Practice Free HPE7-A01 Exam Online Questions
Match the topics with the underlying technologies (Options may be used more than once or not at all.)


Which method is used to onboard a new UXI in an existing environment with 802 1X authentication? (The sensor has no cellular connection)
- A . Use the UXI app on your smartphone and connect the UXI via Bluetooth
- B . Use the Aruba installer app on your smartphone to scan the barcode
- C . Connect the new UXI from an already installed one and adjust the initial configuration.
- D . Use the CLI via the serial cable and adjust the initial configuration.
Which Aruba AP mode is sending captured RF data to Aruba Central for waterfall plot?
- A . Hybrid Mode
- B . Air Monitor
- C . Spectrum Monitor
- D . Dual Mode
C
Explanation:
Spectrum Monitor is an Aruba AP mode that is sending captured RF data to Aruba Central for waterfall plot.
Spectrum Monitor is a mode that allows an AP to scan all channels in both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands and collect information about the RF environment, such as interference sources, noise floor, channel utilization, etc. The AP then sends this data to Aruba Central, which is a cloud-based network management platform that can display the data in various formats, including waterfall plot. Waterfall plot is a graphical representation of the RF spectrum over time, showing the frequency, amplitude, and duration of RF signals. The other options are incorrect because they are either not AP modes or not sending RF data to Aruba Central.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/1-overview/spect
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/1-overview/water
https://www.arubanetworks.com/products/network-management-operations/aruba-central/
A customer wants to deploy a Gateway and take advantage of all the SD-WAN features .
Which persona role option should be selected?
- A . ArubaOS 10 Branch
- B . ArubaOS 10 VPN Concentrator
- C . ArubaOS 10 Wireless
- D . ArubaOS 10 Mobility
A
Explanation:
The persona role option that should be selected to deploy a Gateway and take advantage of all the SD-WAN features is A. ArubaOS 10 Branch.
ArubaOS 10 Branch is a persona that enables the Gateway to provide both LAN and WAN functionality for branch networks. The Gateway can act as a wireless controller, a router, a firewall, and an SD-WAN device. The SD-WAN features include route and tunnel orchestration, dynamic path steering, forward error correction, SaaS traffic optimization, SASE orchestration, and more 1.
The other options are incorrect because:
B) ArubaOS 10 VPN Concentrator: This is a persona that enables the Gateway to act as a VPN concentrator for remote access or site-to-site VPN connections. It does not provide SD-WAN features2.
C) ArubaOS 10 Wireless: This is a persona that enables the Gateway to act as a wireless controller for campus networks. It does not provide SD-WAN features3.
D) ArubaOS 10 Mobility: This is a persona that enables the Gateway to act as a mobility controller for campus networks. It does not provide SD-WAN features.
List the firewall role derivation flow in the correct order

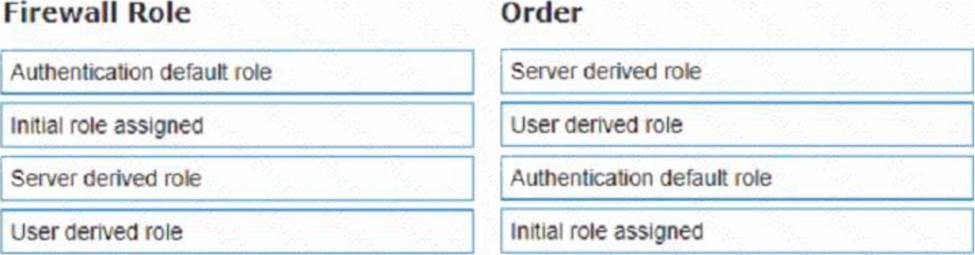
Explanation:
According to the Aruba Documentation Portal1, the firewall role derivation flow in the correct order is:
* Server derived role
* User derived role
* Authentication default role
* Initiation role assigned
A company recently upgraded its campus switching infrastructure with Aruba 6300 CX switches. They have implemented 802.1X authentication on edge ports where laptop and loT devices typically connect. An administrator has noticed that for PoE devices the pons are delivering the maximum wattage instead of what the device actually needs Upon connecting the loT devices, the devices request their specific required wattage through information exchange
- A . Concerned about this waste of electricity, what should the administrator implement to solve this problem?
- B . Enable AAA authentication to exempt LLDP and/or CDP information
- C . Globally enable the QoS trust setting for LLDP and/or CDP
- D . Create device profiles with the correct power definitions.
- E . implement a classifier policy with the correct power definitions.
D
Explanation:
According to the Aruba Documentation Portal1, the Aruba 6300 CX switches support various features to control the PoE devices on specific ports, such as device profiles and classifier policies. These features can help reduce the power consumption and improve the performance of the PoE devices.
1: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.10/HTML/monitoring_6300-6400/Content/Chp_LEDs/fr
https://www.arubanetworks.com/products/switches/6300-series/ 3:
https://docs.samsungknox.com/admin/knox-manage/configure/profile/configure-profile-
policies/configure-profil
Refer to Exhibit:

With Access-1, What needs to be identically configured With MSTP to load-balance VLANS?
- A . Spanning-tree bpdu-guard setting
- B . Spanning-tree instance vlan mapppjng
- C . spanning-tree Cist mapping
- D . Spanning-tree root-guard setting
B
Explanation:
The correct answer is B. Spanning-tree instance VLAN mapping.
To load-balance VLANs with MSTP, you need to configure the same VLAN-to-instance mapping on all switches in the same MST region. This means that you need to assign different VLANs to different MST instances, and then adjust the spanning tree parameters (such as priority, cost, or port role) for each instance to achieve the desired load balancing. For example, you can make one switch the root for instance 1 and another switch the root for instance 2, and then map half of the VLANs to instance 1 and the other half to instance 2.
According to the Cisco document Understand the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (802.1s), one of the steps to configure MST is:
Split your set of VLANs into more instances and configure different MST settings for each of these instances. In order to easily achieve this, elect Bridge D1 to be the root for VLANs 501 through 1000, and Bridge D2 to be the root for VLANs 1 through 500.
These statements are true for this configuration:
Switch D1(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration
Switch D1(config-mst)#instance 1 vlan 501-1000
Switch D1(config-mst)#exit
Switch D1(config)#spanning-tree mst 1 priority 0
Switch D2(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration
Switch D2(config-mst)#instance 2 vlan 1-500
Switch D2(config-mst)#exit
Switch D2(config)#spanning-tree mst 2 priority 0
The above commands create two MST instances, 1 and 2, and map VLANs 501-1000 to instance 1 and VLANs 1-500 to instance 2. Then, they make switch D1 the root for instance 1 and switch D2 the root for instance 2.
The other options are incorrect because:
A) Spanning-tree bpdu-guard setting is a security feature that disables a port if it receives a BPDU from an unauthorized device. It does not affect load balancing with MSTP.
C) Spanning-tree CIST mapping is not a valid command. CIST stands for Common and Internal Spanning Tree, which is the spanning tree instance that runs within an MST region and interacts with other regions or non-MST switches.
D) Spanning-tree root-guard setting is another security feature that prevents a port from becoming a root port if it receives superior BPDUs from another switch. It does not affect load balancing with MSTP.
A company deployed Dynamic Segmentation with their CX switches and Gateways After performing a security audit on their network, they discovered that the tunnels built between the CX switch and the Aruba Gateway are not encrypted. The company is concerned that bad actors could try to insert spoofed messages on the Gateway to disrupt communications or obtain information about the network.
Which action must the administrator perform to address this situation?
- A . Enable Secure Mode Enhanced
- B . Enable Enhanced security
- C . Enable Enhanced PAPI security
- D . Enable GRE security
By default, Best Effort is higher priority than which priority traffic type?
- A . All queues
- B . Background
- C . Internet Control
- D . Network Control
B
Explanation:
This is because Best Effort traffic is all other kinds of non-detrimental traffic that are not sensitive to Quality of Service metrics (jitter, packet loss, latency). A typical example would be peer-to-peer and email applications2. Background traffic is a type of traffic that is used for system maintenance or backup purposes and does not affect the performance or availability of the network3.
Therefore, Best Effort traffic has a higher priority than Background traffic in terms of network resources allocation and management.
1: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaDocPortal/content/docportal.htm
2: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33854306/best-effort-traffic-and-real-time-traffic-difference
3: https://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=25315&seqNum=4
A system engineer needs to preconfigure several Aruba CX 6300 switches that will be sent to a remote office An untrained local field technician will do the rollout of the switches and the mounting of several AP-515s and AP-575S. Cables running to theAPs are not labeled.
The VLANs are already preconfigured to VLAN 100 (mgmt), VLAN 200 (clients), and VLAN 300 (guests).
What is the correct configuration to ensure that APs will work properly?
A)

B)

C)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
C
Explanation:
Option C is the correct configuration to ensure that APs will work properly. It uses the ap command to configure a port profile for APs with VLAN 100 as the native VLAN and VLAN 200 and 300 as tagged VLANs. It also enables LLDP on the ports to discover the APs and assign them to the port profile automatically. The other options are incorrect because they either do not use the ap command, do not enable LLDP, or do not configure the VLANs correctly.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/UG/bk01-ch02.html
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/UG/bk01-ch03.html
