Practice Free HPE6-A85 Exam Online Questions
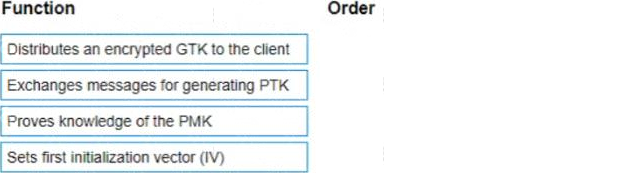
List the WPA 4-Way Handshake functions in the correct order.

Explanation:
The WPA 4-Way Handshake functions in the correct order are as follows:
Exchanges messages for generating PTK
Proves knowledge of the PMK
Distributes an encrypted GTK to the client
Sets first initialization vector (IV)
The process is designed to confirm that both the client and the access point have the correct credentials (such as the PMK), to establish the temporal keys used to encrypt and decrypt data, and to confirm that the client is actually alive and present at the time of the handshake.
You are working with a pair of 6300M switches in a VSF stack. The switch has 48 SmartRate 5G ports, 2 SFP28 ports, and 2 SFP56 ports. Both SFP56 ports are used for stacking.
You need to provide an LACP connection to another identical stack with the maximum available bandwidth possible.
What should you configure?
- A . a 16-member LAG using 2 SFP28 ports and 6 SR5 ports on each switch
- B . an eight-member LAG using 4 SR5 ports on each switch
- C . an eight-member LAG using 2 SFP28 ports and 2 SR5 ports on each switch
- D . a four-member LAG using 2 SFP28 ports on each switch
A
Explanation:
To provide an LACP connection with the maximum available bandwidth, one should configure a link aggregation group (LAG) using all available ports that can be used for data transfer. Since the SFP56 ports are used for stacking, the next best option is to use the 2 SFP28 ports and as many SmartRate 5G (SR5) ports as possible on each switch, which would allow for a 16-member LAG, with 2 SFP28 and 6 SR5 ports on each switch contributing to the LAG.
Which statement is correct when comparing 5 GHz and 6 GHz channels with identical channel widths?
- A . 5 GHz channels travel the same distances and provide different throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels
- B . 5 GHz channels travel different distances and provide different throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels
- C . 5 GHz channels travel the same distances and provide the same throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels
- D . 5 GHz channels travel different distances and provide the same throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels
Which device configuration group types can a user define in Aruba Central during group creation? (Select two.)
- A . Security group
- B . Template group
- C . Default group
- D . Ul group
- E . ESP group
B D
Explanation:
Template group: Allows for configurations to be set based on templates, which can be applied to devices within the group, facilitating standardized settings across multiple devices.
UI group: Configurations in this group are designed to manage and customize the user interface aspects within Aruba Central, providing a tailored experience based on the specific needs of the network or its administrators.
Which device configuration group types can a user define in Aruba Central during group creation? (Select two.)
- A . Security group
- B . Template group
- C . Default group
- D . Ul group
- E . ESP group
B D
Explanation:
Template group: Allows for configurations to be set based on templates, which can be applied to devices within the group, facilitating standardized settings across multiple devices.
UI group: Configurations in this group are designed to manage and customize the user interface aspects within Aruba Central, providing a tailored experience based on the specific needs of the network or its administrators.
The customer has a requirement to create authorization policies for their users with Windows 10 clients, with a requirement Tor authorizing both device and user credentials within one Radius session.
What would be the correct solution for the requirement?
- A . ClearPass 6.9 with EAP-TTLS
- B . ClearPass 6.9 with EAP-TLS
- C . ClearPass 6.9 with PEAP
- D . ClearPass 6.9 with EAP-TEAP
D
Explanation:
EAP-TEAP is a tunnel-based authentication method that supports both device and user authentication within a single RADIUS session. ClearPass 6.9 supports EAP-TEAP as anauthentication method for Windows 10 clients.
References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ClearPass/6.9/Guest/Content/CPPM_UserGuide/EAP-TEAP/EAP-TE
A client connects to an Aruba AP in tunnel mode and is assigned to a VLAN based on the client’s MAC address.
Which client VLAN assignment was configured?
- A . Mixed
- B . Static
- C . Native VLAN
- D . Dynamic
D
Explanation:
When a client connects to an Aruba AP in tunnel mode and is assigned to a VLAN based on the client’s MAC address, this indicates a Dynamic VLAN assignment. The VLAN is determined dynamically at the time of authentication based on the client’s credentials or attributes, such as its MAC address.
Which statement is true for a device with a MAC address of B8-31-B5-80-41-4F?
- A . The device OUI is B8-31-B5 and the device NIC serial number is 80-41-4F
- B . The device OUI is B8-31 and the device NIC serial number is B5-80-41-4F
- C . The device OUI is 80-41-4F and the device NIC serial number is B8-31-B5
- D . The device OUI is B8-31-B5 and the device serial number is MD5 hash is 80-41-4F
A
Explanation:
A MAC address is divided into two parts: the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and the Network Interface Controller (NIC) serial number. The OUI is the first three octets of the MAC address and is unique to the manufacturer. The NIC serial number is the last three octets and is unique to the device itself. Therefore, for the MAC address B8-31-B5-80-41-4F, the OUI is B8-31-B5, and the NIC serial number is 80-41-4F.
How does a single Aruba CX 6300M switch configuration use L3 connectivity to establish routing traffic between switch virtual interfaces 120 and 130?
- A . Routing is enabled by default with Aruba 6300M.
- B . Route leaking must be configured in default VRF.
- C . Delete ‘no routing’ from the SVI interfaces.
- D . Create static routes between SVI 120 and 130.
C
Explanation:
On an Aruba CX 6300M switch, routing between Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs) is enabled by default. Therefore, traffic between SVIs, like 120 and 130, can be routed internally without the need for additional configuration such as route leaking or static routes, as long as there is no ‘no routing’ configuration present on the SVIs.
A network technician is testing a new SSID for a branch office. They are able to connect, get an IP address, and resolve DNS names. However, they are not able to browse the internet.
On the existing SSID at the branch, connectivity to the internet works as expected on the same VLAN as the new SSID. The wireless client should have received a new role to allow internet access.
What should the network technician verify to ensure both SSIDs function in a similar way?
- A . Verify each SSID’s authentication and encryption parameters are enabled and the same.
- B . Verify that the implicit ‘deny all’ is the last entry in the firewall policies.
- C . Verify the new SSID is broadcasting on all the APs at the branch office.
- D . Verify the firewall policies assigned, making sure the rules are correct and ordered properly.
D
Explanation:
When a network technician encounters an issue where a new SSID does not allow internet access despite successful connectivity and DNS resolution, they should verify the firewall policies associated with the new SSID. The firewall policies must include rules that permit traffic to and from the internet and should be correctly ordered to ensure that they are applied as intended. Since the existing SSID functions correctly, comparing the firewall rules between the two can be a useful method of troubleshooting.
