Practice Free 300-510 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.

A service provider technician is working on a multicast issue for a customer. While checking the multicast table, the technician notices that no flags are present for the (1.1.1.1, 239.1.1.1) entry, yet flags are present for the (1.1.1.1, 232.1.1.1) entry.
Which factor might explain this issue?
- A . Only the administratively scoped range is permitted
- B . Only ASM is permitted
- C . Only the default SSM range is permitted
- D . Only GLOP is permitted
Refer to the exhibit.
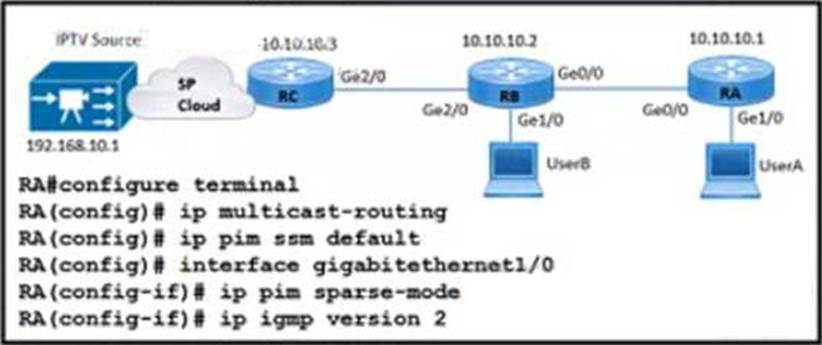
The UserA device fails to recede IPTV streaming traffic from the source While debugging the issue a network engineer finds that routers RB and RC receive the multicast traffic normally RC receives subscription messages from UserA to join the IPTV stream.
Which action must the engineer lake on router RA to correct this problem?
- A . Configure ip pim ssm with ip igmp version 2 on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0.
- B . Remove the ip pim ssm default configuration and replace it with ip pim rp-address 10.10.1.3
- C . Change ip igmp version 2 to ip igmp version 3 on interface GigabitEthernet 1/0.
- D . Configure ip pim bidir-enable in global mode and add ip pim rp-address 10.10.10.3
An engineer is troubleshooting a connectivity issue across the MPLS network and is verifying the forwarding behavior of packets.
Which table does the engineer look at to verify the forwarding behavior of an IP packet as it enters the MPLS network at the ingress LSR?
- A . LFIB
- B . LIB
- C . RIB
- D . FIB
A
Explanation:
https://community.cisco.com/t5/image/serverpage/image-id/44142iC3B9032F415B1395?v=v2
Refer to the exhibit.

Router 1 has established an SR-TE tunnel with router 2.
Which statement describes this configuration?
- A . Router 1 has a list of labels used to explicitly lay out a path to router 2.
- B . Router 1 and router 2 have a bidirectional tunnel set up with dynamic path selection.
- C . Router 1 is the head-end tunnel and has dynamically chosen a path to router 2.
- D . Router 2 is the head-end tunnel and has explicitly set a path to router 1.
Which difference must an engineer consider when choosing whether to implement OSPF or IS-IS as the routing protocol on the network?
- A . The OSPF DR election process is deterministic, and the IS-IS DS election process is not deterministic.
- B . To support fast convergence. OSPF uses the LSA arrival timer and IS-IS uses the PRC-interval timer.
- C . IS-IS supports ordinary, stub, totally-stub. and NSSA areas, but OSPF supports only stub areas.
- D . IS-IS links are associated with either a Level 1 area or a Level 2 area at one time, but OSPF links are associated with multiple areas at one time.
B
Explanation:
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_isis/configuration/15-s/irs-15-s-book/irs-fscnt.html
Refer to the exhibit.

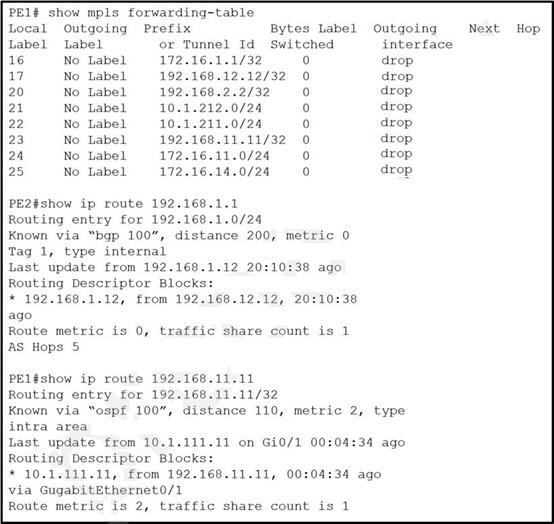
VPN users that are connected to PE routers are facing network issues. Traffic that originates from CE1 drops before reaching CE2. An engineer finds no outgoing traffic statistics on PE1 and PE2 routers toward CE devices and finds that the PE1 router is running the older software image.
Which action must be implemented to resolve the issues?
- A . Enable LDP protocol on PE1 and PE2 routers.
- B . Advertise P1 router loopback on PE1 in OSPF.
- C . Enable CEF-based forwarding on PE1 router.
- D . Advertise PE2 router loopback on PE1 in OSPF.
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/mp_basic/configuration/xe-3s/mp-basic-xe-3s-book/mp-mpls-cisco-rtrs.html
Refer to the exhibit.
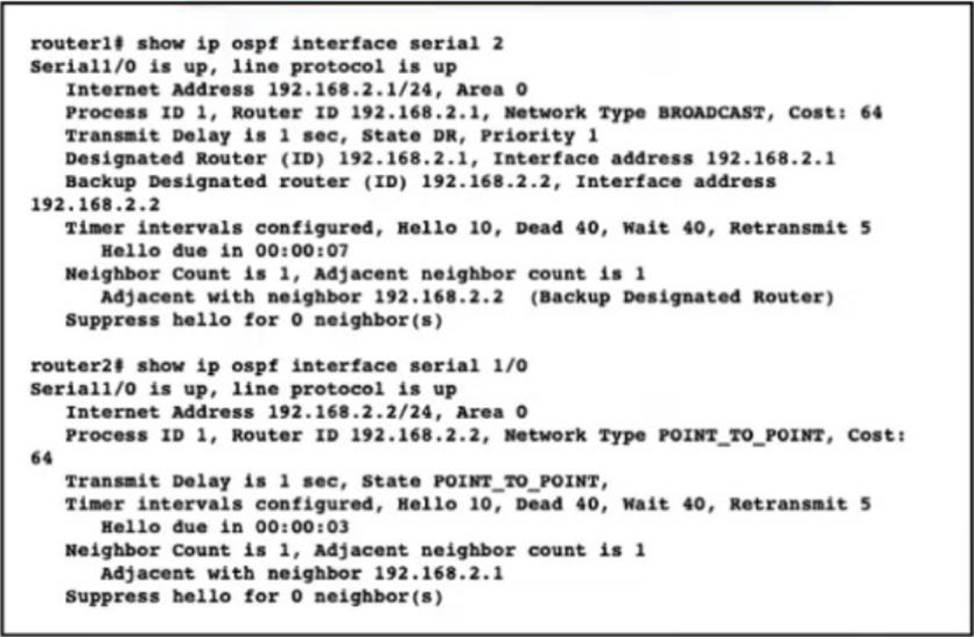
Router 1 and Router2 have shared routes in the OSPF database but the routes are missing from their routing tables. Checking me prefix-list configuration on both routers, the engineer confirmed all networks are allowed.
What action should the engineer take to fa the problem?
- A . Configure the two routers with different process IDs
- B . Configure the two routers with different hello and dead timer values
- C . Switch the DR and BDR roles between the two routers
- D . Configure interface Senal1/0 on Router1 as a point-to-point interface
For which reason can two BGP peers fail to establish a neighbor relationship?
- A . Their BGP send-community strings are misconfigured
- B . Their BGP timers are mismatched
- C . Their remote-as numbers are misconfigured
- D . They are both activated under an IPv4 address family
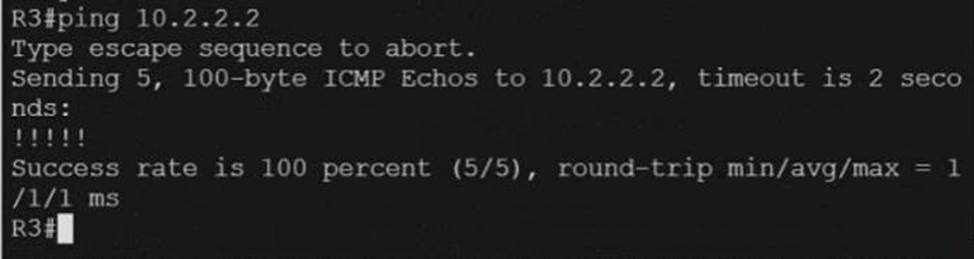
Refer to the exhibit.

Unified MPLS is implemented on this network to provide end-to-end services A network engineer noticed that R3 is failing to receive labels from R1 However, R2 is receiving labels from R1 R3 can ping R1 normally.
Which action resolves the issue?
- A . Add the cdp run command to the link configuration between R1 and R3.
- B . Add the send-label keyword in the R1 neighbor statement for R3.
- C . Configure R1 to run Unified MPLS on both interfaces.
- D . Disable mpls Ip on the link between R1 and R3
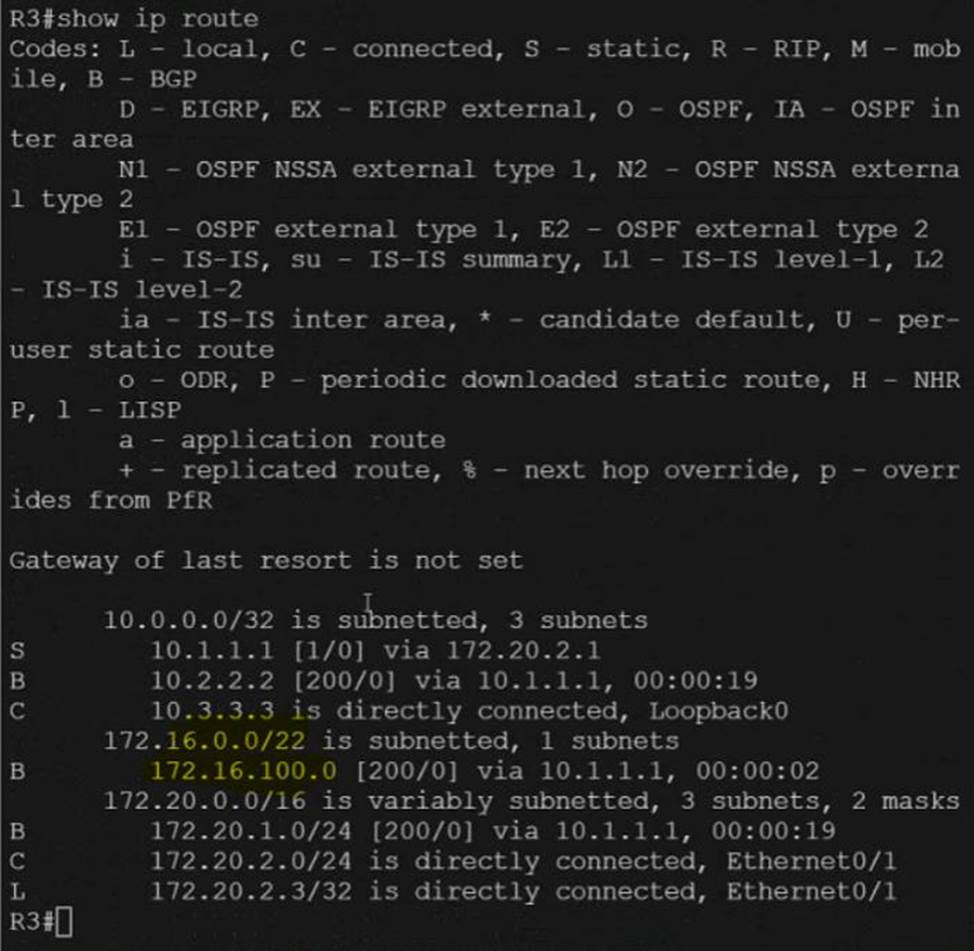
Refer to the exhibit.
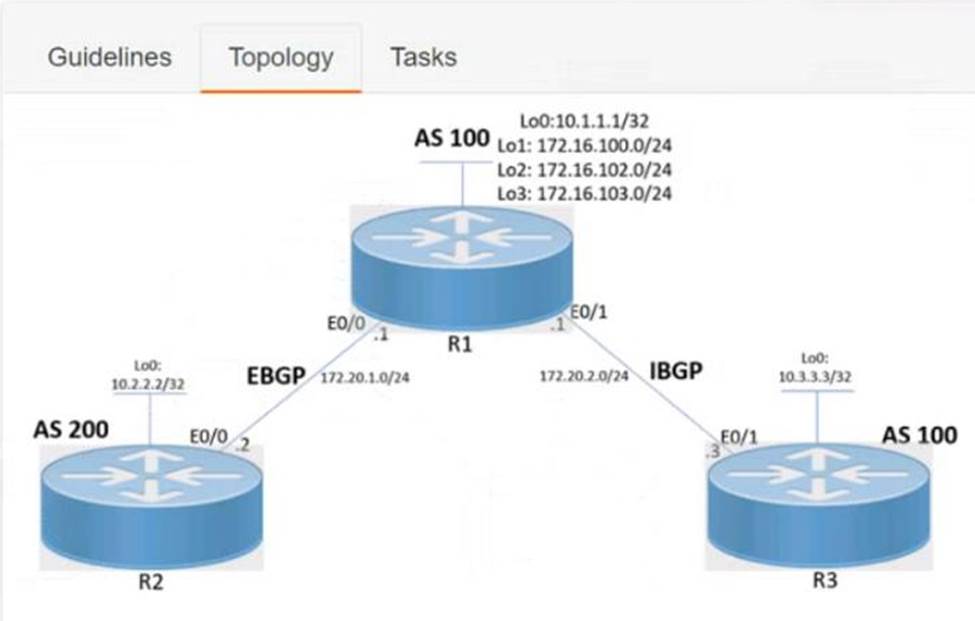
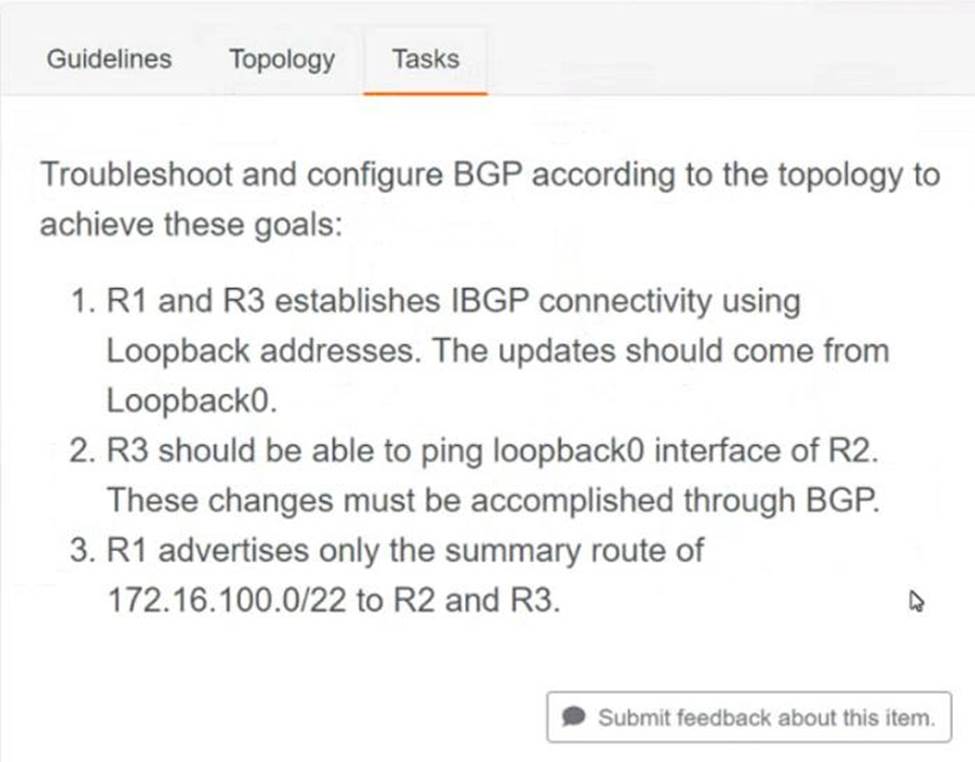
R1
Router bgp 100
Neigh 10.3.3.3 remote-as 100
Neigh 10.3.3.3 update-source loopback0
Address-family ipv4
Neigh 10.3.3.3 next-hop-self
Aggregate-address 172.16.100.0 255.255.252.0 summary-only
Copy run start
R3
Router bgp 100
Neigh 10.1.1.1 remote-as 100
Neigh 10.1.1.1 update-source loopback 0
Copy run start
Verification: –