Practice Free FCP_FGT_AD-7.4 Exam Online Questions
What are two features of collector agent advanced mode? (Choose two.)
- A . In advanced mode, FortiGate can be configured as an LDAP client and group filters can be configured on FortiGate.
- B . Advanced mode supports nested or inherited groups.
- C . In advanced mode, security profiles can be applied only to user groups, not individual users.
- D . Advanced mode uses the Windows convention ―NetBios: DomainUsername.
A, D
Explanation:
Advanced mode allows for configuration as an LDAP client and supports group filtering directly on the FortiGate, as well as nested or inherited groups.
Which statement is a characteristic of automation stitches?
- A . They can be run only on devices in the Security Fabric.
- B . They can be created only on downstream devices in the fabric.
- C . They can have one or more triggers.
- D . They can run multiple actions at the same time.
C
Explanation:
Automation stitches on FortiGate can have one or more triggers, which are conditions or events that activate the automation stitch. The trigger defines when the automation stitch should execute the defined actions. Actions within a stitch can be executed sequentially or in parallel, depending on the configuration.
Reference: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: Automation Stitches
Which two protocols are used to enable administrator access of a FortiGate device? (Choose two.)
- A . SSH
- B . HTTPS
- C . FTM
- D . FortiTelemetry
A,B
Explanation:
The two protocols used to enable administrator access to a FortiGate device are:
An administrator does not want to report the login events of service accounts to FortiGate.
What setting on the collector agent is required to achieve this?
- A . Add the support of NTLM authentication
- B . Add user accounts to the FortiGate group filter
- C . Add user accounts to Active Directory (AD)
- D . Add user accounts to the Ignore User List
D
Explanation:
D. Add user accounts to the Ignore User List
To achieve this, the administrator should add the service accounts to the Ignore User List on the collector agent. This will prevent the login events of these accounts from being reported to FortiGate.
To prevent the reporting of login events of service accounts to FortiGate using the collector agent, the appropriate setting is:
D. Add user accounts to the Ignore User List.
By adding the service accounts to the Ignore User List, you instruct the collector agent to exclude these accounts from reporting login events to FortiGate. This way, events related to the specified users will not be forwarded or logged.
Which of the following statements correctly describes FortiGates route lookup behavior when searching for a suitable gateway? (Choose two)
- A . Lookup is done on the first packet from the session originator
- B . Lookup is done on the last packet sent from the responder
- C . Lookup is done on every packet, regardless of direction
- D . Lookup is done on the first reply packet from the responder
AD
Explanation:
FortiGate performs route lookup based on the trust packet. The trust packet is the first packet of the session that is sent by the session originator. This is the packet that initiates the communication. The route lookup is also done on the trust reply packet, which is the first reply packet received from the responder.
In summary, FortiGate looks at the initial packet from the session originator and the first reply packet from the responder when performing route lookup to determine the suitable gateway.
What are two features of the NGFW profile-based mode? (Choose two.)
- A . NGFW profile-based mode can only be applied globally and not on individual VDOMs.
- B . NGFW profile-based mode must require the use of central source NAT policy
- C . NGFW profile-based mode policies support both flow inspection and proxy inspection.
- D . NGFW profile-based mode supports applying applications and web filtering profiles in a firewall policy.
C, D
Explanation:
NGFW (Next Generation Firewall) profile-based mode in FortiGate allows policies to use both flow-based and proxy-based inspection modes, providing flexibility depending on security and performance requirements. Additionally, profile-based mode supports applying applications and web filtering profiles directly in a firewall policy, allowing granular control over the traffic.
Reference: FortiOS 7.4.1 Administration Guide: NGFW Mode Configuration
Which two statements are true about collector agent advanced mode? (Choose two.)
- A . Security profiles can be applied only to user groups, nor individual users.
- B . FortiGate can be configured as an LDAP client and group filters can be configured on FortiGate.
- C . Advanced mode supports nested or inherited groups.
- D . Advanced mode uses Windows convention-NetBios: DomainUsername.
B,C
Explanation:
In FortiGate’s FSSO (Fortinet Single Sign-On) feature, the collector agent operates in either standard mode or advanced mode.
Here’s an explanation of the statements:
B. FortiGate can be configured as an LDAP client, and group filters can be configured on FortiGate:
In advanced mode, FortiGate can act as an LDAP client, allowing it to directly query Active Directory for user and group information. Group filters can be configured on FortiGate to selectively include or exclude specific groups in the FSSO process. This provides more flexibility and control over which groups are considered for FSSO integration.
C. Advanced mode supports nested or inherited groups:
In advanced mode, FortiGate can recognize and utilize nested group structures in Active Directory. Nested groups refer to groups that contain other groups as members. With advanced mode, FortiGate can accurately reflect the group memberships and apply policies accordingly.
These features enhance the capabilities of FSSO in advanced mode, making it suitable for environments with complex group structures and the need for more granular control over user and group policies.
– In advanced mode, you can configure FortiGate as an LDAP client and configure the group filters on FortiGate.
– Also, advanced mode supports nested or inherited groups.
D. Incorrect, Netbios is Standard mode.
View the exhibit.
date=2022-06-14 time=14:45:16 logid=0317013312 type=utm subtype=webfilter eventtype=ftgd_allow level=notice vd="root" policyid=2 identidx=1 sessionid=31232959 user="anonymous" group="ldap_users" srcip=192.168.1.24 srcport=63355 srcintf="port2" dstip=66.171.121.44 dstport=80 dstintf="port1" service="http" hostname="www.fortinet.com" profiletype="Webfilter_Profile" profile="default" status="passthrough" reqtype="direct" url="/" sentbyte=304 rcvdbyte=60135 msg="URL belongs to an allowed category in policy" method=domain class=0 cat=140 catdesc="custom1"
What two things does this raw log indicate? (Choose two.)
- A . FortiGate allowed the traffic to pass.
- B . 192.168.1.24 is the IP address for www.fortinet.com.
- C . The traffic matches the webfilter profile on firewall policy ID 2.
- D . The traffic originated from 66.171.121.44.
A,C
Explanation:
The raw log indicates the following:
Which two settings are required for SSL VPN to function between two FortiGate devices? (Choose two.)
- A . The client FortiGate requires a manually added route to remote subnets.
- B . The client FortiGate requires a client certificate signed by the CA on the server FortiGate.
- C . The server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate.
- D . The client FortiGate requires the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN.
C,D
Explanation:
The FortiGate can be configured as an SSL VPN client, using an SSL-VPN Tunnel interface type. The FortiGates must have a proper CA certificate installed to verify the certificate chain to the root CA that signed the certificate.
C. The server FortiGate requires a CA certificate to verify the client FortiGate certificate:
When setting up SSL VPN between two FortiGate devices, the server FortiGate needs a CA (Certificate Authority) certificate to verify the client FortiGate’s certificate. This ensures that the client connecting to the VPN is authenticated and trusted.
D. The client FortiGate requires the SSL VPN tunnel interface type to connect SSL VPN:
For the SSL VPN to function, the client FortiGate needs to have the SSL VPN tunnel interface type configured. This interface type is specifically designed for SSL VPN connections, allowing the client FortiGate to establish the VPN tunnel with the server FortiGate.
These two settings together ensure that the SSL VPN connection between the two FortiGate devices is properly authenticated and established, allowing secure communication between them.
Refer to the exhibit.
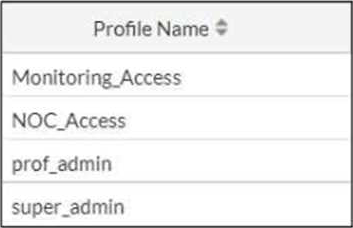
The NOC team connects to the FortiGate GUI with the NOC_Access admin profile. They request that their GUI sessions do not disconnect too early during inactivity.
What must the administrator configure to answer this specific request from the NOC team?
- A . Enable the parameter Never Timeout in the admin profiles
- B . Increase the admintimeout value under config system accprofile super_admin.
- C . Increase the admintimeout value under config system global
- D . Increase the offline value of the Override idle Timeout parameter in the NOC_Access admin profile
C
Explanation:
To adjust the inactivity timeout for GUI sessions, the administrator should increase the admintimeout value in the global settings. This parameter controls how long an administrator’s session can remain idle before it times out and disconnects. This is configured globally and affects all administrators, including those with the "NOC_Access" profile.
