Practice Free AZ-204 Exam Online Questions
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Web app that uses Cosmos DB as a data store.
You create a CosmosDB container by running the following PowerShell script:
$resourceGroupName = "testResourceGroup"
$accountName = "testCosmosAccount"
$databaseName = "testDatabase"
$containerName = "testContainer"
$partitionKeyPath = "/EmployeeId"
$autoscaleMaxThroughput = 5000
New-AzCosmosDBSqlContainer
-ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName
-AccountName $accountName
-DatabaseName $databaseName
-Name $containerName
-PartitionKeyKind Hash
-PartitionKeyPath $partitionKeyPath
-AutoscaleMaxThroughput $autoscaleMaxThroughput
You create the following queries that target the container:
SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.EmployeeId > ‘12345’
SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.UserID = ‘12345’
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.


Explanation:
Box 1: No
You set the highest, or maximum RU/s Tmax you don’t want the system to exceed. The system automatically scales the throughput T such that 0.1* Tmax <= T <= Tmax.
In this example we have autoscaleMaxThroughput = 5000, so the minimum throughput for the container is 500 R/Us.
Box 2: No
First query: SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.EmployeeId > ‘12345’
Here’s a query that has a range filter on the partition key and won’t be scoped to a single physical partition. In order to be an in-partition query, the query must have an equality filter that includes the partition key:
SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.DeviceId > ‘XMS-0001’
Box 3: Yes
Example of In-partition query:
Consider the below query with an equality filter on DeviceId. If we run this query on a container partitioned on DeviceId, this query will filter to a single physical partition.
SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.DeviceId = ‘XMS-0001’
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/how-to-choose-offer
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/how-to-query-container
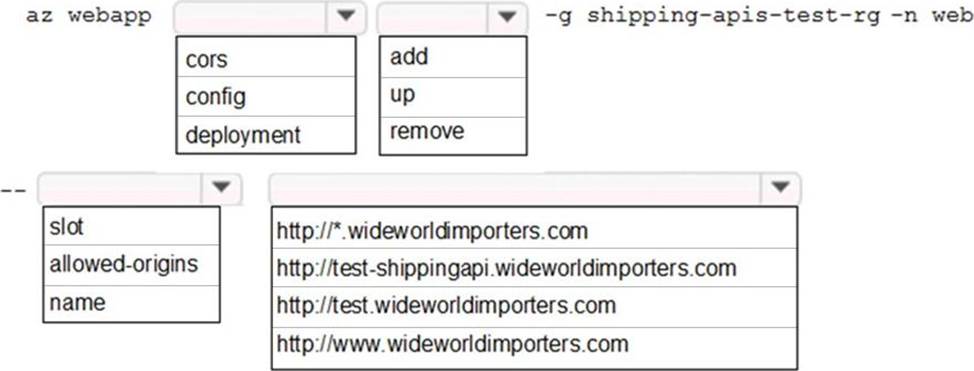
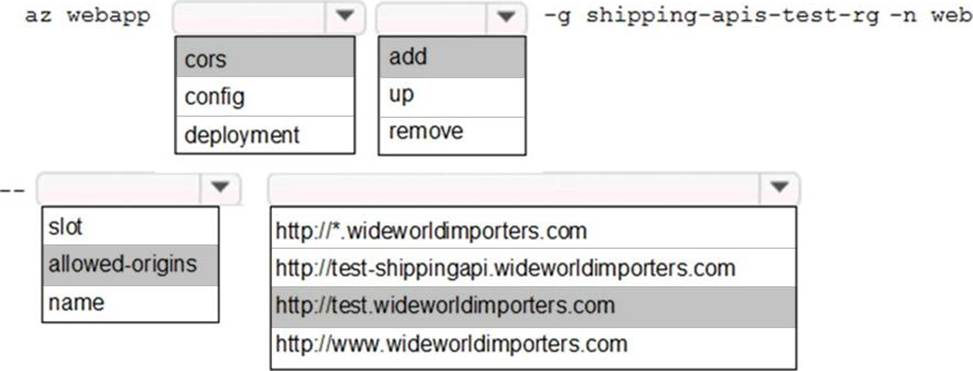
HOTSPOT
You need to update the APIs to resolve the testing error.
How should you complete the Azure CLI command? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation:
Enable Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) on your Azure App Service Web App.
Enter the full URL of the site you want to allow to access your WEB API or * to allow all domains.
Box 1: cors
Box 2: add
Box 3: allowed-origins
Box 4: http://testwideworldimporters.com/
Reference: http://donovanbrown.com/post/How-to-clear-No-Access-Control-Allow-Origin-header-error-with-Azure-App-Service
You need to configure all site configuration settings for the corporate website.
Which three actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A . Create a managed identity.
- B . Update the role assignments for the Azure App Configuration store
- C . Create an Azure Key Vault.
- D . Create an Azure App Configuration store.
- E . Update the role assignments for the Azure Key Vault.
You deploy an Azure App Service web app. You create an app registration for the app in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and Twitter. the app must authenticate users and must use SSL for all communications. The app must use Twitter as the identity provider. You need to validate the Azure AD request in the app code.
What should you validate?
- A . HTTP response code
- B . ID token header
- C . ID token signature
- D . Tenant ID
Call the Documents.Suggest method of the SearchIndexClient and pass the DataSource.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
B
Explanation:
Use the following method:
You have a Standard tier instance of Azure Cache for Radis named redis1 configured with the default settings.
You need to configure a Maxmemory policy to increase the amount of cache available for read operations.
How should you configure the Maxmemory policy?
- A . Decrease the value of maxmemory-reserved.
- B . Increase the value of maxmemory-reserved.
- C . Set the Maxmemory policy to noeviction.
- D . Set the Maxmemory policy to volatile-lru.
DRAG DROP
You are creating a script that will run a large workload on an Azure Batch pool. Resources will be reused and do not need to be cleaned up after use.
You have the following parameters:
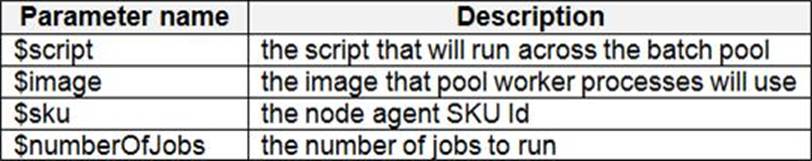
You need to write an Azure CLI script that will create the jobs, tasks, and the pool.
In which order should you arrange the commands to develop the solution? To answer, move the appropriate commands from the list of command segments to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

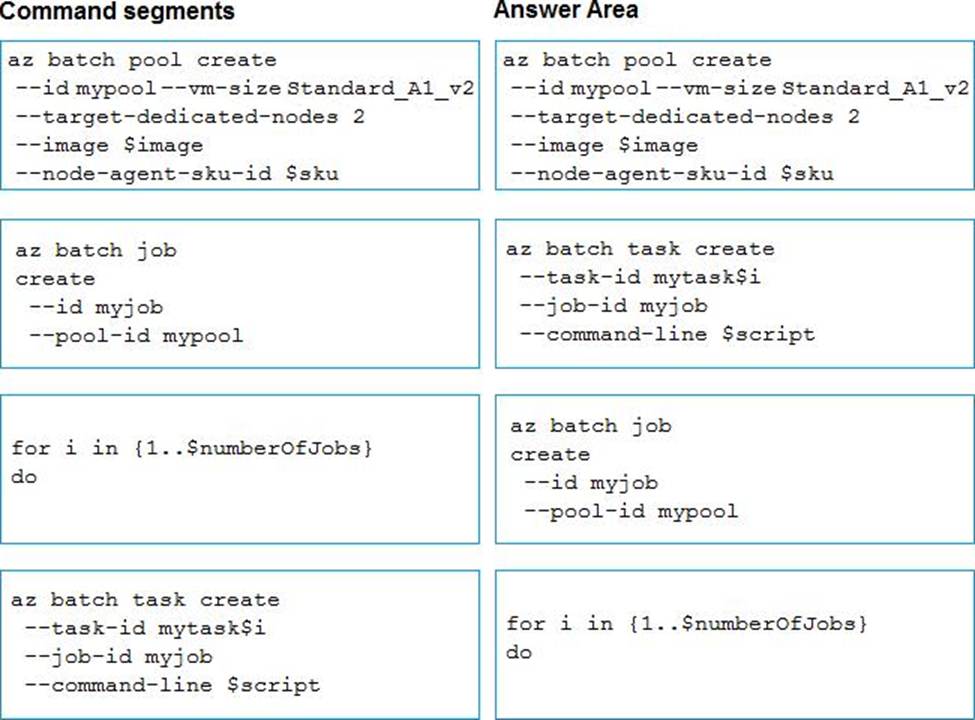
Explanation:
Step 1: az batch pool create
# Create a new Linux pool with a virtual machine configuration. az batch pool create
–id mypool
–vm-size Standard_A1 –target-dedicated 2
–image canonical:ubuntuserver:16.04-LTS
–node-agent-sku-id "batch.node.ubuntu 16.04"
Step 2: az batch job create
# Create a new job to encapsulate the tasks that are added. az batch job create
–id myjob
–pool-id mypool
Step 3: az batch task create
# Add tasks to the job. Here the task is a basic shell command. az batch task create
–job-id myjob –task-id task1
–command-line "/bin/bash -c ‘printenv AZ_BATCH_TASK_WORKING_DIR’"
Step 4: for i in {1..$numberOfJobs} do
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/bs-latn-ba/azure/batch/scripts/batch-cli-sample-run-job
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You develop an HTTP triggered Azure Function app to process Azure Storage blob data. The app is triggered using an output binding on the blob.
The app continues to time out after four minutes. The app must process the blob data.
You need to ensure the app does not time out and processes the blob data.
Solution: Update the functionTimeout property of the host.json project file to 10 minutes.
Does the solution meet the goal?
- A . Yes
- B . No
B
Explanation:
Instead pass the HTTP trigger payload into an Azure Service Bus queue to be processed by a queue trigger function and return an immediate HTTP success response.
Note: Large, long-running functions can cause unexpected timeout issues.
General best practices include:
Whenever possible, refactor large functions into smaller function sets that work together and return responses fast. For example, a webhook or HTTP trigger function might require an acknowledgment response within a certain time limit; it’s common for webhooks to require an immediate response.
You can pass the HTTP trigger payload into a queue to be processed by a queue trigger function. This approach lets you defer the actual work and return an immediate response.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-best-practices
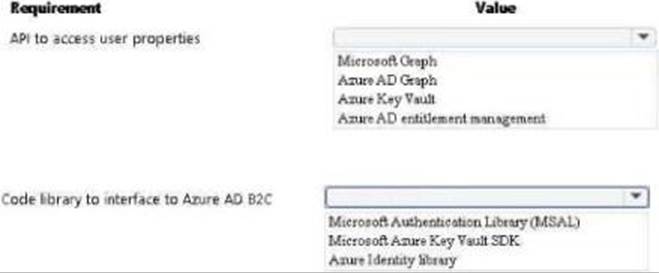
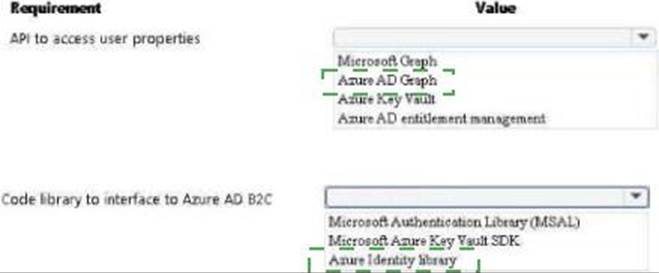
HOTSPOT
You develop and deploy a web app to Azure App service. The web app allows users to authenticate by using social identity providers through the Azure B2C service. All user profile information is stored in Azure B2C.
You must update the web app to display common user properties from Azure B2C to include the following information:
✑ Email address
✑ Job title
✑ First name
✑ Last name
You need to implem
✑ Office Locationent the user properties in the web app.
A company is developing a solution that allows smart refrigerators to send temperature information to a central location. You have an existing Service Bus.
The solution must receive and store message until they can be processed. You create an Azure Service Bus Instance by providing a name, pricing tier, subscription, resource group, and location.
You need to complete the configuration.
Which Azure CLI or PowerShell command should you run?
A)

B)

C)

D)

- A . Option A
- B . Option B
- C . Option C
- D . Option D
A
Explanation:
A service bus instance has already been created (Step 2 below). Next is step 3, Create a Service Bus queue.
Note:
Steps:
Step 1: # Create a resource group
resourceGroupName="myResourceGroup"
az group create –name $resourceGroupName –location eastus
Step 2: # Create a Service Bus messaging namespace with a unique name namespaceName=myNameSpace$RANDOM
az servicebus namespace create –resource-group $resourceGroupName –name $namespaceName –location eastus
Step 3: # Create a Service Bus queue
az servicebus queue create –resource-group $resourceGroupName –namespace-name $namespaceName –name BasicQueue
Step 4: # Get the connection string for the namespace
connectionString=$(az servicebus namespace authorization-rule keys list –resource-group
$resourceGroupName –namespace-name $namespaceName –name RootManageSharedAccessKey –query primaryConnectionString –output tsv)
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/service-bus-messaging/service-bus-quickstart-cli
