Practice Free CAS-005 Exam Online Questions
Audit findings indicate several user endpoints are not utilizing full disk encryption During me remediation process, a compliance analyst reviews the testing details for the endpoints and notes the endpoint device configuration does not support full disk encryption.
Which of the following is the most likely reason me device must be replaced’
- A . The HSM is outdated and no longer supported by the manufacturer
- B . The vTPM was not properly initialized and is corrupt.
- C . The HSM is vulnerable to common exploits and a firmware upgrade is needed
- D . The motherboard was not configured with a TPM from the OEM supplier.
- E . The HSM does not support sealing storage
D
Explanation:
The most likely reason the device must be replaced is that the motherboard was not configured with a TPM (Trusted Platform Module) from the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) supplier.
Why TPM is Necessary for Full Disk Encryption:
Hardware-Based Security: TPM provides a hardware-based mechanism to store encryption keys securely, which is essential for full disk encryption.
Compatibility: Full disk encryption solutions, such as BitLocker, require TPM to ensure that the encryption keys are securely stored and managed.
Integrity Checks: TPM enables system integrity checks during boot, ensuring that the device has not been tampered with.
Other options do not directly address the requirement for TPM in supporting full disk encryption:
A security architect must make sure that the least number of services as possible is exposed in order to limit an adversary’s ability to access the systems.
Which of the following should the architect do first?
- A . Enforce Secure Boot.
- B . Perform attack surface reduction.
- C . Disable third-party integrations.
- D . Limit access to the systems.
B
Explanation:
Attack surface reduction focuses on minimizing unnecessary services, open ports, and vulnerabilities, reducing the exposure to potential adversaries. This aligns with zero trust and least privilege principles.
Secure Boot (A) helps ensure system integrity but does not minimize exposed services.
Disabling third-party integrations (C) may help, but broader attack surface reduction is the best first step.
Limiting access (D) is important but does not directly reduce exposed services.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX (CAS-005) Exam Objectives – Domain 2.0 (Security Architecture), Section on Attack Surface Management and Reduction
A global manufacturing company has an internal application mat is critical to making products This application cannot be updated and must Be available in the production area A security architect is implementing security for the application.
Which of the following best describes the action the architect should take-?
- A . Disallow wireless access to the application.
- B . Deploy Intrusion detection capabilities using a network tap
- C . Create an acceptable use policy for the use of the application
- D . Create a separate network for users who need access to the application
D
Explanation:
Creating a separate network for users who need access to the application is the best action to secure an internal application that is critical to the production area and cannot be updated.
Why Separate Network?
Network Segmentation: Isolates the critical application from the rest of the network, reducing the risk of compromise and limiting the potential impact of any security incidents.
Controlled Access: Ensures that only authorized users have access to the application, enhancing security and reducing the attack surface.
Minimized Risk: Segmentation helps in protecting the application from vulnerabilities that could be exploited from other parts of the network.
Other options, while beneficial, do not provide the same level of security for a critical application:
DRAG DROP

An organization is planning for disaster recovery and continuity of operations.
INSTRUCTIONS
Review the following scenarios and instructions. Match each relevant finding to the affected host. After associating scenario 3 with the appropriate host(s), click the host to select the appropriate corrective action for that finding.
Each finding may be used more than once.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please click the Reset All button.
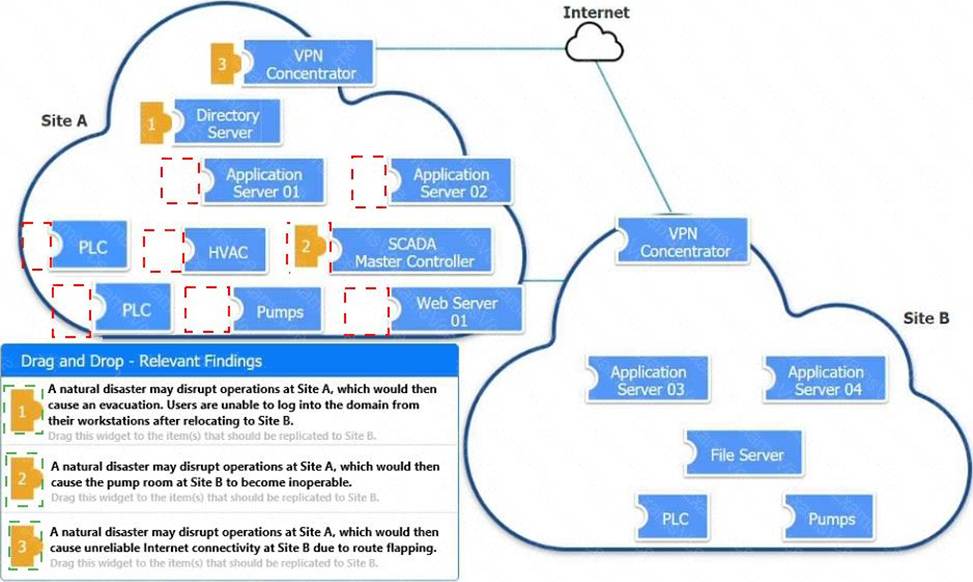
Explanation:
A computer screen shot of a diagram Description automatically generated

A screenshot of a computer error Description automatically generated

A financial services organization is using Al lo fully automate the process of deciding client loan rates.
Which of the following should the organization be most concerned about from a privacy perspective?
- A . Model explainability
- B . Credential Theft
- C . Possible prompt Injections
- D . Exposure to social engineering
A
Explanation:
When using AI to fully automate the process of deciding client loan rates, the primary concern from a
privacy perspective is model explainability.
Why Model Explainability is Critical:
Transparency: It ensures that the decision-making process of the AI model can be understood and explained to stakeholders, including clients.
Accountability: Helps in identifying biases and errors in the model, ensuring that the AI is making fair and unbiased decisions.
Regulatory Compliance: Various regulations require that decisions, especially those affecting individuals’ financial status, can be explained and justified.
Trust: Builds trust among users and stakeholders by demonstrating that the AI decisions are transparent and justifiable.
Other options, such as credential theft, prompt injections, and social engineering, are significant
concerns but do not directly address the privacy and fairness implications of automated decision-
making.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide
"The Importance of Explainability in AI," IEEE Xplore
GDPR Article 22, "Automated Individual Decision-Making, Including Profiling"
A security configure is building a solution to disable weak CBC configuration for remote access connections lo Linux systems.
Which of the following should the security engineer modify?
- A . The /etc/openssl.conf file, updating the virtual site parameter
- B . The /etc/nsswith.conf file, updating the name server
- C . The /etc/hosts file, updating the IP parameter
- D . The /etc/etc/sshd, configure file updating the ciphers
D
Explanation:
The sshd_config file is the main configuration file for the OpenSSH server. To disable weak CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) ciphers for SSH connections, the security engineer should modify the sshd_config file to update the list of allowed ciphers. This file typically contains settings for the SSH daemon, including which encryption algorithms are allowed.
By editing the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and updating the Ciphers directive, weak ciphers can be removed, and only strong ciphers can be allowed. This change ensures that the SSH server does not use insecure encryption methods.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide
OpenSSH manual pages (man sshd_config)
CIS Benchmarks for Linux
An organization is developing on Al-enabled digital worker to help employees complete common tasks such as template development, editing, research, and scheduling. As part of the Al workload
the organization wants to Implement guardrails within the platform.
Which of the following should the company do to secure the Al environment?
- A . Limn the platform’s abilities to only non-sensitive functions
- B . Enhance the training model’s effectiveness.
- C . Grant the system the ability to self-govern
- D . Require end-user acknowledgement of organizational policies.
A
Explanation:
Limiting the platform’s abilities to only non-sensitive functions helps to mitigate risks associated with AI operations. By ensuring that the AI-enabled digital worker is only allowed to perform tasks that do not involve sensitive or critical data, the organization reduces the potential impact of any security breaches or misuse.
Enhancing the training model’s effectiveness (Option B) is important but does not directly address
security guardrails. Granting the system the ability to self-govern (Option C) could increase risk as it
may act beyond the organization’s control. Requiring end-user acknowledgement of organizational
policies (Option D) is a good practice but does not implement technical guardrails to secure the AI
environment.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide
NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5, "Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations"
ISO/IEC 27001, "Information Security Management"
An analyst reviews a SIEM and generates the following report:

Only HOST002 is authorized for internet traffic.
Which of the following statements is accurate?
- A . The VM002 host is misconfigured and needs to be revised by the network team.
- B . The HOST002 host is under attack, and a security incident should be declared.
- C . The SIEM platform is reporting multiple false positives on the alerts.
- D . The network connection activity is unusual, and a network infection is highly possible.
D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed
Understanding the Security Event:
HOST002 is the only device authorized for internet traffic. However, the SIEM logs show that VM002 is making network connections to web.corp.local.
This indicates unauthorized access, which could be a sign of lateral movement or network infection.
This is a red flag for potential malware, unauthorized software, or a compromised host.
Why Option D is Correct:
Unusual network traffic patterns are often an indicator of a compromised system.
VM002 should not be communicating externally, but it is.
This suggests a possible breach or malware infection attempting to communicate with a command-and-control (C2) server.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A (Misconfiguration): While a misconfiguration could explain the unauthorized connections, the pattern of activity suggests something more malicious.
B (Security incident on HOST002): The issue is not with HOST002. The suspicious activity is from VM002.
C (False positives): The repeated pattern of unauthorized connections makes false positives unlikely.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Official Study Guide: Chapter on SIEM & Incident Analysis
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics: Lateral Movement & Network-based Attacks
NIST 800-94: Guidelines for Network Intrusion Detection and Analysis
A building camera is remotely accessed and disabled from the remote console application during off-hours.
A security analyst reviews the following logs:

Which of the following actions should the analyst take to best mitigate the threat?
- A . Implement WAF protection for the web application.
- B . Upgrade the firmware on the camera.
- C . Only allow connections from approved IPs.
- D . Block IP 104.18.16.29 on the firewall.
C
Explanation:
The logs indicate unauthorized access from 104.18.16.29, an external IP, to the building camera’s administrative console during off-hours. Restricting access only to approved IPs ensures that only authorized personnel can remotely control the cameras, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and manipulation.
Implementing WAF protection (A) secures against web application attacks but does not restrict unauthorized administrative access.
Upgrading the firmware (B) is good security hygiene but does not immediately mitigate the active threat.
Blocking IP 104.18.16.29 (D) is a temporary measure, as an attacker can switch to another IP. A better long-term solution is whitelisting trusted IPs.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX (CAS-005) Exam Objectives – Domain 4.0 (Security Operations), Section on Access Control and Network Security
SIMULATION
You are tasked with integrating a new B2B client application with an existing OAuth workflow that must meet the following requirements:
. The application does not need to know the users’ credentials.
. An approval interaction between the users and the HTTP service must be orchestrated.
. The application must have limited access to users’ data.
INSTRUCTIONS
Use the drop-down menus to select the action items for the appropriate locations. All placeholders must be filled.


Authorization Server:
Action Item: Grant access
The authorization server’s role is to authenticate the user and then issue an authorization code or token that the client application can use to access resources. Granting access involves the server authenticating the resource owner and providing the necessary tokens for the client application. Resource Server:
Action Item: Access issued tokens
The resource server is responsible for serving the resources requested by the client application. It must verify the issued tokens from the authorization server to ensure the client has the right permissions to access the requested data.
B2B Client Application:
Action Item: Authorize access to other applications
The B2B client application must handle the OAuth flow to authorize access on behalf of the user without requiring direct knowledge of the user’s credentials. This includes obtaining authorization tokens from the authorization server and using them to request access to the resource server.
Detailed
OAuth 2.0 is designed to provide specific authorization flows for web applications, desktop applications, mobile phones, and living room devices.
The integration involves multiple steps and components, including:
Resource Owner (User):
The user owns the data and resources that are being accessed.
Client Application (B2B Client Application):
Requests access to the resources controlled by the resource owner but does not directly handle the user’s credentials. Instead, it uses tokens obtained through the OAuth flow. Authorization Server:
Handles the authentication of the resource owner and issues the access tokens to the client application upon successful authentication.
Resource Server:
Hosts the resources that the client application wants to access. It verifies the access tokens issued by the authorization server before granting access to the resources. OAuth Workflow:
The resource owner accesses the client application.
The client application redirects the resource owner to the authorization server for authentication. The authorization server authenticates the resource owner and asks for consent to grant access to the client application.
Upon consent, the authorization server issues an authorization code or token to the client application.
The client application uses the authorization code or token to request access to the resources from the resource server.
The resource server verifies the token with the authorization server and, if valid, grants access to the
requested resources.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Provides comprehensive information on various authentication and authorization protocols, including OAuth.
OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework (RFC 6749): The official documentation detailing the OAuth 2.0 framework, its flows, and components.
OAuth 2.0 Simplified: A book by Aaron Parecki that provides a detailed yet easy-to-understand explanation of the OAuth 2.0 protocol.
By ensuring that each component in the OAuth workflow performs its designated role, the B2B client
application can securely access the necessary resources without compromising user credentials, adhering to the principle of least privilege.
