Practice Free 2V0-41.24 Exam Online Questions
Which two steps must an NSX administrator take to integrate VMware Identity Manager in NSX to support role-based access control? (Choose two.)
- A . Create a SAML authentication in VMware Identity Manager using the NSX Manager FQDN.
- B . Add NSX Manager as a Service Provider (SP) in VMware Identity Manager.
- C . Enter the Identity Provider (IdP) metadata URL in NSX Manager.
- D . Enter the service URL, Client Secret, and SSL thumbprint in NSX Manager.
- E . Create an OAuth 2.0 client in VMware Identity Manager.
B, C
Explanation:
Adding NSX Manager as a Service Provider (SP) in VMware Identity Manager is necessary to enable SAML-based single sign-on (SSO), which allows VMware Identity Manager to manage and authenticate users accessing NSX.
Entering the Identity Provider (IdP) metadata URL in NSX Manager is required to establish a connection between NSX and VMware Identity Manager, enabling NSX to use VMware Identity Manager as the IdP for authentication.
Which VMware NSX Portfolio product can be described as a distributed analysis solution that provides visibility and dynamic security policy enforcement for NSX environments?
- A . NSX Manager
- B . NSX Distributed IDS/IPS
- C . NSX Intelligence
- D . NSX Cloud
C
Explanation:
NSX Intelligence is a distributed analytics solution within the VMware NSX Portfolio that provides visibility and dynamic security policy enforcement in NSX environments. It enables detailed traffic analysis, identifies security threats, and helps in the automated creation and enforcement of security policies based on observed network traffic patterns and behaviors.
DRAG DROP
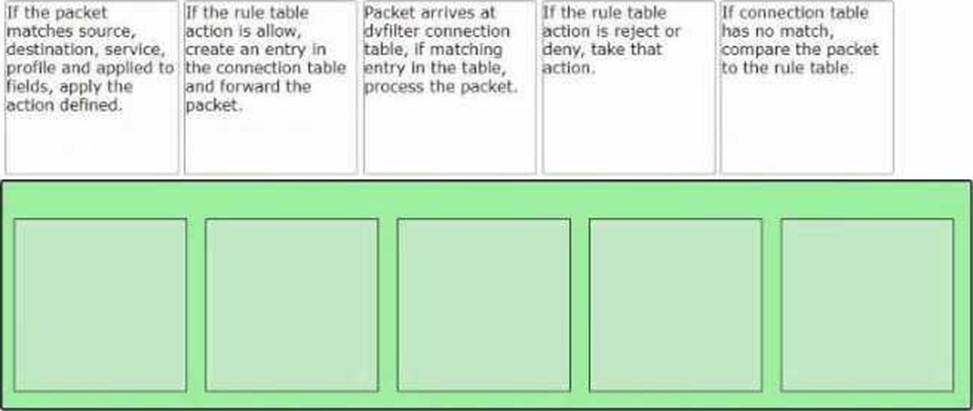
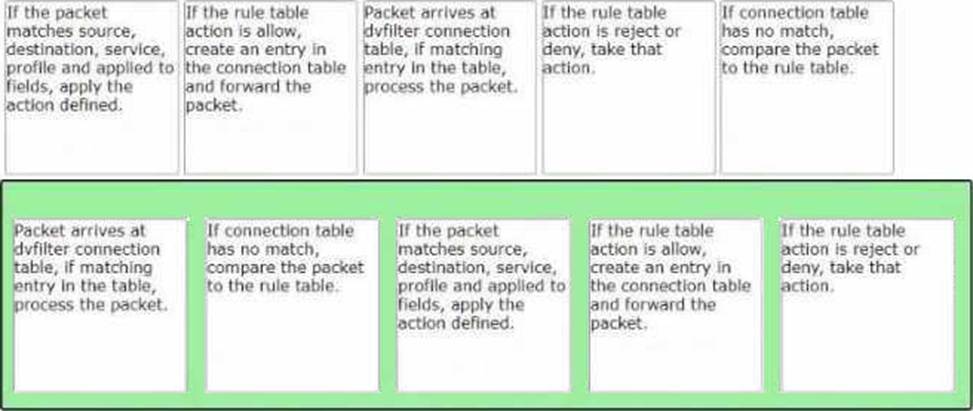
Sort the rule processing steps of the Distributed Firewall. Order responses from left to right.
Explanation:
The correct order of the rule processing steps of the Distributed Firewall is as follows:
Packet arrives at vfilter connection table. If matching entry in the table, process the packet.
If connection table has no match, compare the packet to the rule table.
If the packet matches source, destination, service, profile and applied to fields, apply the action defined.
If the rule table action is allow, create an entry in the connection table and forward the packet.
If the rule table action is reject or deny, take that action.
This order is based on the description of how the Distributed Firewall works in the web search results1. The first step is to check if there is an existing connection entry for the packet in the vfilter connection table, which is a cache of flow entries for rules with an allow action. If there is a match, the packet is processed according to the connection entry. If there is no match, the packet is compared to the rule table, which contains all the security policy rules. The rules are evaluated from top to bottom until a match is found. The match criteria include source, destination, service, profile and applied to fields. The action defined by the matching rule is applied to the packet. The action can be allow, reject or deny. If the action is allow, a new connection entry is created for the packet and the packet is forwarded to its destination. If the action is reject or deny, the packet is dropped and an ICMP message or a TCP reset message is sent back to the source.
A customer is preparing to deploy a VMware Kubernetes solution in an NSX environment.
What is the minimum MTU size for the UPLINK profile?
- A . 1700
- B . 1500
- C . 1550
- D . 1650
A
Explanation:
For a VMware Kubernetes deployment in an NSX environment, the minimum recommended MTU size for the UPLINK profile is 1700. This allows sufficient space for the additional overhead introduced by encapsulation protocols, such as Geneve, used in NSX-T Data Center, ensuring optimal performance and avoiding fragmentation.
Which two of the following features are supported for the Standard NSX Application Platform Deployment? (Choose two.)
- A . NSX Intrusion Detection and Prevention
- B . NSX Intelligence
- C . NSX Network Detection and Response
- D . NSX Malware Prevention Metrics
- E . NSX Intrinsic Security
CD
Explanation:
The NSX Application Platform Deployment features are divided into three form factors: Evaluation,
Standard, and Advanced. Each form factor determines which NSX features can be activated or
installed on the platform1. The Evaluation form factor supports only NSX Intelligence, which provides
network visibility and analytics for NSX-T environments2. The Standard form factor supports both
NSX Intelligence and NSX Network Detection and Response, which provides network threat
detection and response capabilities for NSX-T environments3. The Advanced form factor supports all
four features: NSX Intelligence, NSX Network Detection and Response, NSX Malware Prevention, and
NSX Metrics1.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/nsx-application-platform/GUID-85CD2728-8081-45CE-9A4A-D72F49779D6A.html
Which NSX CLI command is used to change the authentication policy for local users?
- A . set hardening-policy
- B . get auth-policy minimum-password-length
- C . set cli-timeout
- D . set auth-policy
D
Explanation:
The set auth-policy command in the NSX CLI is used to configure the authentication policy for local users. This command allows administrators to adjust settings related to password policies, lockout policies, and other authentication-related parameters for local user accounts on NSX Manager.
Which two statements are correct about East-West Malware Prevention? (Choose two.)
- A . A SVM is deployed on every ESXi host.
- B . NSX Application Platform must have Internet access.
- C . An agent must be installed on every ESXi host.
- D . An agent must be installed on every NSX Edge node.
- E . NSX Edge nodes must have Internet access.
AB
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-0A8BF7D8-9C2E-48A5-8219-17C00F1EC13A.html https://www.wwt.com/blog/primer-series-napp-malware-prevention
Which two statements are correct about East-West Malware Prevention? (Choose two.)
- A . A SVM is deployed on every ESXi host.
- B . NSX Application Platform must have Internet access.
- C . An agent must be installed on every ESXi host.
- D . An agent must be installed on every NSX Edge node.
- E . NSX Edge nodes must have Internet access.
AB
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-0A8BF7D8-9C2E-48A5-8219-17C00F1EC13A.html https://www.wwt.com/blog/primer-series-napp-malware-prevention
What are two valid BGP Attributes that can be used to influence the route path traffic will take? (Choose two.)
- A . AS-Path Prepend
- B . BFD
- C . Cost
- D . MED
AD
Explanation:
AS-Path Prepend: This attribute allows you to prepend one or more AS numbers to the AS path of a route, making it appear longer and less preferable to other BGP routers. You can use this attribute to manipulate the inbound traffic from your BGP peers by advertising a longer AS path for some routes and a shorter AS path for others.
MED: This attribute stands for Multi-Exit Discriminator and allows you to specify a preference value for a route among multiple exit points from an AS. You can use this attribute to manipulate the outbound traffic to your BGP peers by advertising a lower MED value for some routes and a higher MED value for others.
Which CLI command is used for packet capture on the ESXi Node?
- A . tcpdump
- B . set capture
- C . pktcap-uw
- D . debug
C
Explanation:
The pktcap-uw command is specifically used on ESXi hosts for packet capture. It provides a detailed packet capture utility that allows administrators to capture traffic at various points on the ESXi host, such as virtual switches, uplinks, and VMkernel interfaces, making it a powerful tool for network troubleshooting on ESXi nodes.
