
You can then deploy policies and apps to these groups.
You can create any device categories you want. For example:
– Point-of-sale device
– Demonstration device
– Sales
– Accounting
– Manager
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/enrollment/enrollment-restrictions-set
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/enrollment/device-group-mapping
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune Suite.
You use Microsoft Intune to deploy and manage Windows devices.
You have 100 devices from users that left your company.
You need to repurpose the devices for new users by removing all the data and applications installed by the previous users. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you do?
F. Deploy a new configuration profile to the devices.
G. Perform a Windows Autopilot reset on the devices.
H. Perform an in-place upgrade on the devices.
I. Perform a clean installation of Windows 11 on the devices.
Explanation:
Windows Autopilot Reset takes the device back to a business-ready state, allowing the next user to sign in and get productive quickly and simply. Specifically, Windows Autopilot Reset:
Removes personal files, apps, and settings.
Reapplies a device’s original settings.
Sets the region, language, and keyboard to the original values.
Maintains the device’s identity connection to Azure AD.
Maintains the device’s management connection to Intune.
The Windows Autopilot Reset process automatically keeps information from the existing device:
Wi-Fi connection details.
Provisioning packages previously applied to the device.
A provisioning package present on a USB drive when the reset process is started.
Azure Active Directory device membership and MDM enrollment information.
SCEP certificates.
Windows Autopilot Reset blocks the user from accessing the desktop until this information is restored, including reapplying any provisioning packages. For devices enrolled in an MDM service, Windows
Autopilot Reset also blocks until an MDM sync is completed. When Autopilot reset is used on a device, the device’s primary user is removed. The next user who signs in after the reset will be set as the primary user.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/autopilot/windows-autopilot-reset
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune Suite.
You use Microsoft Intune to deploy and manage Windows devices.
You have 100 devices from users that left your company.
You need to repurpose the devices for new users by removing all the data and applications installed by the previous users. The solution must minimize administrative effort.
What should you do?
F. Deploy a new configuration profile to the devices.
G. Perform a Windows Autopilot reset on the devices.
H. Perform an in-place upgrade on the devices.
I. Perform a clean installation of Windows 11 on the devices.
Explanation:
Windows Autopilot Reset takes the device back to a business-ready state, allowing the next user to sign in and get productive quickly and simply. Specifically, Windows Autopilot Reset:
Removes personal files, apps, and settings.
Reapplies a device’s original settings.
Sets the region, language, and keyboard to the original values.
Maintains the device’s identity connection to Azure AD.
Maintains the device’s management connection to Intune.
The Windows Autopilot Reset process automatically keeps information from the existing device:
Wi-Fi connection details.
Provisioning packages previously applied to the device.
A provisioning package present on a USB drive when the reset process is started.
Azure Active Directory device membership and MDM enrollment information.
SCEP certificates.
Windows Autopilot Reset blocks the user from accessing the desktop until this information is restored, including reapplying any provisioning packages. For devices enrolled in an MDM service, Windows
Autopilot Reset also blocks until an MDM sync is completed. When Autopilot reset is used on a device, the device’s primary user is removed. The next user who signs in after the reset will be set as the primary user.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/autopilot/windows-autopilot-reset
HOTSPOT
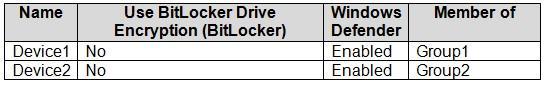
In Microsoft Intune, you have the device compliance policies shown in the following table.
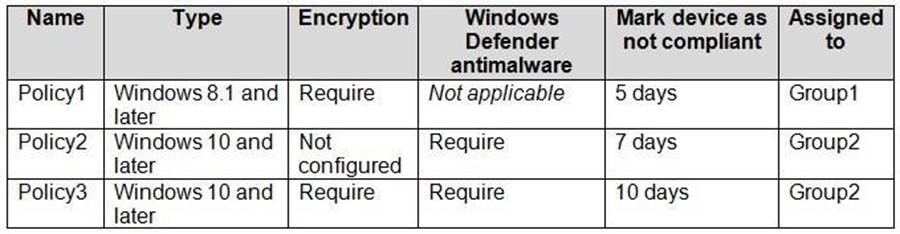
The Intune compliance policy settings are configured as shown in the following exhibit.

On June 1, you enroll Windows 10 devices in Intune as shown in the following table.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Explanation:
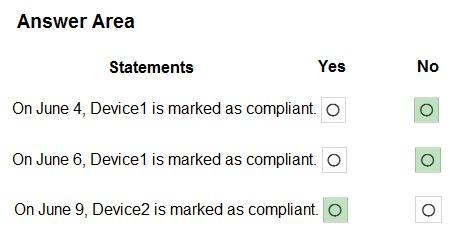
Box 1: No
Device1 has Windows 10, Bitlocker disabled, Windows Defender enabled.
Device1 is member of Group1.
Policy1 applies to Group1.
Policy1 required Bitlocker.
Policy1 has a 5 days grace period.
Box 2: No
Device1 would be marked as non-compliant.
Box 3: Yes
Device2 is Windows 10, Bitlocker disabled, and member of Group2.
Policy2 and Policy3 are assigned to Group2.
Policy3 required BitLocker.
Policy3 has a 10 day grace period.
Policy2 is met. Device2 is marked as compliant.
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune Suite.
You use Intune to manage all devise.
Users have iOS devices with Microsoft apps installed.
You need to prevent users from cutting, copying, and pasting data between Microsoft Excel and other apps installed on the devices.
What should you configure?
- A . an app protection policy
- B . an app configuration policy
- C . an iOS app provisioning profile
- D . policies for Microsoft Office apps
A
Explanation:
Troubleshoot restricting cut, copy, and paste between applications
The cut, copy, and paste feature is commonly used to transfer data between applications (apps). Restricting
this feature may not work as expected. To troubleshoot these issues, first ensure that the issues and configurations discussed in the Troubleshooting data transfer between apps document are addressed.
When reviewing Intune *app protection policy (APP)* settings in the Intune admin center, refer to the following table to make sure the desired settings are applied.
* Restrict cut, copy, and paste between other apps Blocked
Block copy and paste function to and from all managed apps.
* Etc.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/mem/intune/app-protection-policies/troubleshoot-cut-copy-
paste
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription.
Each user is assigned a Windows 365 Enterprise license.
You need to deploy Cloud PCs that will be Microsoft Entra hybrid joined.
What should you do first?
- A . Create an Azure network connection (ANC).
- B . Create a provisioning policy.
- C . Create a configuration profile in Microsoft Intune.
- D . Upload a custom image.
A
Explanation:
Overview of Windows 365 deployment
After your organization has purchased one or more Windows 365 licenses, the Windows 365 node in Microsoft Intune will become active for management. At this point, you can provision Cloud PCs.
To set up your system to provision on-demand Cloud PCs to your users, follow these steps:
HOTSPOT
You have the device configuration profile shown in the following exhibit.
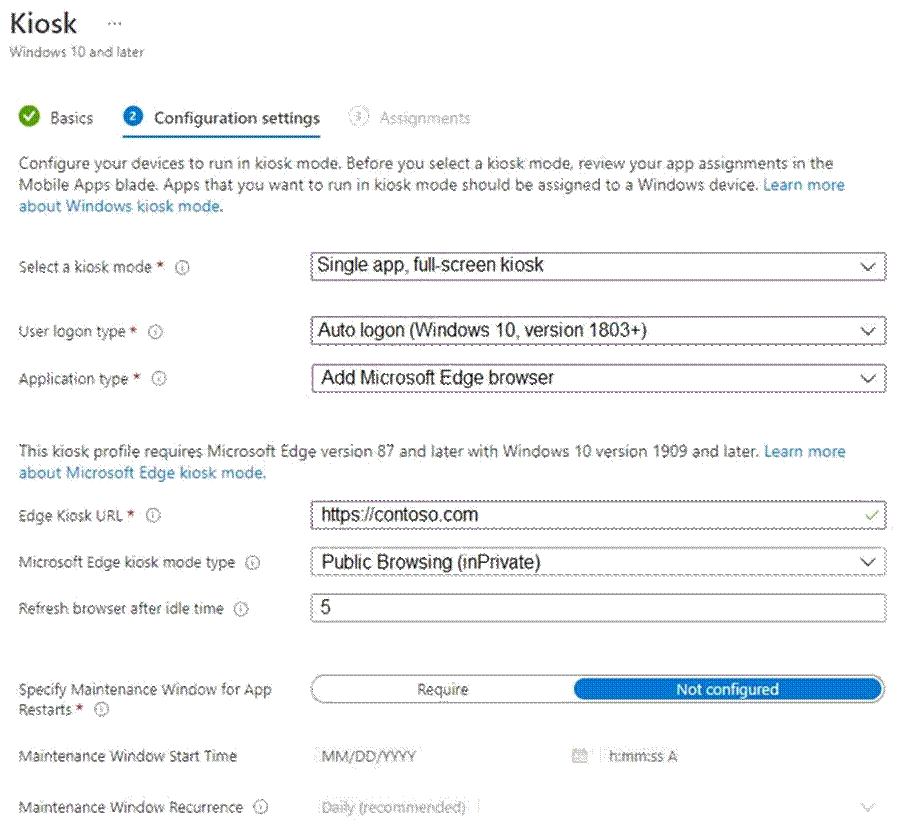
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
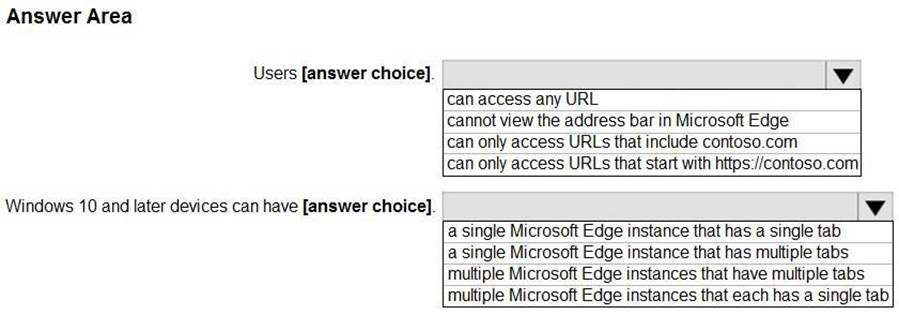

Explanation:
Box 1: can access any URL
We see: Public Browsing (InPrivate).
Microsoft Edge kiosk mode type: Select the kiosk mode type. Both options help protect user data.
Public Browsing (InPrivate): Runs a limited multi-tab version of Microsoft Edge. Users can browse publicly, or end their browsing session.
Digital/Interactive Signage (InPrivate): Opens a URL full screen, and only shows the content on that website.
Box 2: a single Microsoft Edge instance that has multiple tabs
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/kiosk-settings-windows
