Practice Free 2V0-41.24 Exam Online Questions
Which two are supported by L2 VPN clients? (Choose two.)
- A . NSX Autonomous Edge
- B . NSX Edge
- C . NSX for vSphere Edge
- D . 3rd party Hardware VPN Device
B, D
Explanation:
The NSX Edge supports L2 VPN (Layer 2 VPN) functionality, which allows it to connect different Layer 2 networks over an IP transport.
Third-party hardware VPN devices can also be used as L2 VPN clients, providing connectivity between different Layer 2 networks through an external device.
Which three DHCP Services are supported by NSX? (Choose three.)
- A . Gateway DHCP
- B . Segment DHCP
- C . DHCP Relay
- D . Port DHCP per VNF
- E . VRF DHCP Server
A, B, C
Explanation:
Gateway DHCP: NSX supports DHCP services configured on the gateway, allowing it to provide IP addresses to clients within the network.
Segment DHCP: NSX can provide DHCP services at the segment level, where DHCP is configured directly on a network segment to assign IP addresses to connected clients.
DHCP Relay: NSX supports DHCP Relay, which allows forwarding of DHCP requests to an external DHCP server for IP address assignment.
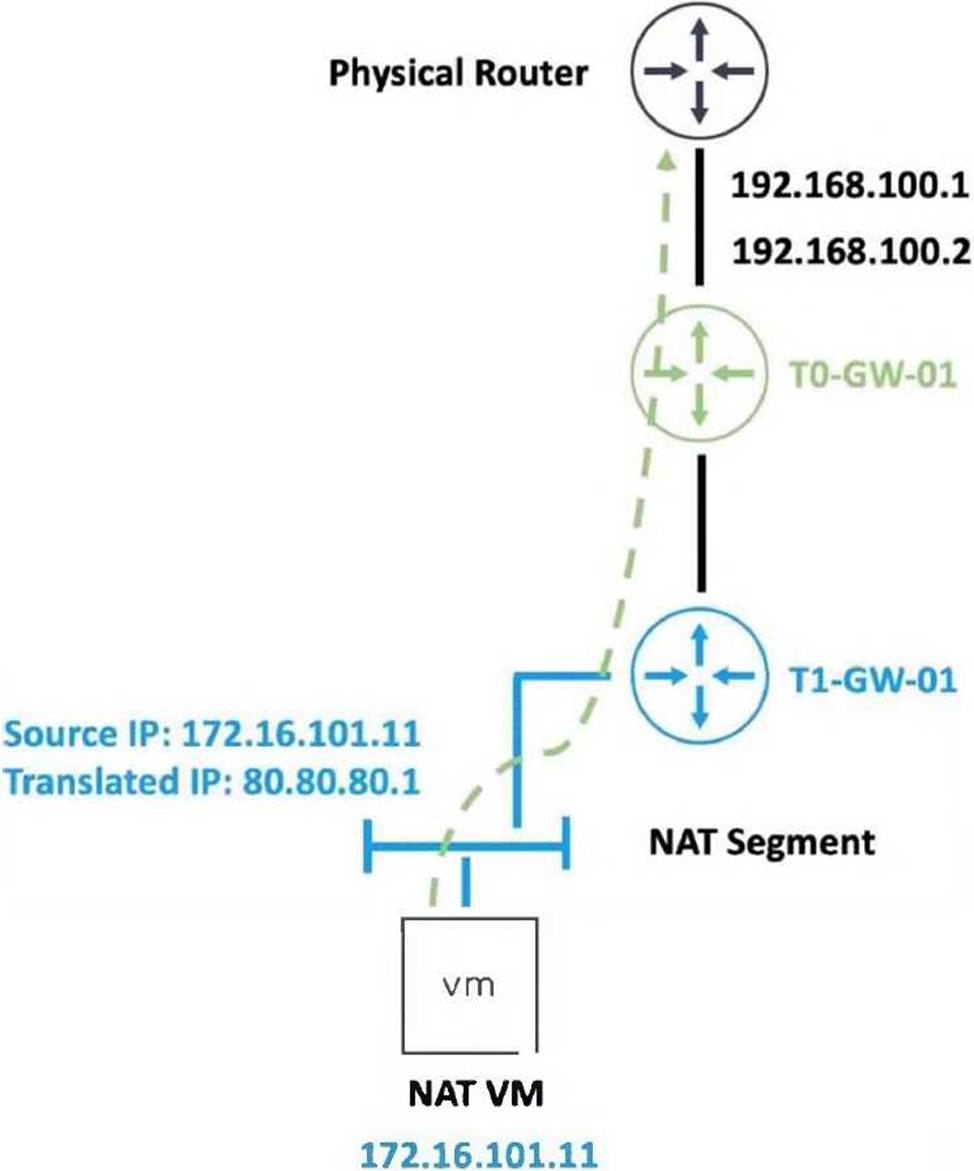
Refer to the exhibit.
An administrator would like to change the private IP address of the NAT VM 172.16.101.11 to a public address of 80.80.80.1 as the packets leave the NAT-Segment network.
Which type of NAT solution should be implemented to achieve this?
- A . NAT64
- B . Reflexive NAT
- C . DNAT
- D . SNAT
D
Explanation:
Source NAT (SNAT) is used to translate the private IP address (172.16.101.11) of the NAT VM to a public IP address (80.80.80.1) as the packets leave the NAT-Segment network. SNAT changes the source IP of outbound packets, allowing private IP addresses within the internal network to be mapped to public IP addresses for communication with external networks.
What are three NSX Manager roles? (Choose three.)
- A . master
- B . manager
- C . controller
- D . cloud
- E . policy
- F . zookeeper
A, C, F
Explanation:
master: The master role in NSX Manager is responsible for managing and coordinating the other NSX Manager nodes in the cluster.
policy: The policy role handles the policy-driven API and configuration, allowing administrators to define and manage network and security policies.
controller: The controller role in NSX Manager manages control plane functions and handles routing, switching, and other network state information required for NSX operations.
Which CLI command would an administrator use to allow syslog on an ESXi transport node when using the esxcli utility?
- A . esxcli network firewall ruleset set -a -e false
- B . esxcli network firewall ruleset set -r syslog -e false
- C . esxcli network firewall ruleset -e syslog
- D . esxcli network firewall ruleset set -r syslog -e true
D
Explanation:
The esxcli network firewall ruleset set -r syslog -e true command is used to enable the firewall ruleset for syslog on an ESXi host. Setting the -e flag to true allows syslog traffic through the ESXi firewall, enabling remote logging for syslog messages from the transport node.
Which two built-in VMware tools will help identify the cause of packet loss on VLAN Segments? (Choose two.)
- A . Flow Monitoring
- B . Traceflow
- C . Live Flow
- D . Packet Capture
- E . Activity Monitoring
B, D
Explanation:
Traceflow: This tool helps in troubleshooting network issues by injecting synthetic packets into the network and observing their path. It allows administrators to trace the packet flow across various network segments, making it easier to identify points of packet loss.
Packet Capture: This tool enables detailed inspection of traffic by capturing packets at specific points in the network. It allows administrators to analyze packet headers and payloads to determine if packet loss is occurring and to identify possible causes.
Which NSX feature can be leveraged to achieve consistent policy configuration and simplicity across sites?
- A . VRF Lite
- B . Ethernet VPN
- C . NSX MTML5 UI
- D . NSX Federation
D
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, this is the NSX feature that can be leveraged to achieve consistent policy configuration and simplicity across sites:
NSX Federation: This feature allows you to create and manage a global network infrastructure that spans across multiple sites using a single pane of glass. You can use this feature to synchronize policies, segments, gateways, firewalls, VPNs, load balancers, and other network services across sites.
An administrator has connected two virtual machines on the same overlay segment. Ping between both virtual machines is successful.
What type of network boundary does this represent?
- A . Layer 2 bridge
- B . Layer 2 broadcast domain
- C . Layer 2 VPN
- D . Layer 3 route
B
Explanation:
When two virtual machines are connected on the same overlay segment, they are part of the same Layer 2 broadcast domain. In this case, the communication between the two VMs is happening within the same broadcast domain, which means that broadcast traffic can be sent to all devices on the segment. Since the ping is successful, the two VMs can communicate directly over Layer 2 without needing routing.
An architect receives a request to apply distributed firewall in a customer environment without making changes to the network and vSphere environment. The architect decides to use Distributed Firewall on VDS.
Which two of the following requirements must be met in the environment? (Choose two.)
- A . vCenter 8.0 and later
- B . NSX version must be 3.2 and later
- C . NSX version must be 3.0 and later
- D . VDS version 6.6.0 and later
BD
Explanation:
Distributed Firewall on VDS is a feature of NSX-T Data Center that allows users to install Distributed Security for vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) without the need to deploy an NSX Virtual Distributed Switch (N-VDS). This feature provides NSX security capabilities such as Distributed Firewall (DFW), Distributed IDS/IPS, Identity Firewall, L7 App ID, FQDN Filtering, NSX Intelligence, and NSX Malware Prevention. To enable this feature, the following requirements must be met in the environment: The NSX version must be 3.2 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports Distributed Security for VDS.
The VDS version must be 6.6.0 and later1. This is the minimum version that supports the NSX host preparation operation that activates the DFW with the default rule set to allow.
Reference: Overview of NSX IDS/IPS and NSX Malware Prevention
An NSX administrator is creating a Tier-1 Gateway configured in Active-Standby High Availability
Mode. In the event of node failure, the failover policy should not allow the original failed node to
become the Active node upon recovery.
Which failover policy meets this requirement?
- A . Enable Preemptive
- B . Non-Preemptive
- C . Preemptive
- D . Disable Preemptive
B
Explanation:
In Non-Preemptive failover policy, once a failover occurs and a new Active node is designated, the original failed node will not automatically become the Active node upon recovery. This setting ensures that the failover does not revert to the original node after it comes back online, maintaining the stability of the network by keeping the current Active node as is.
