Practice Free FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
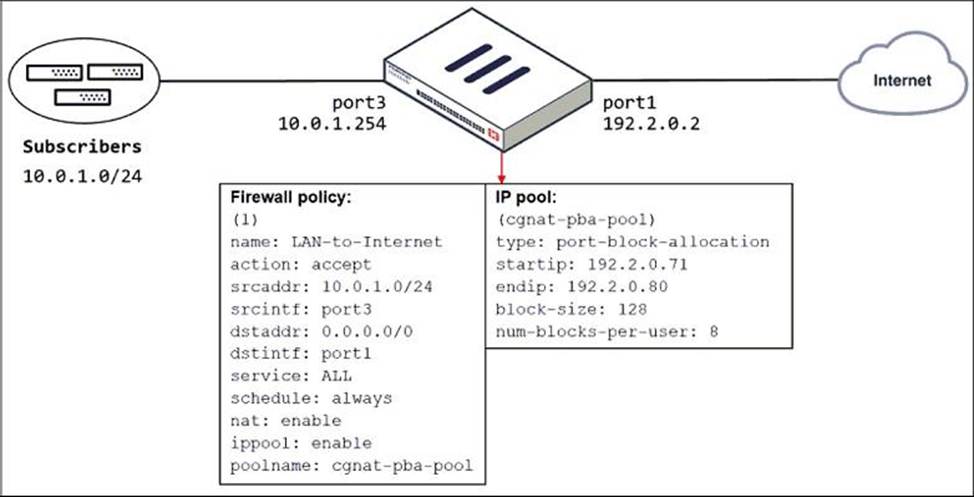
The exhibit shows a diagram of a FortiGate device connected to the network and the firewall policy and IP pool configuration on the FortiGate device.
Which two actions does FortiGate take on internet traffic sourced from the subscribers? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate allocates port blocks per user, based on the configured range of internal IP addresses.
- B . FortiGate allocates port blocks on a first-come, first-served basis.
- C . FortiGate generates a system event log for every port block allocation made per user.
- D . FortiGate allocates 128 port blocks per user.
B,C
Explanation:
B: FortiGate allocates port blocks on a first-come, first-served basis
C: For logging purposes, when FortiGate allocates a port block to a host, it generates a system event log to inform the administrator
Not A: FortiGate allocates a block size and number per host for a range of external addresses
Not D: It allows 8 blocks of 128 ports per host
FortiGate allocates port blocks on a first-come, first-served basis.
For logging purposes, when FortiGate allocates a port block to a host, it generates a system event log to inform the administrator.
Refer to the exhibit.

The exhibit shows a diagram of a FortiGate device connected to the network and the firewall policy and IP pool configuration on the FortiGate device.
Which two actions does FortiGate take on internet traffic sourced from the subscribers? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate allocates port blocks per user, based on the configured range of internal IP addresses.
- B . FortiGate allocates port blocks on a first-come, first-served basis.
- C . FortiGate generates a system event log for every port block allocation made per user.
- D . FortiGate allocates 128 port blocks per user.
B,C
Explanation:
B: FortiGate allocates port blocks on a first-come, first-served basis
C: For logging purposes, when FortiGate allocates a port block to a host, it generates a system event log to inform the administrator
Not A: FortiGate allocates a block size and number per host for a range of external addresses
Not D: It allows 8 blocks of 128 ports per host
FortiGate allocates port blocks on a first-come, first-served basis.
For logging purposes, when FortiGate allocates a port block to a host, it generates a system event log to inform the administrator.
An administrator needs to configure VPN user access for multiple sites using the same soft FortiToken.
Each site has a FortiGate VPN gateway.
What must an administrator do to achieve this objective?
- A . The administrator can register the same FortiToken on more than one FortiGate.
- B . The administrator must use a FortiAuthenticator device.
- C . The administrator can use a third-party radius OTP server.
- D . The administrator must use the user self-registration server.
B
Explanation:
B. The administrator must use a FortiAuthenticator device.
B is correct due to the FortiToken, a different OTP cannot use FortiToken. So we have to choose the fortiAuthenticator.
To achieve VPN user access for multiple sites using the same soft FortiToken, the administrator can use a FortiAuthenticator device. FortiAuthenticator is designed to provide centralized authentication services for Fortinet devices, including VPN authentication. It allows for the centralized management of user identities, authentication methods, and FortiTokens. By using FortiAuthenticator, the administrator can register the same FortiToken for users across multiple FortiGate devices, providing a seamless and centralized user access experience.
Which two statements are true about the Security Fabric rating? (Choose two.)
- A . The Security Fabric rating is a free service that comes bundled with all FortiGate devices.
- B . Many of the security issues can be fixed immediately by clicking Apply where available.
- C . The Security Fabric rating must be run on the root FortiGate device in the Security Fabric.
- D . It provides executive summaries of the four largest areas of security focus.
B,C
Explanation:
B. Many of the security issues can be fixed immediately by clicking Apply where available: This statement is true. The Security Fabric rating often identifies security issues that can be resolved immediately by clicking "Apply" where available, making it a valuable tool for quickly addressing security concerns.
C. The Security Fabric rating must be run on the root FortiGate device in the Security Fabric: This statement is also true. The Security Fabric rating must be run on the root FortiGate device in the Security Fabric to provide an overall security rating and analysis of the Security Fabric.
On checks that support Easy Apply, you can run the remediation on all the associated VDOMs.
To view the complete network, you must access the topology views on the root FortiGate in the Security
Fabric.
Incorrect:
Which two statements about SSL VPN between two FortiGate devices are true? (Choose two.)
- A . The client FortiGate requires a client certificate signed by the CA on the server FortiGate.
- B . The client FortiGate requires a manually added route to remote subnets.
- C . The client FortiGate uses the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
- D . Server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate.
C,D
Explanation:
C. The client FortiGate uses the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
D. Server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate. Incorrect:
Which two settings must you configure when FortiGate is being deployed as a root FortiGate in a Security Fabric topology? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiManager IP address
- B . FortiAnalyzer IP address
- C . Pre-authorize downstream FortiGate devices
- D . Fabric name
B,D
Explanation:
The correct choices for settings to configure when FortiGate is being deployed as a root FortiGate in a Security Fabric topology are:
B. FortiAnalyzer IP address – This setting is required to send logs and reports to the FortiAnalyzer for analysis and storage.
D. Fabric name – This setting is essential to identify the Security Fabric and differentiate it from other fabrics in the network.
Refer to the exhibit to view the firewall policy.
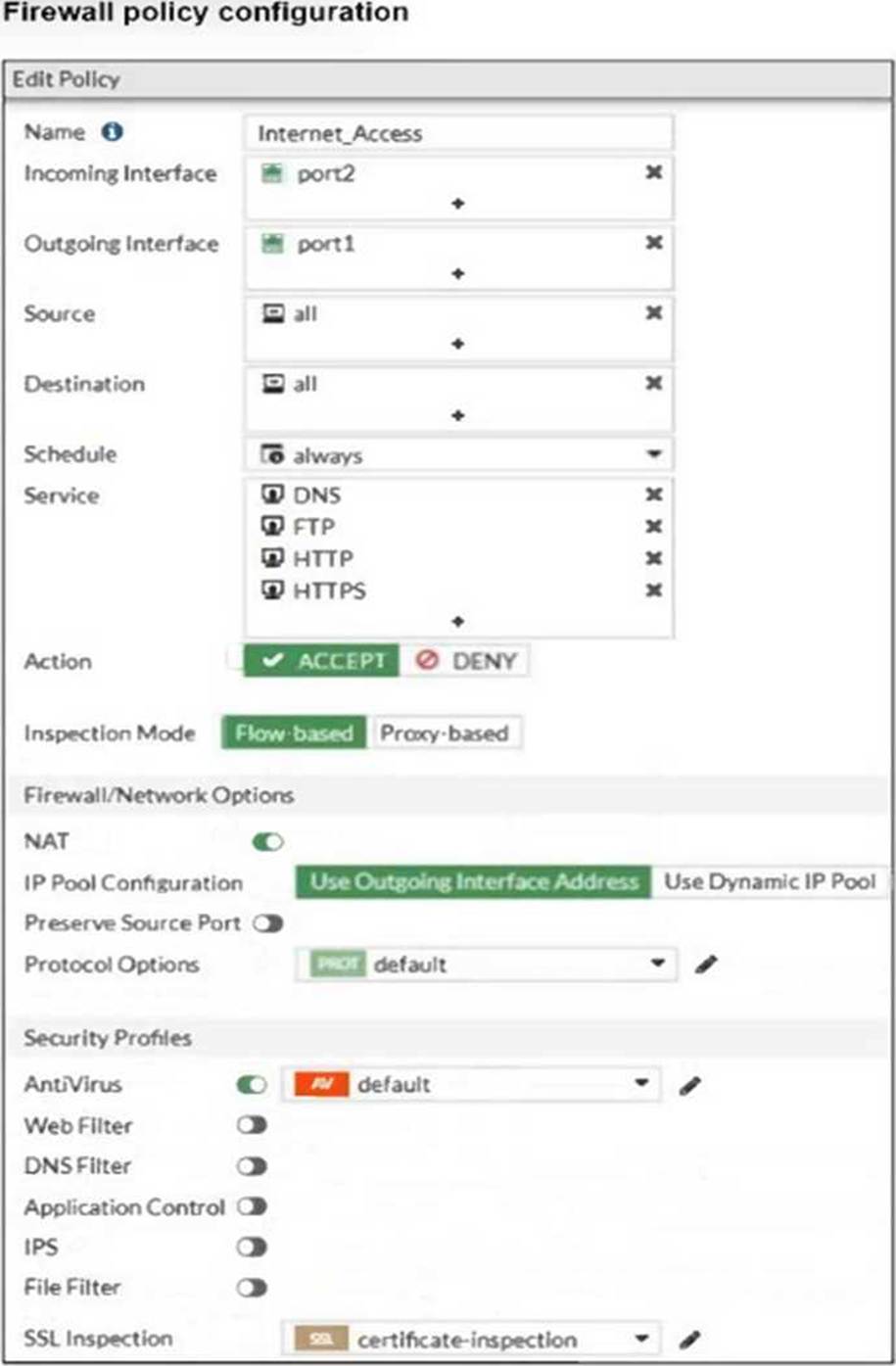
Why would the firewall policy not block a well-known virus, for example eicar?
- A . The action on the firewall policy is not set to deny.
- B . The firewall policy is not configured in proxy-based inspection mode.
- C . Web filter is not enabled on the firewall policy to complement the antivirus profile.
- D . The firewall policy does not apply deep content inspection.
B
Explanation:
The firewall policy shown in the exhibit is configured in flow-based inspection mode. In flow-based inspection, certain security features, such as deep content inspection, might not be as effective as in proxy-based mode. Proxy-based inspection is necessary for thorough content inspection, which includes identifying and blocking well-known viruses like EICAR.
Reference: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: Inspection Modes
Which two statements are true about the RPF check? (Choose two.)
- A . The RPF check is run on the first sent packet of any new session.
- B . The RPF check is run on the first reply packet of any new session.
- C . The RPF check is run on the first sent and reply packet of any new session.
- D . RPF is a mechanism that protects FortiGuard and your network from IP spoofing attacks.
A,D
Explanation:
RPF protect against IP spoofin attacks. The source IP address is checked against the routing table for a return path. RPF is only carried out on: The first packet in the session, not on reply.
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a radius server configuration.
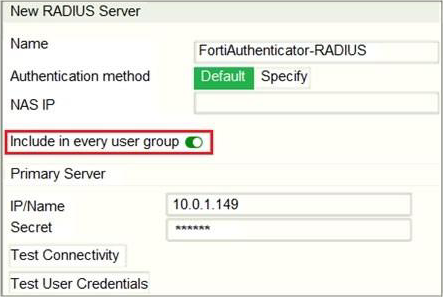
An administrator added a configuration for a new RADIUS server. While configuring, the administrator selected the Include in every user group option.
What will be the impact of using Include in every user group option in a RADIUS configuration?
- A . This option places the RADIUS server, and all users who can authenticate against that server, into every FortiGate user group.
- B . This option places all FortiGate users and groups required to authenticate into the RADIUS server, which, in this case, is FortiAuthenticator.
- C . This option places all users into every RADIUS user group, including groups that are used for the LDAP server on FortiGate.
- D . This option places the RADIUS server, and all users who can authenticate against that server, into
every RADIUS group.
A
Explanation:
The Include in every User Group option adds the RADIUS server and all users that can authenticate against it, to every user group created on FortiGate. So, you should enable this option only in very specific scenarios (for example, when only administrators can authenticate against the RADIUS server and policies are ordered from least restrictive to most restrictive).
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial configuration from the remote authentication server.

Why does the FortiGate administrator need this configuration?
- A . To authenticate only the Training user group.
- B . To set up a RADIUS server Secret
- C . To authenticate and match the Training OU on the RADIUS server.
- D . To authenticate Any FortiGate user groups.
C
Explanation:
The configuration shown in the exhibit indicates that the FortiGate is using a Fortinet-specific RADIUS attribute (Fortinet-Group-Name) with the value "Training." This setup allows the FortiGate to authenticate users against the RADIUS server and match them to the "Training" Organizational Unit (OU). By doing so, only users within this specific group or OU can be authenticated and allowed access through the FortiGate.
Reference: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: RADIUS Server Configuration
