Practice Free MD-102 Exam Online Questions
Your company implements Microsoft Entra ID, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Intune.
The company’s security policy states the following:
Personal devices do not need to be enrolled in Intune.
![]()
Users must authenticate by using a PIN before they can access corporate email data.
![]()
Users can use their personal iOS and Android devices to access corporate cloud services.
![]()
Users must be prevented from copying corporate email data to a cloud storage service other than Microsoft OneDrive for Business.
![]()
You need to configure a solution to enforce the security policy.
What should you create?
E. a device configuration profile from the Microsoft Intune admin center
F. a data loss prevention (DLP) policy from the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
G. an insider risk management policy from the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
H. an app protection policy from the Microsoft Intune admin center
Explanation:
By implementing app-level policies, you can restrict access to company resources and keep data within the purview of your IT department.
Note: The important benefits of using App protection policies are the following:
Protecting your company data at the app level. Because mobile app management doesn’t require device management, you can protect company data on both managed and unmanaged devices. The management is centered on the user identity, which removes the requirement for device management.
End-user productivity isn’t affected and policies don’t apply when using the app in a personal context. The policies are applied only in a work context, which gives you the ability to protect company data without touching personal data.
App protection policies makes sure that the app-layer protections are in place. For example, you can:
Require a PIN to open an app in a work context
Control the sharing of data between apps
Prevent the saving of company app data to a personal storage location
MDM, in addition to MAM, makes sure that the device is protected. For example, you can require a PIN to access the device, or you can deploy managed apps to the device. You can also deploy apps to devices through your MDM solution, to give you more control over app management.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/app-protection-policy
Your company implements Microsoft Entra ID, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Intune.
The company’s security policy states the following:
Personal devices do not need to be enrolled in Intune.
![]()
Users must authenticate by using a PIN before they can access corporate email data.
![]()
Users can use their personal iOS and Android devices to access corporate cloud services.
![]()
Users must be prevented from copying corporate email data to a cloud storage service other than Microsoft OneDrive for Business.
![]()
You need to configure a solution to enforce the security policy.
What should you create?
E. a device configuration profile from the Microsoft Intune admin center
F. a data loss prevention (DLP) policy from the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
G. an insider risk management policy from the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
H. an app protection policy from the Microsoft Intune admin center
Explanation:
By implementing app-level policies, you can restrict access to company resources and keep data within the purview of your IT department.
Note: The important benefits of using App protection policies are the following:
Protecting your company data at the app level. Because mobile app management doesn’t require device management, you can protect company data on both managed and unmanaged devices. The management is centered on the user identity, which removes the requirement for device management.
End-user productivity isn’t affected and policies don’t apply when using the app in a personal context. The policies are applied only in a work context, which gives you the ability to protect company data without touching personal data.
App protection policies makes sure that the app-layer protections are in place. For example, you can:
Require a PIN to open an app in a work context
Control the sharing of data between apps
Prevent the saving of company app data to a personal storage location
MDM, in addition to MAM, makes sure that the device is protected. For example, you can require a PIN to access the device, or you can deploy managed apps to the device. You can also deploy apps to devices through your MDM solution, to give you more control over app management.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/app-protection-policy
Your company implements Microsoft Entra ID, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Intune.
The company’s security policy states the following:
Personal devices do not need to be enrolled in Intune.
![]()
Users must authenticate by using a PIN before they can access corporate email data.
![]()
Users can use their personal iOS and Android devices to access corporate cloud services.
![]()
Users must be prevented from copying corporate email data to a cloud storage service other than Microsoft OneDrive for Business.
![]()
You need to configure a solution to enforce the security policy.
What should you create?
E. a device configuration profile from the Microsoft Intune admin center
F. a data loss prevention (DLP) policy from the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
G. an insider risk management policy from the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
H. an app protection policy from the Microsoft Intune admin center
Explanation:
By implementing app-level policies, you can restrict access to company resources and keep data within the purview of your IT department.
Note: The important benefits of using App protection policies are the following:
Protecting your company data at the app level. Because mobile app management doesn’t require device management, you can protect company data on both managed and unmanaged devices. The management is centered on the user identity, which removes the requirement for device management.
End-user productivity isn’t affected and policies don’t apply when using the app in a personal context. The policies are applied only in a work context, which gives you the ability to protect company data without touching personal data.
App protection policies makes sure that the app-layer protections are in place. For example, you can:
Require a PIN to open an app in a work context
Control the sharing of data between apps
Prevent the saving of company app data to a personal storage location
MDM, in addition to MAM, makes sure that the device is protected. For example, you can require a PIN to access the device, or you can deploy managed apps to the device. You can also deploy apps to devices through your MDM solution, to give you more control over app management.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/app-protection-policy
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that uses Microsoft Intune Suite.
You use Microsoft Intune to manage devices.
You use Windows Autopilot to deploy Windows 11 to devices.
A support engineer reports that when a deployment fails, they cannot collect deployment logs from failed device.
You need to ensure that when a deployment fails, the deployment logs can be collected.
What should you configure?
- A . the automatic enrollment settings
- B . the Windows Autopilot deployment profile
- C . the enrollment status page (ESP) profile
- D . the device configuration profile
C
Explanation:
Troubleshooting the Enrollment Status Page
To troubleshoot ESP issues, it’s important to get more information about the ESP settings that are received by the device, and the applications and policies that are tracked at each stage. All ESP settings and tracking information are logged in the device registry.
Collect logs
You can enable the ability for users to collect ESP logs in the ESP policy. When a timeout occurs in the ESP, the user can select the option to Collect logs.
Note: Windows Autopilot diagnostics page
On Windows 11, you can open the Autopilot diagnostic page to view additional detailed troubleshooting information about the Autopilot provisioning process. To enable the Autopilot diagnostics page:
HOTSPOT
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant that contains the users shown in the following table.

You have devices enrolled in Microsoft Intune as shown in the following table.

From Intune, you create and send a custom notification named Notification1 to Group1.
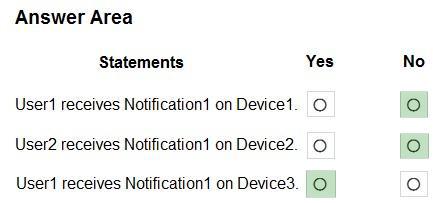
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Explanation:
Box 1: No
Not to a Windows device.
Note: Send custom notifications in Intune
Use Microsoft Intune to send custom notifications to the users of managed iOS/iPadOS and Android devices. These messages appear as standard push notifications from the Company Portal app and from the Microsoft Intune app on a user’s device, just as notifications from other applications on the device appear. Intune custom notifications aren’t supported by macOS and Windows devices.
Box 2: No
Not to User2, as it is not a member of Group1.
Note: You can send notifications to users in groups.
Box 3: Yes
User1 is member of Group1, and Device3 uses iOS.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/mem/intune/remote-actions/custom-notifications
To configure Microsoft Defender Firewall, create a Group Policy Object (GPO) and configure Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.
Explanation:
C: Use Microsoft Intune to configure and manage Microsoft Defender Antivirus
You can use the Microsoft Intune family of products to configure Microsoft Defender Antivirus scans, like Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager.
Configure Microsoft Defender Antivirus scans in Intune
* Go to the Microsoft Intune admin center (https://endpoint.microsoft.com), and sign in.
* Navigate to Endpoint Security.
* Under Manage, choose Antivirus.
* Select your Microsoft Defender Antivirus policy.
* Under Manage, choose Properties.
* Next to Configuration settings, choose Edit.
* Expand the Scan section, and review or edit your scanning settings.
* Choose Review + save.
E: Create Windows Firewall rules in Intune
To get started, Open the Microsoft Intune admin center, and then go to Devices > Windows > Configuration profiles > Create profile > Choose Windows 10 and later as the platform, Choose Templates, then Endpoint protection as the profile type. Select Windows Defender Firewall.
Reference: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/operating-system-security/network-security/windows-
firewall/create-windows-firewall-rules-in-intune
HOTSPOT
Your on-premises network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a user account named Admin1 and the resources shown in the following table.

You have a Microsoft 365 E5 subscription.
You have a Microsoft Entra tenant that syncs with contoso.com.
Admin1 plans to use Windows Autopilot to deploy 100 Windows 11 devices. The deployment must meet the following requirements:
The devices must be Microsoft Entra hybrid joined during the deployment.
![]()
Computer objects must be created in OU1.
![]()
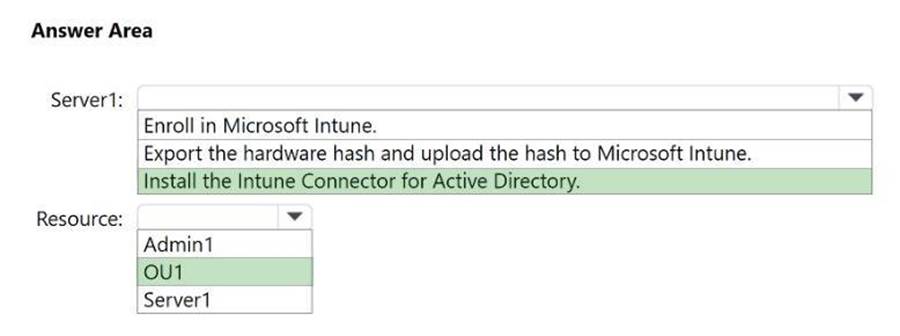
You need to configure Server1 and Active Directory delegation to support the deployment. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Explanation:
Box 1: Install the Intune Connector for Active Directory Server1
Deploy Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices by using Intune and Windows Autopilot Intune connector server prerequisites
The Intune Connector for Active Directory must be installed on a computer that’s running Windows Server 2016 or later with .NET Framework version 4.7.2 or later.
The server hosting the Intune Connector must have access to the internet and your Active Directory.
Box 2: OU1
Resource
The organizational unit that has the rights to create computers must match:
The organizational unit entered in the Domain Join profile.
If no profile is selected, the computer’s domain name for your domain.
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune.
You have 500 corporate-owned Android devices enrolled as fully managed devices.
You need to prepare an app named App1 for deployment to the devices.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
* From the Intune Company Portal, download App1.
* Sync App1 with Intune.
* From the Managed Google Play Store, approve App1.
* Create an OEMConfig profile.
Explanation:
C: Add a Managed Google Play store app in the Managed Google Play console (Alternative)
If you prefer to synchronize a Managed Google Play app with Intune rather than adding it directly using Intune, use the following steps.
E. Go to the Managed Google Play store. Sign in with the same account you used to configure the connection between Intune and Android Enterprise.
F. Search the store and select the app you want to assign by using Intune.
G. On the page that displays the app, click Approve.
In the following example, the Microsoft Excel app has been chosen.
A window for the app opens asking you to give permissions for the app to perform various operations.
You have a Microsoft 365 subscription that includes Microsoft Intune.
You have 500 corporate-owned Android devices enrolled as fully managed devices.
You need to prepare an app named App1 for deployment to the devices.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
* From the Intune Company Portal, download App1.
* Sync App1 with Intune.
* From the Managed Google Play Store, approve App1.
* Create an OEMConfig profile.
Explanation:
C: Add a Managed Google Play store app in the Managed Google Play console (Alternative)
If you prefer to synchronize a Managed Google Play app with Intune rather than adding it directly using Intune, use the following steps.
E. Go to the Managed Google Play store. Sign in with the same account you used to configure the connection between Intune and Android Enterprise.
F. Search the store and select the app you want to assign by using Intune.
G. On the page that displays the app, click Approve.
In the following example, the Microsoft Excel app has been chosen.
A window for the app opens asking you to give permissions for the app to perform various operations.
DRAG DROP
You have an on-premises Active Directory domain that syncs to a Microsoft Entra tenant.
The tenant contains computers that run Windows 10. The computers are hybrid Microsoft Entra joined and enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
The Microsoft Office settings on the computers are configured by using a Group Policy Object (GPO).
You need to migrate the GPO to Intune.
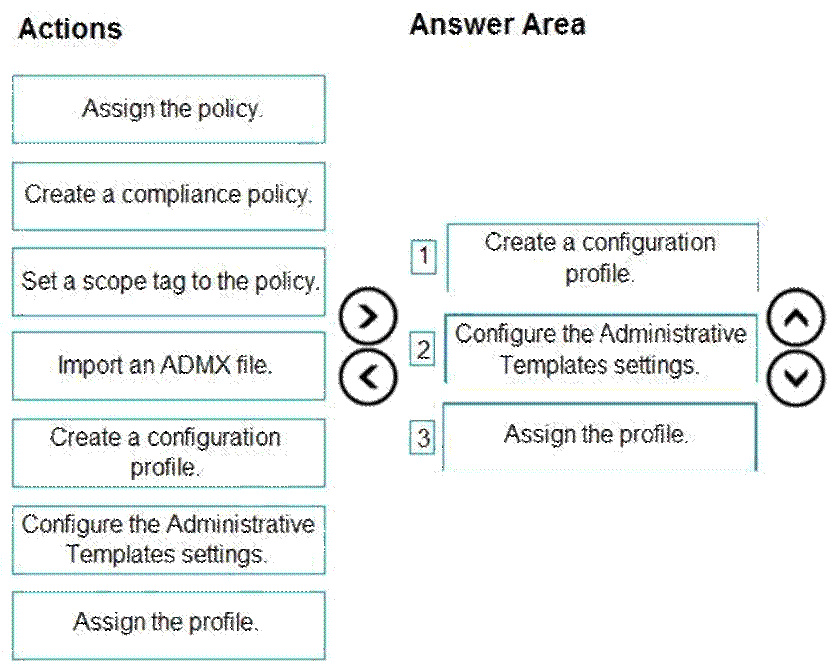
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Explanation:
Step 1: Create a configuration profile
Create the template
