Practice Free 200-301 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
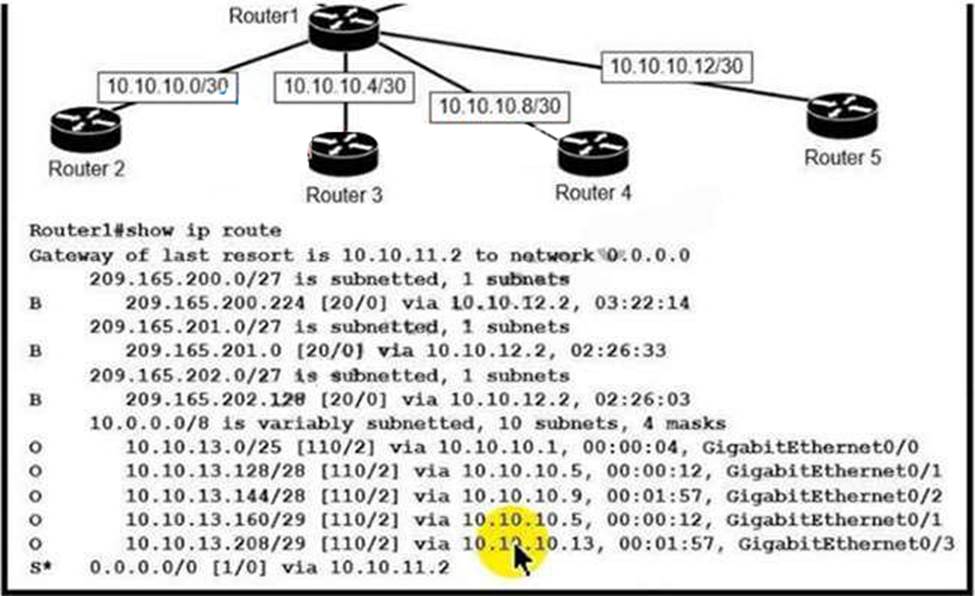
Which next-hop IP address does Routed use for packets destined to host 10 10.13.158?
- A . 10.10.10.5
- B . 10.10.11.2
- C . 10.10.12.2
- D . 10.10.10.9
Which IP header field is changed by a Cisco device when QoS marking is enabled?
- A . Header Checksum
- B . Type of service
- C . DSCP
- D . ECN
DRAG DROP
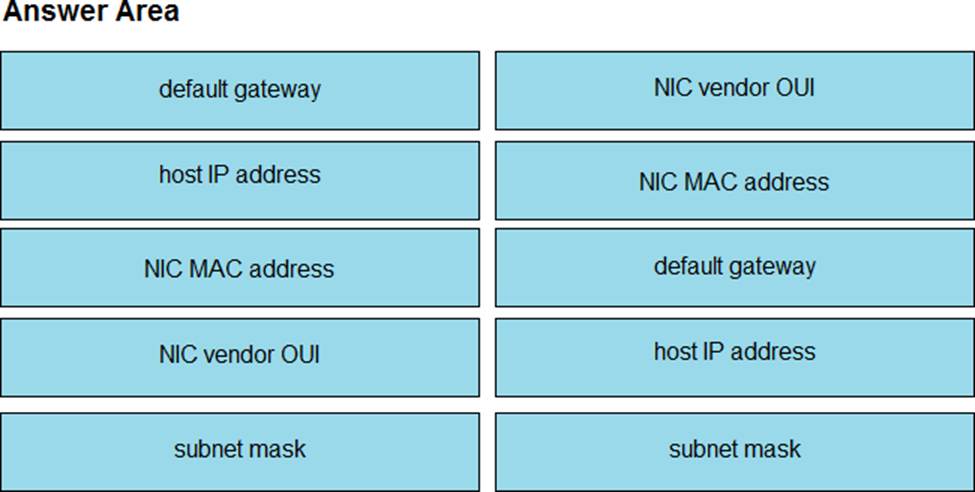
Refer to the exhibit.

Drag and drop the networking parameters from the left onto the correct values on the right.
Explanation:
NIC vendor OUI C> 00:0C:22
NIC MAC address C> 00:0C:22:83:79:A3
default gateway C> 192.168.1.193
host IP address C> 192.168.1.200
subnet mask C> 255.255.255.192
The “ip route” and “ip addr show eth1” are Linux commands.
+ “ip route”: display the routing table
+ “ip addr show eth1”: get depth information (only on eth1 interface) about your network interfaces like IP Address, MAC Address information
Which technology is appropriate for communication between an SDN controller and applications running over the network?
- A . OpenFlow
- B . REST API
- C . NETCONF
- D . Southbound API
A network administrator wants the syslog server to filter incoming messages into different files based on their Importance.
Which filtering criteria must be used?
- A . level
- B . message body
- C . process ID
- D . facility
What is a difference between RADIUS and TACACS+?
- A . RADIUS is most appropriate for dial authentication, but TACACS+ can be used for multiple types of authentication
- B . TACACS+ encrypts only password information and RADIUS encrypts the entire payload
- C . TACACS+ separates authentication and authorization, and RADIUS merges them
- D . RADIUS logs all commands that are entered by the administrator, but TACACS+ logs only start, stop, and interim commands
which IPv6 address block forwards packets to a multicast address rather than a unicast address?
- A . 2000::/3
- B . FC00::/7
- C . FE80::/10
- D . FF00::/12
What are two benefits of controller-based networking compared to traditional networking?
- A . controller-based increases network bandwidth usage, while traditional lightens the load on the network.
- B . controller-based inflates software costs, while traditional decreases individual licensing costs
- C . Controller-based reduces network configuration complexity, while traditional increases the potential for errors
- D . Controller-based provides centralization of key IT functions. While traditional requires distributes management function
- E . controller-based allows for fewer network failure, while traditional increases failure rates.
CD
Explanation:
Cisco DNA Center Device Management
in Which way does a spine and-leaf architecture allow for scalability in a network when additional access ports are required?
- A . A spine switch and a leaf switch can be added with redundant connections between them
- B . A spine switch can be added with at least 40 GB uplinks
- C . A leaf switch can be added with a single connection to a core spine switch.
- D . A leaf switch can be added with connections to every spine switch
D
Explanation:
Spine-leaf architecture is typically deployed as two layers: spines (such as an aggregation layer), and leaves (such as an access layer). Spine-leaf topologies provide high-bandwidth, low-latency, nonblocking server-to-server connectivity.
Leaf (aggregation) switches are what provide devices access to the fabric (the network of spine and leaf switches) and are typically deployed at the top of the rack. Generally, devices connect to the leaf switches.
Devices can include servers, Layer 4-7 services (firewalls and load balancers), and WAN or Internet routers. Leaf switches do not connect to other leaf switches. In spine-and-leaf architecture, every leaf should connect to every spine in a full mesh.
Spine (aggregation) switches are used to connect to all leaf switches and are typically deployed at the end or middle of the row. Spine switches do not connect to other spine switches.
What prevents a workstation from receiving a DHCP address?
- A . DTP
- B . STP
- C . VTP
- D . 802.10
