Practice Free MD-102 Exam Online Questions
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that contains two security groups named Group1 and Group2.
Microsoft 365 uses Microsoft Intune Suite.
You use Microsoft Intune to manage devices.
You need to assign roles in Intune to meet the following requirements:
The members of Group1 must manage Intune roles and assignments.
![]()
The members of Group2 must assign existing apps and policies to users and devices.
![]()
The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
Which role should you assign to each group? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Explanation:
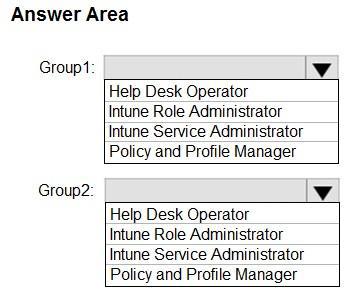
Box 1: Intune Service Administrator
The members of Group1 must manage Intune roles and assignments.
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage who has access to your organization’s resources and what they can do with those resources. By assigning roles to your Intune users, you can limit what they can see and change. Each role has a set of permissions that determine what users with that role can access and change within your organization.
To create, edit, or assign roles, your account must have one of the following permissions in Azure AD:
Global Administrator
Intune Service Administrator (also known as Intune Administrator)
Box 2: Help desk operator
The members of Group2 must assign existing apps and policies to users and devices.
Microsoft Intune built-in roles
Built-in roles use pre-defined rules based on common Intune scenarios. Alternatively, custom roles are built
upon rules that are strictly defined by you.
Here are the built-in roles that you can assign:
* Help desk operator
Assign the help desk operator role to users who assign apps and policies to users and devices.
Incorrect:
* Policy and profile manager
Assign the policy and profile manager role to users manage compliance policy, configuration profiles and Apple enrollment.
* Etc.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/role-based-access-control
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/business-premium/m365bp-intune-admin-roles-in-the-mac
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that contains two security groups named Group1 and Group2.
Microsoft 365 uses Microsoft Intune Suite.
You use Microsoft Intune to manage devices.
You need to assign roles in Intune to meet the following requirements:
The members of Group1 must manage Intune roles and assignments.
![]()
The members of Group2 must assign existing apps and policies to users and devices.
![]()
The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
Which role should you assign to each group? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:


Explanation:
Box 1: Intune Service Administrator
The members of Group1 must manage Intune roles and assignments.
Role-based access control (RBAC) helps you manage who has access to your organization’s resources and what they can do with those resources. By assigning roles to your Intune users, you can limit what they can see and change. Each role has a set of permissions that determine what users with that role can access and change within your organization.
To create, edit, or assign roles, your account must have one of the following permissions in Azure AD:
Global Administrator
Intune Service Administrator (also known as Intune Administrator)
Box 2: Help desk operator
The members of Group2 must assign existing apps and policies to users and devices.
Microsoft Intune built-in roles
Built-in roles use pre-defined rules based on common Intune scenarios. Alternatively, custom roles are built
upon rules that are strictly defined by you.
Here are the built-in roles that you can assign:
* Help desk operator
Assign the help desk operator role to users who assign apps and policies to users and devices.
Incorrect:
* Policy and profile manager
Assign the policy and profile manager role to users manage compliance policy, configuration profiles and Apple enrollment.
* Etc.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/role-based-access-control
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/business-premium/m365bp-intune-admin-roles-in-the-mac
HOTSPOT
To which devices do Policy1 and Policy2 apply? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Explanation:
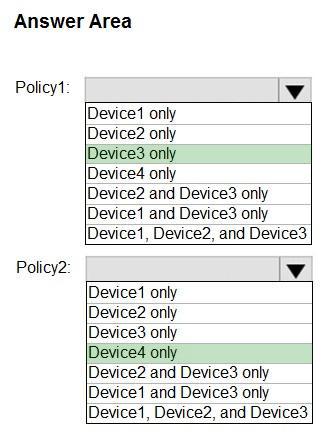
Box 1: Device 3 only
Policy1 applies to Device3 (Android)
Box 2: Device 4 only
Policy2 applies to Device4 (iOS)
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/device-profile-assign
Manage, maintain, and protect devices
Testlet 2
Case study
Overview
ADatum Corporation is a consulting company that has a main office in Montreal and branch offices in Seattle and New York.
ADatum has a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription.
Environment
Network Environment
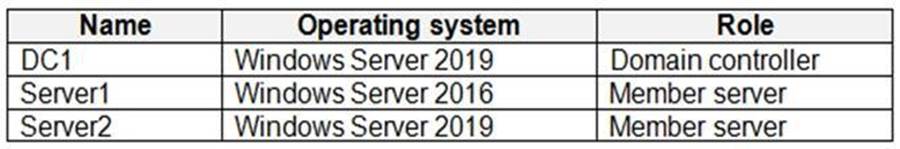
The network contains an on-premises Active Directory domain named adatum.com. The domain contains the servers shown in the following table.
ADatum has a hybrid Azure AD tenant named adatum.com.
Users and Groups
The adatum.com tenant contains the users shown in the following table.
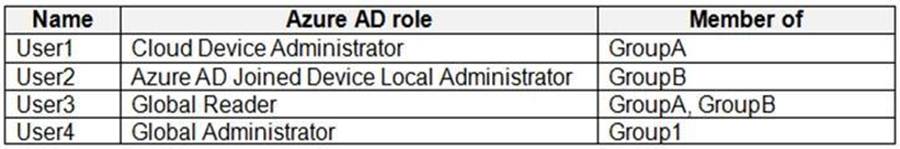
All users are assigned a Microsoft Office 365 license and an Enterprise Mobility + Security E3 license.
Enterprise State Roaming is enabled for Group1 and GroupA.
Group1 and Group2 have a Membership type of Assigned.
Devices
ADatum has the Windows 10 devices shown in the following table.
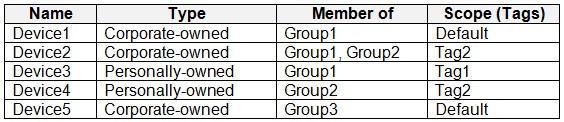
The Windows 10 devices are joined to Azure AD and enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
The Windows 10 devices are configured as shown in the following table.
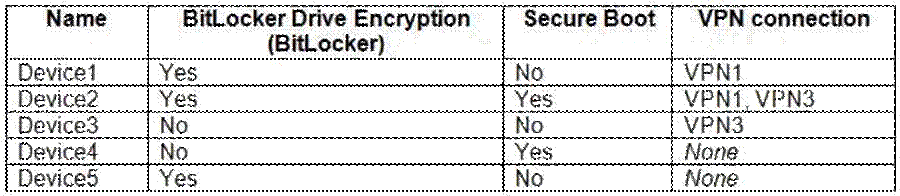
All the Azure AD joined devices have an executable file named C:AppA.exe and a folder named D:
Folder1.
Microsoft Intune Configuration
Microsoft Intune has the compliance policies shown in the following table.
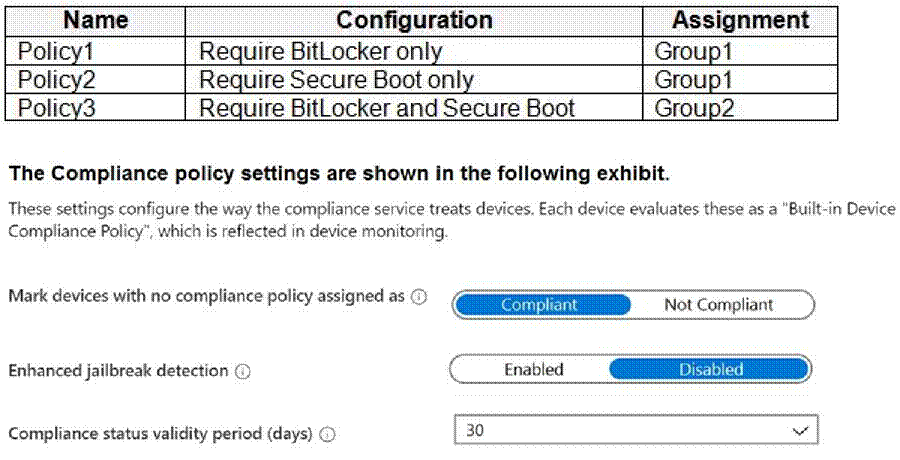
The Automatic Enrollment settings have the following configurations:
MDM user scope: GroupA
![]()
MAM user scope: GroupB
![]()
You have an Endpoint protection configuration profile that has the following Controlled folder access settings:
Name: Protection1
![]()
Folder protection: Enable
![]()
List of apps that have access to protected folders: C:*AppA.exe
![]()
List of additional folders that need to be protected: D:Folder1 Assignments:
![]()
![]()
– Included groups: Group2, GroupB
Windows Autopilot Configuration
ADatum has a Windows Autopilot deployment profile configured as shown in the following exhibit.

Currently, there are no devices deployed by using Windows Autopilot.
The Intune connector for Active Directory is installed on Server1.
Requirements
Planned Changes
ADatum plans to implement the following changes:
Purchase a new Windows 10 device named Device6 and enroll the device in Intune
![]()
New computers will be deployed by using Windows Autopilot and will be hybrid Azure AD joined.
![]()
Deployed a network boundary configuration profile that will have the following settings:
![]()
E. Name: Boundary1
F. Network boundary: 192.168.1.0/24
G. Scope tags: Tag1
H. Assignments:
Included groups: Group1, Group2
Deploy two VPN configuration profiles named Connection1 and Connection2 that will have the following settings:
![]()
E. Name: Connection1
F. Connection name: VPN1
G. Connection type: L2TP
* Assignments:
Included groups: Group1, Group2, GroupA
Excluded groups: —
* Name: Connection2
* Connection name: VPN2
* Connection type: IKEv2
* Assignments:
Included groups: GroupA
Excluded groups: GroupB
Technical Requirements
ADatum must meet the following technical requirements:
Users in GroupA must be able to deploy new computers.
![]()
Administrative effort must be minimized.
![]()
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription. The subscription contains 500 computers that run Windows 11 and are enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
You need to manage the deployment of monthly security updates. The solution must meet the following requirements:
Updates must be deployed to a group of test computers for quality assurance.
![]()
Updates must be deployed automatically 15 days after the quality assurance testing.
![]()
What should you create in the Microsoft Intune admin center?
E. a device configuration profile
F. a feature update policy
G. a security baseline
H. an update ring
You have a Microsoft 365 tenant that contains the devices shown in the following table.
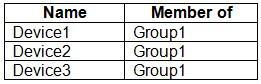
The devices are managed by using Microsoft Intune.
You create a compliance policy named Policy1 and assign Policy1 to Group1. Policy1 is configured to mark a device as Compliant only if the device security settings match the settings specified in the policy.
You discover that devices that are not members of Group1 are shown as Compliant.
You need to ensure that only devices that are assigned a compliance policy can be shown as Compliant. All other devices must be shown as Not compliant.
What should you do from the Microsoft Intune admin center?
- A . From Device compliance, configure the Compliance policy settings.
- B . From Endpoint security, configure the Conditional access settings.
- C . From Tenant administration, modify the Diagnostic settings.
- D . From Policy1, modify the actions for noncompliance.
A
Explanation:
There are two parts to compliance policies in Intune:
Compliance policy settings C Tenant- wide settings that are like a built-in compliance policy that every device receives. Compliance policy settings set a baseline for how compliance policy works in your Intune environment, including whether devices that haven’t received any device compliance policies are compliant or noncompliant.
Device compliance policy C Platform-specific rules you configure and deploy to groups of users or devices.
These rules define requirements for devices, like minimum operating systems or the use of disk encryption.
Devices must meet these rules to be considered compliant.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/protect/device-compliance-get-started
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription and 100 unmanaged iPad devices.
You need to deploy a specific iOS update to the devices. Users must be prevented from manually installing a more recent version of iOS.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
E. Create a device configuration profile.
F. Enroll the devices in Microsoft Intune by using the Intune Company Portal.
G. Create a compliance policy.
H. Create an iOS app provisioning profile.
I. Enroll the devices in Microsoft Intune by using Apple Business Manager.
Explanation:
A: iOS and iPadOS device settings to allow or restrict features using Intune
There are different settings you can control on iOS and iPadOS devices. As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to allow or disable features, set password rules, allow or restrict specific apps, and more.
This feature applies to:
iOS/iPadOS
These settings are added to a device configuration profile in Intune, and then assigned or deployed to your iOS/iPadOS devices.
E: Enroll iOS and iPadOS devices in Microsoft Intune
Personal and organization-owned devices can be enrolled in Intune. Once they’re enrolled, they receive the policies and profiles you create. You have the following options when enrolling iOS/iPadOS devices:
Automated device enrollment (ADE)
Apple Configurator
BYOD: User and Device enrollment
Automated Device Enrollment (ADE) (supervised)
Previously called Apple Device Enrollment Program (DEP). Use on devices owned by your organization. This option configures settings using Apple Business Manager (ABM) or Apple School Manager (ASM). It enrolls a large number of devices, without you ever touching the devices. These devices are purchased from Apple, have your preconfigured settings, and can be shipped directly to users or schools. You create an enrollment profile in the Intune admin center, and push this profile to the devices.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/device-restrictions-ios https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/deployment-guide-enrollment-ios-ipados
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription and 100 unmanaged iPad devices.
You need to deploy a specific iOS update to the devices. Users must be prevented from manually installing a more recent version of iOS.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
E. Create a device configuration profile.
F. Enroll the devices in Microsoft Intune by using the Intune Company Portal.
G. Create a compliance policy.
H. Create an iOS app provisioning profile.
I. Enroll the devices in Microsoft Intune by using Apple Business Manager.
Explanation:
A: iOS and iPadOS device settings to allow or restrict features using Intune
There are different settings you can control on iOS and iPadOS devices. As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to allow or disable features, set password rules, allow or restrict specific apps, and more.
This feature applies to:
iOS/iPadOS
These settings are added to a device configuration profile in Intune, and then assigned or deployed to your iOS/iPadOS devices.
E: Enroll iOS and iPadOS devices in Microsoft Intune
Personal and organization-owned devices can be enrolled in Intune. Once they’re enrolled, they receive the policies and profiles you create. You have the following options when enrolling iOS/iPadOS devices:
Automated device enrollment (ADE)
Apple Configurator
BYOD: User and Device enrollment
Automated Device Enrollment (ADE) (supervised)
Previously called Apple Device Enrollment Program (DEP). Use on devices owned by your organization. This option configures settings using Apple Business Manager (ABM) or Apple School Manager (ASM). It enrolls a large number of devices, without you ever touching the devices. These devices are purchased from Apple, have your preconfigured settings, and can be shipped directly to users or schools. You create an enrollment profile in the Intune admin center, and push this profile to the devices.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/device-restrictions-ios https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/deployment-guide-enrollment-ios-ipados
You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription and 100 unmanaged iPad devices.
You need to deploy a specific iOS update to the devices. Users must be prevented from manually installing a more recent version of iOS.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
E. Create a device configuration profile.
F. Enroll the devices in Microsoft Intune by using the Intune Company Portal.
G. Create a compliance policy.
H. Create an iOS app provisioning profile.
I. Enroll the devices in Microsoft Intune by using Apple Business Manager.
Explanation:
A: iOS and iPadOS device settings to allow or restrict features using Intune
There are different settings you can control on iOS and iPadOS devices. As part of your mobile device management (MDM) solution, use these settings to allow or disable features, set password rules, allow or restrict specific apps, and more.
This feature applies to:
iOS/iPadOS
These settings are added to a device configuration profile in Intune, and then assigned or deployed to your iOS/iPadOS devices.
E: Enroll iOS and iPadOS devices in Microsoft Intune
Personal and organization-owned devices can be enrolled in Intune. Once they’re enrolled, they receive the policies and profiles you create. You have the following options when enrolling iOS/iPadOS devices:
Automated device enrollment (ADE)
Apple Configurator
BYOD: User and Device enrollment
Automated Device Enrollment (ADE) (supervised)
Previously called Apple Device Enrollment Program (DEP). Use on devices owned by your organization. This option configures settings using Apple Business Manager (ABM) or Apple School Manager (ASM). It enrolls a large number of devices, without you ever touching the devices. These devices are purchased from Apple, have your preconfigured settings, and can be shipped directly to users or schools. You create an enrollment profile in the Intune admin center, and push this profile to the devices.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/configuration/device-restrictions-ios https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/fundamentals/deployment-guide-enrollment-ios-ipados
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft Intune subscription.
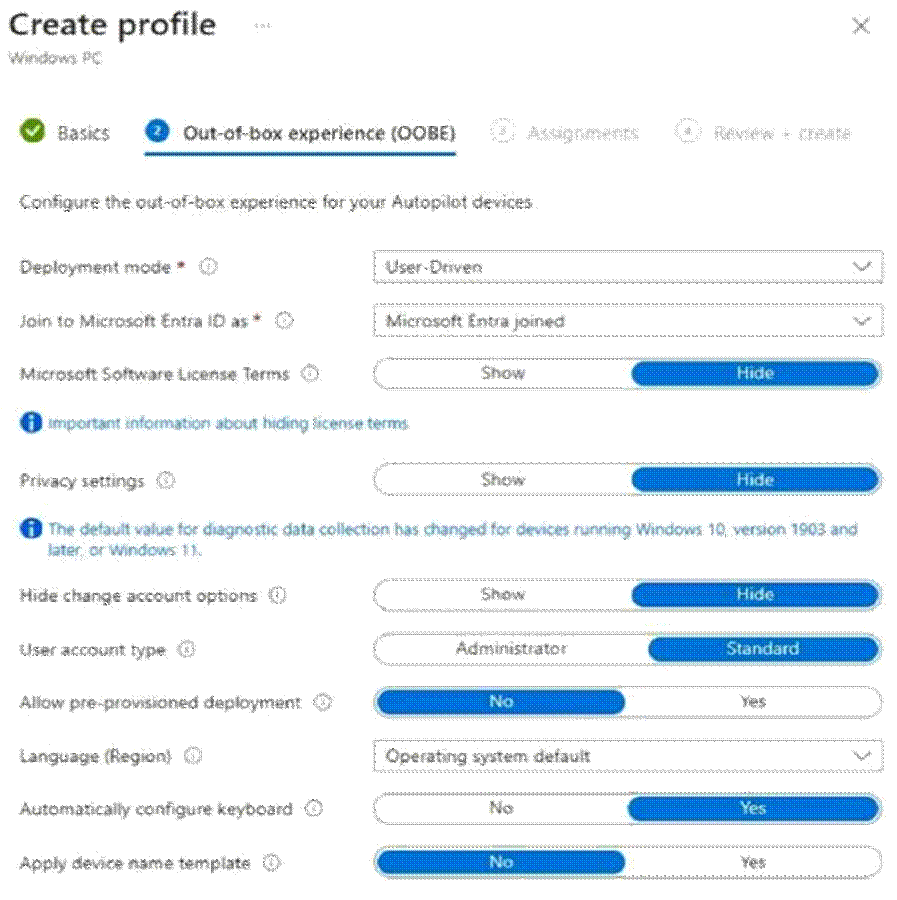
You are creating a Windows Autopilot deployment profile named Profile1 as shown in the following exhibit.
Profile1 will be deployed to Windows 10 devices.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Explanation:
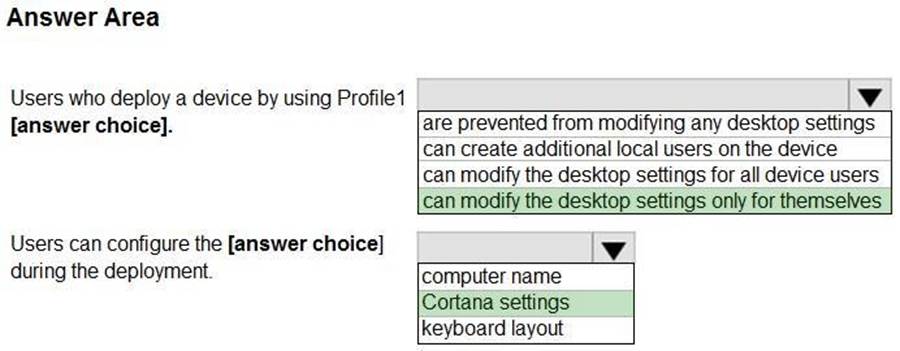
Box 1: can modify the desktop settings only for themselves
We see: User account type: Standard (not Administrator)
Incorrect:
* can create additional local users on the device
* can modify the desktop settings for all device users
Box 2: Cortana settings
Incorrect:
* computer name
We see: Hide change account options: Hide
* keyboard layout
We see: Automatically configure keyboard: Yes
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/autopilot/profiles
DRAG DROP
You have a Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT) deployment share named DS1.
You import a Windows 11 image to DS1.
You have an executable installer for an application named App1.
You need to ensure that App1 will be installed for all the task sequences that deploy the image.
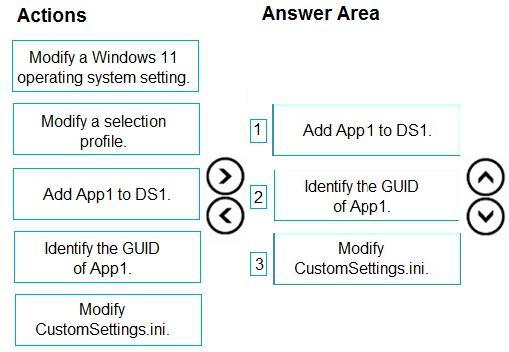
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Explanation:
Step 1: Add App1 to DS1
First add the application in the MDT console.
Step 2: Identify the GUID of App1.
Install an application when deploying Windows
Step 3: Modify CustomSettings.ini
It is possible in the CustomSettings.ini file, to check the default program to add the following line:
ApplicationsXXX ={GUID-APPLICATION}
or to force the installation of the application box checked and grayed out:
MandatoryApplicationsXXX ={GUID-APPLICATION}
XXX = numerical value from 000 to 999
Reference: https://rdr-it.com/en/mdt-installation-of-applications-when-deploying-windows/
