Practice Free MD-102 Exam Online Questions
DRAG DROP
You have 500 Windows 10 devices enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
You plan to use Exploit protection in Microsoft Intune to enable the following system settings on the devices:
Data Execution Prevention (DEP)
Force randomization for images (Mandatory ASLR)
You need to configure a Windows 10 device that will be used to create a template file.
Which protection areas on the device should you configure in the Windows Security app before you create the template file? To answer, drag the appropriate protection areas to the correct settings. Each protection area may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:

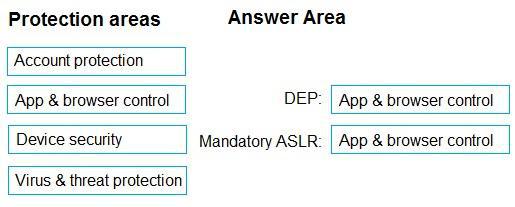
Explanation:
Box 1: App & browser control

Note: Data Execution Prevention (DEP): This mitigation prevents code from being run from data-only memory pages.
Box 2: App & browser control
Force randomization for images (Mandatory ASLR). This mitigation forcibly relocates images not compiled with /DYNAMICBASE.
Reference: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/app-browser-control-in-windows-security-8f68fb65-ebb4-3cfb-
4bd7-ef0f376f3dc3
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription and use Microsoft Intune.
You plan to implement a Microsoft Cloud PKI solution that will deploy personal user certificates to all Windows devices.
What is the minimum number of configuration profiles required to support the solution?
F. 1
G. 2
H. 3
I. 4
Explanation:
To implement a Microsoft Cloud PKI solution and deploy personal user certificates to Windows devices, you typically need at least two configuration profiles:
SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) or PKCS Certificate Profile: This profile is required to issue and deploy the user certificates to devices.
Trusted Certificate Profile: This profile is necessary to distribute the trusted root or intermediate certificate authority (CA) to ensure that the certificates issued by the CA are trusted by the devices.
These two profiles are essential for deploying and managing personal certificates using Microsoft Intune.
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune and contains a user named Admin1.
Admin1 must use the Microsoft Intune admin center to perform the following tasks:
Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune.
![]()
Create, assign, and delete Windows 365 Cloud PC provisioning policies.
![]()
You need to assign the required roles to Admin1. The solution must meet the following requirements:
Follow the principle of least privilege.
![]()
Minimize administrative effort.
![]()
What should you do?
- A . Assign Admin1 the Help Desk Operator role.
- B . Assign Admin1 the Cloud PC Reader role.
- C . Assign Admin1 the Cloud PC Administrator role.
- D . Create a custom Microsoft Entra role and assign the role to Admin1.
- E . Create a custom Intune role and assign the role to Admin1.
E
Explanation:
Windows 365 Enterprise, Role-based access control
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage who has access to your organization’s resources and
what they can do with those resources. You can assign roles for your Cloud PCs by using the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Custom roles
You can create custom roles for Windows 365 in Microsoft Intune admin center.
The following permissions are available when creating custom roles.

Etc.
Incorrect:
Not A:
Global Reader (This role is equivalent to the Intune Help Desk Operator role).
Read-only permissions.
—
Cloud PC built-in roles
The following built-in roles are available for Cloud PC:
(not C) * Cloud PC Administrator (not Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune)
Manages all aspects of Cloud PCs, like:
OS image management
Azure network connection configuration
Provisioning
(not B) * Cloud PC Reader Administrator (not Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune)
Views Cloud PC data available in the Windows 365 node in Microsoft Intune, but can’t make changes.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-365/enterprise/role-based-access
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune and contains a user named Admin1.
Admin1 must use the Microsoft Intune admin center to perform the following tasks:
Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune.
![]()
Create, assign, and delete Windows 365 Cloud PC provisioning policies.
![]()
You need to assign the required roles to Admin1. The solution must meet the following requirements:
Follow the principle of least privilege.
![]()
Minimize administrative effort.
![]()
What should you do?
- A . Assign Admin1 the Help Desk Operator role.
- B . Assign Admin1 the Cloud PC Reader role.
- C . Assign Admin1 the Cloud PC Administrator role.
- D . Create a custom Microsoft Entra role and assign the role to Admin1.
- E . Create a custom Intune role and assign the role to Admin1.
E
Explanation:
Windows 365 Enterprise, Role-based access control
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage who has access to your organization’s resources and
what they can do with those resources. You can assign roles for your Cloud PCs by using the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Custom roles
You can create custom roles for Windows 365 in Microsoft Intune admin center.
The following permissions are available when creating custom roles.

Etc.
Incorrect:
Not A:
Global Reader (This role is equivalent to the Intune Help Desk Operator role).
Read-only permissions.
—
Cloud PC built-in roles
The following built-in roles are available for Cloud PC:
(not C) * Cloud PC Administrator (not Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune)
Manages all aspects of Cloud PCs, like:
OS image management
Azure network connection configuration
Provisioning
(not B) * Cloud PC Reader Administrator (not Create and assign apps and policies to users and devices by using Intune)
Views Cloud PC data available in the Windows 365 node in Microsoft Intune, but can’t make changes.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-365/enterprise/role-based-access
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune. The subscription contains the users shown in the following table.

Group2 and Group3 are members of Group1.
All the users use Microsoft Excel.
From the Microsoft Intune admin center, you create the policies shown in the following table.

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:


Explanation:
Box 1: No
User1 is member of Group1 and Group2.
Policy1 with priority 0 is assigned to Group1: default file format for Excel is.ods.
Policy2 with priority 1 is assigned to Group2: default file format for Excel is.xlsb.
Note: Key points to remember about policy order
Policies are assigned an order of priority.
Devices receive the first applied policy only.
You can change the order of priority for policies.
Default policies are given the lowest order of priority.
Box 2: Yes
User2 is member of Group2.
Group2 and Group3 are members of Group1.
Box 3: No
User3 is member of Group3.
Group2 and Group3 are members of Group1.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/defender-business/mdb-policy-order
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune. The subscription contains the users shown in the following table.

Group2 and Group3 are members of Group1.
All the users use Microsoft Excel.
From the Microsoft Intune admin center, you create the policies shown in the following table.

For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:


Explanation:
Box 1: No
User1 is member of Group1 and Group2.
Policy1 with priority 0 is assigned to Group1: default file format for Excel is.ods.
Policy2 with priority 1 is assigned to Group2: default file format for Excel is.xlsb.
Note: Key points to remember about policy order
Policies are assigned an order of priority.
Devices receive the first applied policy only.
You can change the order of priority for policies.
Default policies are given the lowest order of priority.
Box 2: Yes
User2 is member of Group2.
Group2 and Group3 are members of Group1.
Box 3: No
User3 is member of Group3.
Group2 and Group3 are members of Group1.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/defender-business/mdb-policy-order
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune. The subscription contains corporate-owned, fully managed Android Enterprise devices.
You plan to deploy a configuration profile that will have a device restrictions profile type named Profile1.
Profile1 will assign maintenance windows for system updates.
What should you configure from the Configuration settings for Profile1?
E. Device experience
F. General
G. Connectivity
H. Power Settings
Explanation:
Intune service, Android Enterprise device settings list to allow or restrict features on corporate-owned devices using Intune
General
Fully managed, dedicated, and corporate-owned work profile devices
General Settings include:
* System update: Choose an option to define how the device handles over-the-air updates. Your options
* Maintenance window: Installs updates automatically during a daily maintenance window that you set in Intune. Installation tries daily for 30 days, and can fail if there’s insufficient space or battery levels. After 30 days, Android prompts users to install.
This setting applies to operating system and Play Store app updates. Any maintenance window takes precedence over in-progress device changes.
Use this option for dedicated devices, such as kiosks, as single-app dedicated device foreground apps can be updated.
* Etc.
Device1, Device2, and Device3
Explanation:
The Device query feature in Microsoft Intune allows querying for specific device details, such as installed software and patch levels. This feature is available for Microsoft Entra joined devices, which in this case is Device1 (Windows 11). Devices that are only Microsoft Entra registered (such as Device2 and Device3) do not support the full range of device querying features available for fully joined devices.
Device1, Device2, and Device3
Explanation:
The Device query feature in Microsoft Intune allows querying for specific device details, such as installed software and patch levels. This feature is available for Microsoft Entra joined devices, which in this case is Device1 (Windows 11). Devices that are only Microsoft Entra registered (such as Device2 and Device3) do not support the full range of device querying features available for fully joined devices.
You have 1,000 computers that run Windows 10 and are members of an Active Directory domain.
You need to capture the event logs from the computers to Azure.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:


Explanation:
Box 1: Log Analytics
Box 2: Install the Azure Monitoring Agent
Azure Monitor agent currently supports the following core functionality:
F. Collect guest logs and metrics from any machine in Azure, in other clouds, or on-premises. Azure Arc-enabled servers are required for machines outside of Azure.
G. Centrally manage data collection configuration using data collection rules, and management configuration using Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates or policies.
H. Use Windows event filtering or multi-homing for Windows or Linux logs.
I. Improved extension management.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/platform/agent-windows
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/agents/azure-monitor-agent-migration
