Practice Free JN0-280 Exam Online Questions
Question #51
What is the primary purpose of OSPF in network routing?
- A . To redistribute routes between autonomous systems.
- B . To provide path vector routing within an autonomous system.
- C . To offer dynamic routing within an autonomous system using link-state information.
- D . To encrypt data traffic between different networks.
Correct Answer: C
Question #52
In a Spine/Leaf IP-Fabric architecture, what is the primary role of the leaf switches?
- A . To provide direct connectivity to servers.
- B . To interconnect different data centers.
- C . To perform deep packet inspection.
- D . To manage the overall data center network.
Correct Answer: A
Question #53
What are two common reasons for BGP routes to be in the hidden state? (Choose two.)
- A . Routes are being rejected by a policy
- B . Routes are being filtered from the inet.2 routing table
- C . The next hop is unresolvable
- D . The BGP neighbor is in a different autonomous system
Correct Answer: AC
Question #54
What are two consequences of having all network devices in a single collision domain? (Choose two.)
- A . The amount of network resource consumption does not change.
- B . The chance of packet collision is decreased.
- C . The chance of packet collision is increased.
- D . The amount of network resource consumption is increased.
Correct Answer: C, D
C, D
Explanation:
A collision domain is a network segment where data packets can "collide" with one another when being sent on the same network medium.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Increased Collision Probability:
If all devices are in a single collision domain, the likelihood of packet collisions increases as more devices attempt to send packets simultaneously, leading to network inefficiencies. Increased Resource Consumption:
More collisions result in increased network resource consumption as devices need to retransmit packets, causing higher utilization of bandwidth and slowing down network performance. Juniper
Reference: Collision Domains: Proper network segmentation using switches reduces collision domains, thereby improving network performance and reducing packet collisions.
C, D
Explanation:
A collision domain is a network segment where data packets can "collide" with one another when being sent on the same network medium.
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
Increased Collision Probability:
If all devices are in a single collision domain, the likelihood of packet collisions increases as more devices attempt to send packets simultaneously, leading to network inefficiencies. Increased Resource Consumption:
More collisions result in increased network resource consumption as devices need to retransmit packets, causing higher utilization of bandwidth and slowing down network performance. Juniper
Reference: Collision Domains: Proper network segmentation using switches reduces collision domains, thereby improving network performance and reducing packet collisions.
Question #55
You are troubleshooting a downed BGP session.
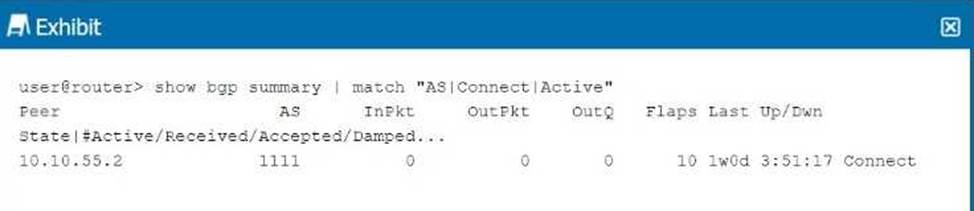
Referring to the exhibit, what is the cause of the problem?
- A . The UDP session between the peers has not been established.
- B . The local peer has sent an Open message but not received one from the remote peer.
- C . The TCP session between the peers has not been established.
- D . The local peer has sent an Update message but not received one from the remote peer.
Correct Answer: C
C
Explanation:
The BGP session in the exhibit shows the state as Connect, which indicates that the TCP session between the BGP peers has not been fully established. Step-by-Step Breakdown:
BGP State "Connect":
The Connect state is the second stage in the BGP finite state machine (FSM). At this stage, BGP is trying to establish a TCP session with the peer, but the session has not yet been successfully established.
A successful TCP three-way handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) is required before BGP can progress to the OpenSent state, where the peers exchange BGP Open messages.
Possible Causes:
A firewall blocking TCP port 179.
Incorrect IP addresses or network connectivity issues between the BGP peers. Juniper
Reference: BGP Troubleshooting: In Junos, if a BGP session is stuck in the Connect state, the issue is likely due to a failure in establishing the underlying TCP connection.
C
Explanation:
The BGP session in the exhibit shows the state as Connect, which indicates that the TCP session between the BGP peers has not been fully established. Step-by-Step Breakdown:
BGP State "Connect":
The Connect state is the second stage in the BGP finite state machine (FSM). At this stage, BGP is trying to establish a TCP session with the peer, but the session has not yet been successfully established.
A successful TCP three-way handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) is required before BGP can progress to the OpenSent state, where the peers exchange BGP Open messages.
Possible Causes:
A firewall blocking TCP port 179.
Incorrect IP addresses or network connectivity issues between the BGP peers. Juniper
Reference: BGP Troubleshooting: In Junos, if a BGP session is stuck in the Connect state, the issue is likely due to a failure in establishing the underlying TCP connection.
Question #56
Referring to the exhibit, what needs to be done to make this a valid IP fabric?
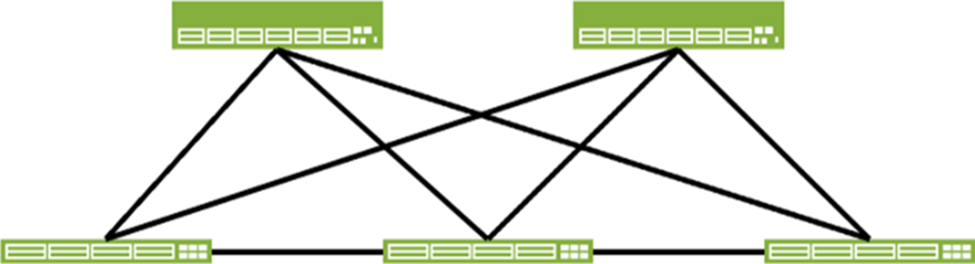
- A . Remove the connection between the leaf nodes
- B . Remove one of the redundant links between a leaf node and a spine node
- C . Add two connections between the spine nodes
- D . Add a connection between the spine nodes
Correct Answer: A
