Practice Free JN0-636 Exam Online Questions
Exhibit
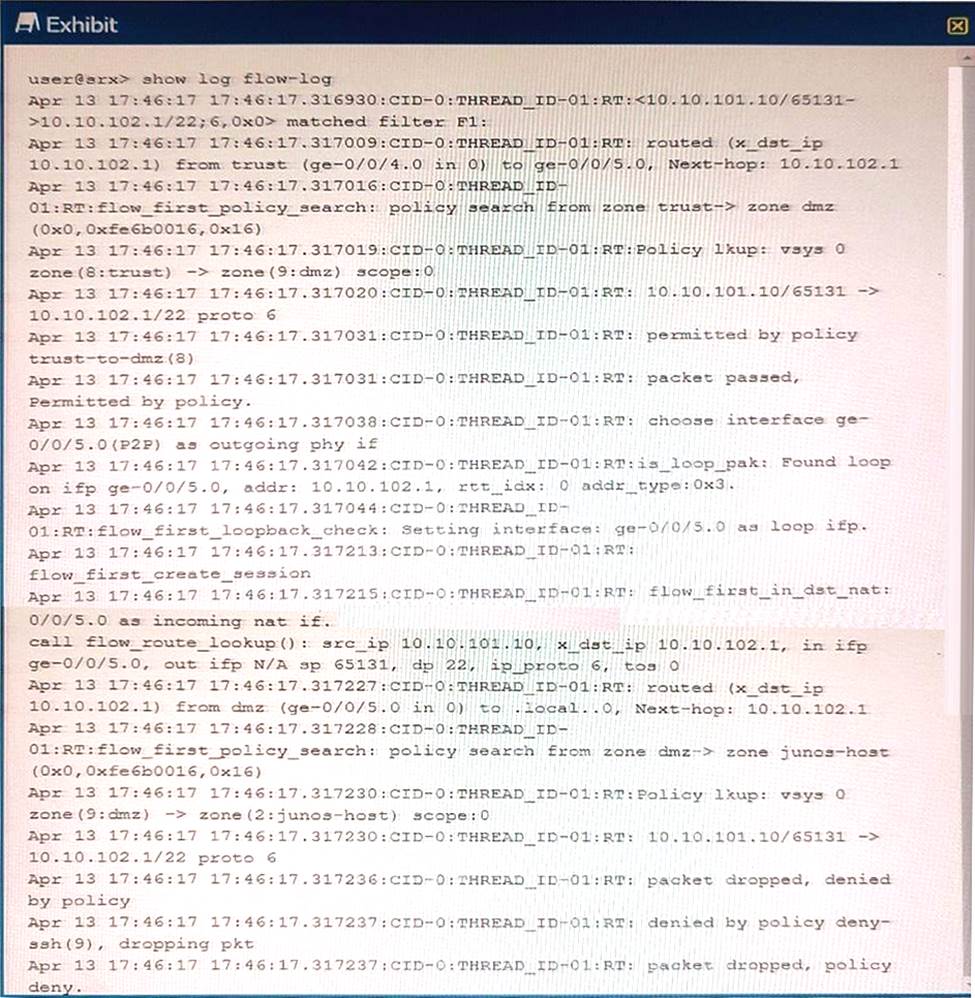
Referring to the exhibit, which three statements are true? (Choose three.)
- A . The packet’s destination is to an interface on the SRX Series device.
- B . The packet’s destination is to a server in the DMZ zone.
- C . The packet originated within the Trust zone.
- D . The packet is dropped before making an SSH connection.
- E . The packet is allowed to make an SSH connection.
Your organization has multiple Active Directory domain to control user access. You must ensure that security polices are passing traffic based upon the user’s access rights.
What would you use to assist your SRX series devices to accomplish this task?
- A . JIMS
- B . Junos Space
- C . JSA
- D . JATP Appliance
A
Explanation:
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/topic-map/security-user-auth-configure-jims.html
Exhibit
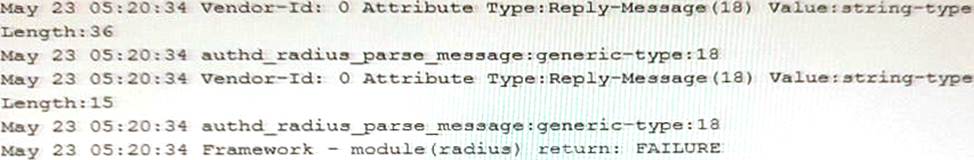
You configure a traceoptions file called radius on your returns the output shown in the exhibit
What is the source of the problem?
- A . An incorrect password is being used.
- B . The authentication order is misconfigured.
- C . The RADIUS server IP address is unreachable.
- D . The RADIUS server suffered a hardware failure.
You are connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site.You must ensure that all traffic is secured and sent directly between sites In this scenario, which VPN should be used?
- A . IPsec ADVPN
- B . hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN
- C . Layer 2 VPN
- D . full mesh Layer 3 VPN with EBGP
Exhibit:
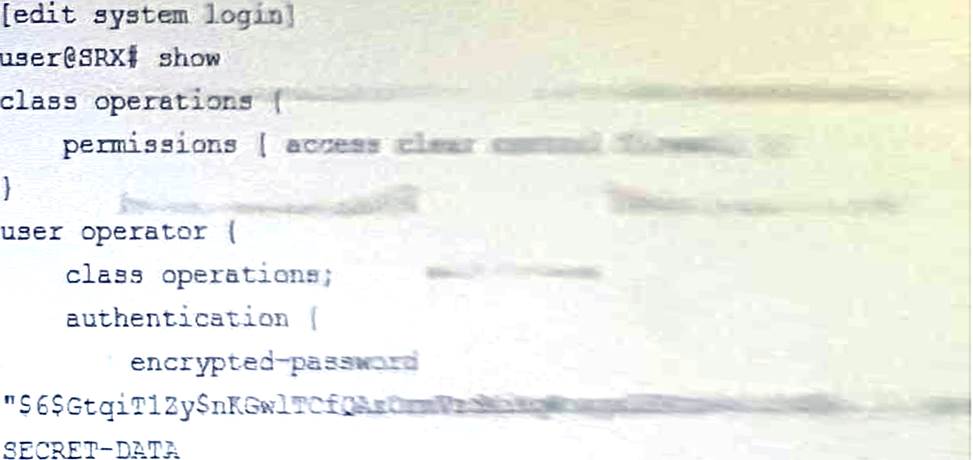
Referring to the exhibit, the operator user is unable to save configuration files to a usb stick the is plugged into SRX.
What should you do to solve this problem?
- A . Add the floppy permission flag to the operations class
- B . Add the system-control permission flag to the operation class
- C . Add the interface-control permission flag to the operation class
- D . Add the system permission flag to the operation class
B
Explanation:
To solve the problem of the operator user being unable to save configuration files to a USB stick that is plugged into SRX, you need to add the system-control permission flag to the operations class.
The other options are incorrect because:
A) Adding the floppy permission flag to the operations class is not sufficient or necessary to save configuration files to a USB stick. The floppy permission flag allows the user to access the floppy drive, but not the USB drive. The USB drive is accessed by the system permission flag, which is already included in the operations class1.
C) Adding the interface-control permission flag to the operations class is also not sufficient or necessary to save configuration files to a USB stick. The interface-control permission flag allows the user to configure and monitor interfaces, but not to save configuration files. The configuration permission flag, which is also already included in the operations class, allows the user to save configuration files1.
D) Adding the system permission flag to the operations class is redundant and ineffective to save configuration files to a USB stick. The system permission flag allows the user to access the system directory, which includes the USB drive. However, the operations class already has the system permission flag by default1. The problem is not the lack of system permission, but the lack of system-control permission.
Therefore, the correct answer is B. You need to add the system-control permission flag to the operations class to solve the problem. The system-control permission flag allows the user to perform system-level operations, such as rebooting, halting, or snapshotting the device1. These operations are required to mount, unmount, and copy files to and from the USB drive2. To add the system-control permission flag to the operations class, you need to perform the following steps:
Enter the configuration mode: user@host> configure
Navigate to the system login class hierarchy: user@host# edit system login class operations
Add the system-control permission flag: user@host# set permissions system-control
Commit the changes: user@host# commit
Reference: login (System)
How to mount a USB drive on EX/SRX/MX/QFX Series platforms to import/export files
Exhibit
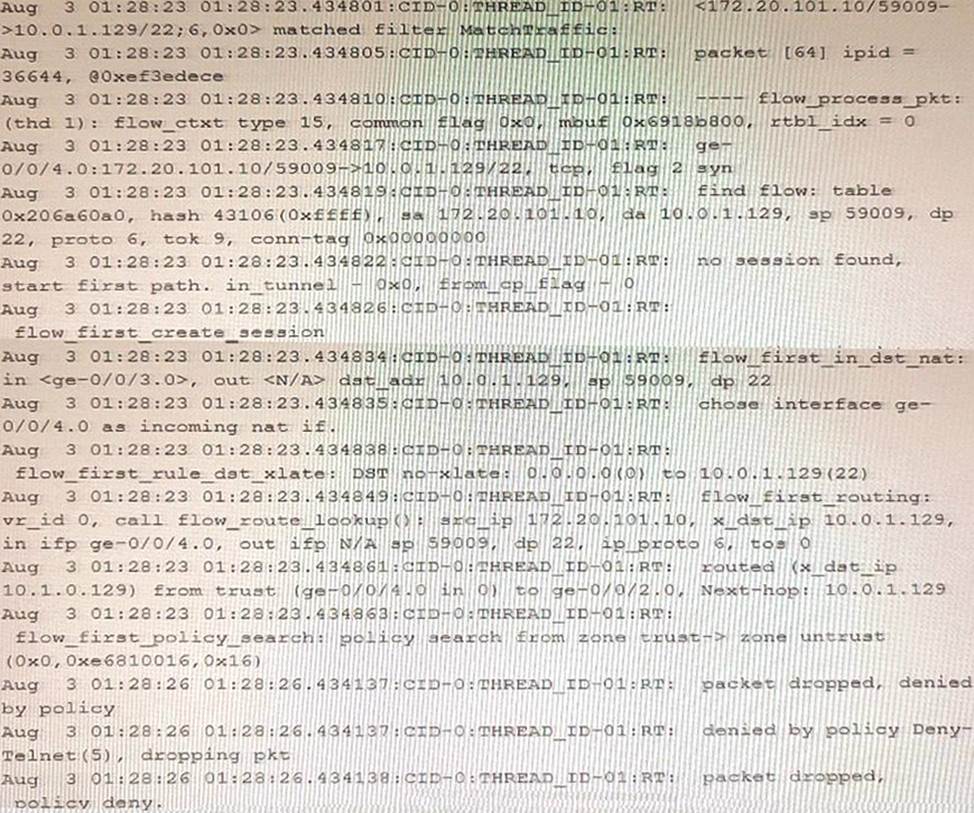
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is true?
- A . This custom block list feed will be used before the Juniper Seclntel
- B . This custom block list feed cannot be saved if the Juniper Seclntel block list feed is configured.
- C . This custom block list feed will be used instead of the Juniper Seclntel block list feed
- D . This custom block list feed will be used after the Juniper Seclntel block list feed.
Exhibit
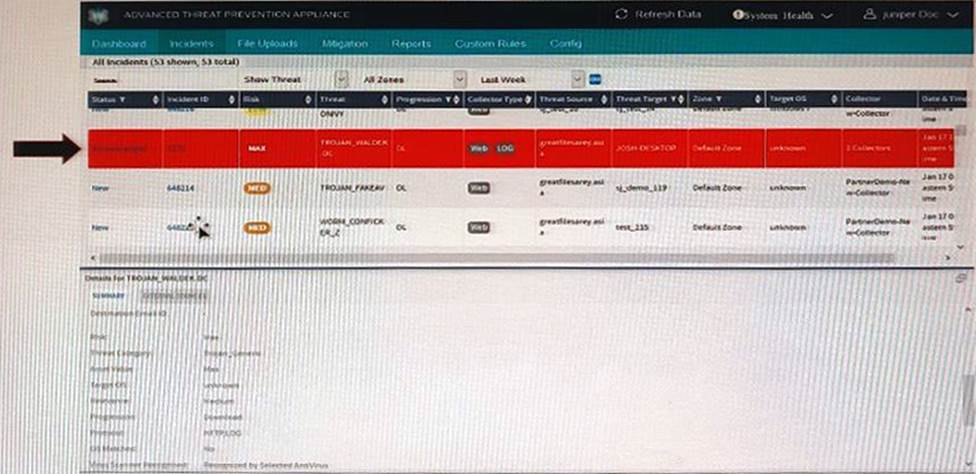
The highlighted incident (arrow) shown in the exhibit shows a progression level of "Download" in the kill chain.
What are two appropriate mitigation actions for the selected incident? (Choose two.)
- A . Immediate response required: Block malware IP addresses (download server or CnC server)
- B . Immediate response required: Wipe infected endpoint hosts.
- C . Immediate response required: Deploy IVP integration (if configured) to confirm if the endpoint has executed the malware and is infected.
- D . Not an urgent action: Use IVP to confirm if machine is infected.
Click the Exhibit button.

When attempting to enroll an SRX Series device to JATP, you receive the error shown in the exhibit.
What is the cause of the error?
- A . The fxp0 IP address is not routable
- B . The SRX Series device certificate does not match the JATP certificate
- C . The SRX Series device does not have an IP address assigned to the interface that accesses JATP
- D . A firewall is blocking HTTPS on fxp0
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://kb.juniper.net/InfoCenter/index?page=content&id=KB33979&cat=JATP_SERIES&actp=LIST
you are connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site. You must ensure that traffic passes corporate headquarter.
- A . In this scenario, which VPN should be used?
- B . full mesh IPsec VPNs with tunnels between all sites
- C . a full mesh Layer 3 VPN with the BGP route reflector behind the corporate firewall device
- D . a Layer 3 VPN with the corporate firewall acting as the hub device
- E . hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN with the corporate firewall acting as the hub device
D
Explanation:
You are connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site. You must ensure that traffic passes through the corporate headquarters. In this scenario, the VPN that should be used is:
D) Hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN with the corporate firewall acting as the hub device. A hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN is a type of VPN that connects multiple remote sites to a central site, or hub, over a public network. The hub site acts as a gateway for the remote sites and provides security and routing services. The remote sites, or spokes, communicate with each other through the hub site. The hub site and the spoke sites use IPsec tunnels to encrypt and authenticate the traffic between them. A hub-and-spoke IPsec VPN is suitable for connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site, because it allows you to control the traffic flow and enforce security policies at the hub site. The corporate firewall can act as the hub device and provide IPsec VPN services to the remote sites1.
The other options are incorrect because:
A) Full mesh IPsec VPNs with tunnels between all sites. A full mesh IPsec VPN is a type of VPN that connects every site to every other site over a public network. Each site has an IPsec tunnel with every other site, forming a mesh topology. A full mesh IPsec VPN provides direct and secure communication between any pair of sites, but it also requires a large number of IPsec tunnels and complex configuration. A full mesh IPsec VPN is not suitable for connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site, because it does not ensure that traffic passes through the corporate headquarters site, and it may introduce unnecessary overhead and complexity2.
B) A full mesh Layer 3 VPN with the BGP route reflector behind the corporate firewall device. A full mesh Layer 3 VPN is a type of VPN that uses MPLS and BGP to provide Layer 3 connectivity and routing between multiple sites over a service provider’s network. Each site has a BGP session with every other site, forming a full mesh topology. A BGP route reflector is a device that reduces the number of BGP sessions required in a full mesh topology by reflecting routes between its clients. A full mesh Layer 3 VPN with the BGP route reflector behind the corporate firewall device is not suitable for connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site, because it does not ensure that traffic passes through the corporate firewall device, and it may require additional configuration and coordination with the service provider3.
C) A Layer 3 VPN with the corporate firewall acting as the hub device. A Layer 3 VPN is a type of VPN that uses MPLS and BGP to provide Layer 3 connectivity and routing between multiple sites over a service provider’s network. A Layer 3 VPN can have different topologies, such as full mesh, hub-and-spoke, or partial mesh. A Layer 3 VPN with the corporate firewall acting as the hub device is not suitable for connecting two remote sites to your corporate headquarters site, because the corporate firewall may not support MPLS and BGP, and it may require additional configuration and coordination with the service provider3.
Reference: Hub-and-Spoke VPNs Overview Full Mesh VPNs Overview Layer 3 VPNs Overview
You want to use selective stateless packet-based forwarding based on the source address.
In this scenario, which command will allow traffic to bypass the SRX Series device flow daemon?
- A . set firewall family inet filter bypaa3_flowd term t1 then skip―services accept
- B . set firewall family inet filter bypass_flowd term t1 then routing-instance stateless
- C . set firewall family inet filter bypas3_flowd term t1 then virtual-channel stateless
- D . set firewall family inet filter bypass__f lowd term t1 then packet―mode
