Practice Free 2V0-41.24 Exam Online Questions
An administrator wants to validate the BGP connection status between the Tier-0 Gateway and the upstream physical router.
What sequence of commands could be used to check this status on NSX Edge node?
- A . – enable <LR-D>
– get vrf <ID>
– show bgp neighbor B.
– get gateways
– vrf <number>
– get bgp neighbor C.
– set vrf <ID>
– show logical-routers
– show <LR-D> bgp D.
– show logical-routers
– get vrf
– show ip route bgp
A
Explanation:
To validate the BGP connection status between the Tier-0 Gateway and the upstream physical router on an NSX Edge node, the correct sequence involves enabling the specific logical router (Tier-0 Gateway), checking the VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) context, and then using the show bgp neighbor command to view the BGP session status.
enable <LR-D>: This command enables the logical router interface (Tier-0 Gateway) to access its configuration.
get vrf <ID>: This command checks the specific VRF (used for routing separation) to see the associated routing table.
show bgp neighbor: This command displays the status of the BGP connection, including details about the neighbor relationships and their state.
An NSX administrator wants to create a Tier-0 Gateway to support equal cost multi-path (ECMP) routing.
Which failover detection protocol must be used to meet this requirement?
- A . Host Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
- B . Beacon Probing (BP)
- C . Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
- D . Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)
D
Explanation:
To support Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) routing in an NSX environment, Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) must be used for failover detection. BFD is a rapid failure detection protocol that works with ECMP to provide fast failure detection between routers. It helps in detecting link failures more quickly than traditional protocols, ensuring that traffic is routed through available paths as quickly as possible.
An administrator has deployed 10 Edge Transport Nodes in their NSX Environment, but has forgotten to specify an NTP server during the deployment.
What is the efficient way to add an NTP server to all 10 Edge Transport Nodes?
- A . Use a Node Profile
- B . Use Transport Node Profile
- C . Use the CLI on each Edge Node
- D . Use a PowerCLI script
B
Explanation:
Using a Transport Node Profile allows the administrator to apply configuration changes, such as specifying an NTP server, across multiple Edge Transport Nodes efficiently. This method is scalable and avoids the need for manual configuration on each individual node. Once the Transport Node Profile is updated, the configuration can be pushed to all associated nodes.
Which three protocols could an NSX administrator use to transfer log messages to a remote log server? (Choose three.)
- A . HTTPS
- B . SSH
- C . TCP
- D . UDP
- E . SSL
- F . TLS
C, D, F
Explanation:
Both TCP and UDP are commonly used protocols for transferring log messages in syslog configurations. TCP is preferred when reliability is needed, while UDP is used for faster, connectionless transmission.
TLS can be used to secure the log messages being sent over TCP, ensuring encrypted transmission to the remote log server.
What should an NSX administrator check to verify that VMware Identity Manager integration is successful?
- A . From the NSX Ul the status of the VMv/are Identity Manager Integration must be Enabled’
- B . From the NSX CLI the status of the VMware Identity Manager Integration must be Configured’
- C . From VMware Identity Manager the status of the remote access application must be green
- D . From the NSX Ul the URI in the address bar must have locaMalstf part of it.
B
Explanation:
To verify that VMware Identity Manager integration is successful with NSX, the administrator should check the NSX UI for the integration status. If it is configured correctly, the status should be marked as "Enabled," indicating that the integration is active and functioning.
Which command on ESXi is used to verify the Local Control Plane connectivity with Central Control Plane?
- A . esxcli network ip connection list | grep netcpa
- B . esxcli network ip connection list | grep ccpd
- C . esxcli network ip connection list | grep 1234
- D . esxcli network ip connection list | grep 1235
A
Explanation:
The netcpa process is responsible for Local Control Plane (LCP) connectivity with the Central Control Plane (CCP) in NSX. Using the command esxcli network ip connection list | grep netcpa, administrators can verify the connectivity status between the LCP on the ESXi host and the CCP, ensuring proper communication for NSX operations.
An NSX administrator is using ping to check connectivity between VM1 running on ESXi1 to VM2 running on ESXi2. The ping tests fail. The administrator knows the maximum transmission unit size on the physical switch is 1600.
Which command does the administrator use to check the VMware kernel ports for tunnel end point communication?
- A . vmkping ++netstack=geneve -d -s 1572 <destination IP address>
- B . vmkping ++netstack=vxlan -d -s 1572 <destination IP address>
- C . esxcli network diag ping CH <destination IP address>
- D . esxcli network diag ping -I vmk0 -H <destination IP address>
A
Explanation:
The vmkping ++netstack=geneve -d -s 1572 <destination IP address> command is used to check connectivity for VMware kernel ports specifically for Geneve tunnel endpoints (TEPs). The -s 1572 option sets the packet size to test within the 1600 MTU limit, accounting for the Geneve encapsulation overhead. The -d option enables the "Don’t Fragment" bit, ensuring the packet isn’t fragmented along the path, which is essential for verifying MTU consistency across the network.
An NSX administrator has deployed a single NSX Manager node and will be adding two additional nodes to form a 3-node NSX Management Cluster for a production environment. The administrator will deploy these two additional nodes and Cluster VIP using the NSX UI.
What two are the prerequisites for this configuration? (Choose two.)
- A . The cluster configuration must be completed using API.
- B . All nodes must be in the same subnet.
- C . All nodes must be in separate subnets.
- D . A compute manager must be configured.
- E . NSX Manager must reside on a Windows Server.
B, D
Explanation:
For a 3-node NSX Manager cluster, all nodes must be within the same subnet to ensure proper communication and functionality between them.
A compute manager must be configured before adding nodes to the cluster, as it provides the necessary integration between the NSX Manager and the underlying virtualization infrastructure (such as vSphere or vCenter).
Which three selections are capabilities of Network Topology? (Choose three.)
- A . Display how the different NSX components are interconnected.
- B . Display the VMs connected to Segments.
- C . Display how the Physical components are interconnected.
- D . Display the uplinks configured on the Tier-1 Gateways.
- E . Display the uplinks configured on the Tier-0 Gateways.
A, B, C
Explanation:
Display how the different NSX components are interconnected.
Network Topology in NSX provides a visual representation of how different NSX components (like Edge nodes, Logical Routers, and other NSX components) are interconnected. Display the VMs connected to Segments.
It also allows you to see which VMs are connected to specific segments (logical switches).
Display how the Physical components are interconnected.
The Network Topology view includes information about how physical network components are connected, providing a comprehensive overview of both the virtual and physical networking infrastructure.
HOTSPOT
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator configured NSX Advanced Load Balancer to load balance the production web server traffic, but the end users are unable to access the production website by using the VIP address.
Which of the following Tier-1 gateway route advertisement settings needs to be enabled to resolve the problem? Mark the correct answer by clicking on the image.
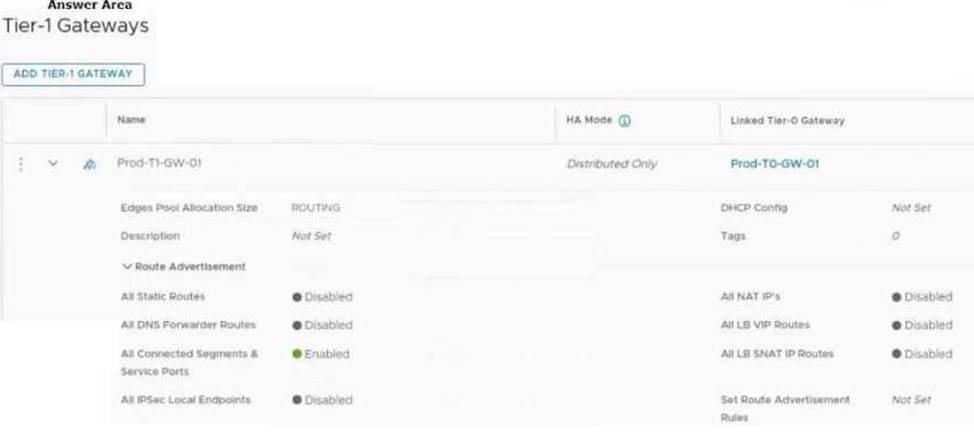
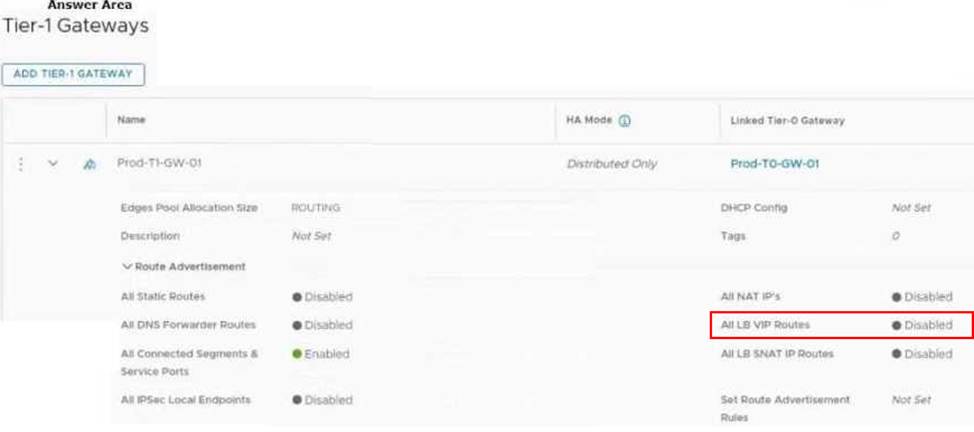
Explanation:
The correct answer is to enable the option All LB VIP Routes on the Tier-1 gateway route advertisement settings. This option allows the Tier-1 gateway to advertise the NSX Advanced Load Balancer LB VIP routes to the Tier-0 gateway and other peer routers, so that the end users can reach the production website by using the VIP address1. The other options are not relevant for this scenario.
To mark the correct answer by clicking on the image, you can click on the toggle switch next to All LB VIP Routes to turn it on. The switch should change from gray to blue, indicating that the option is enabled. See the image below for reference:
