Practice Free 200-301 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
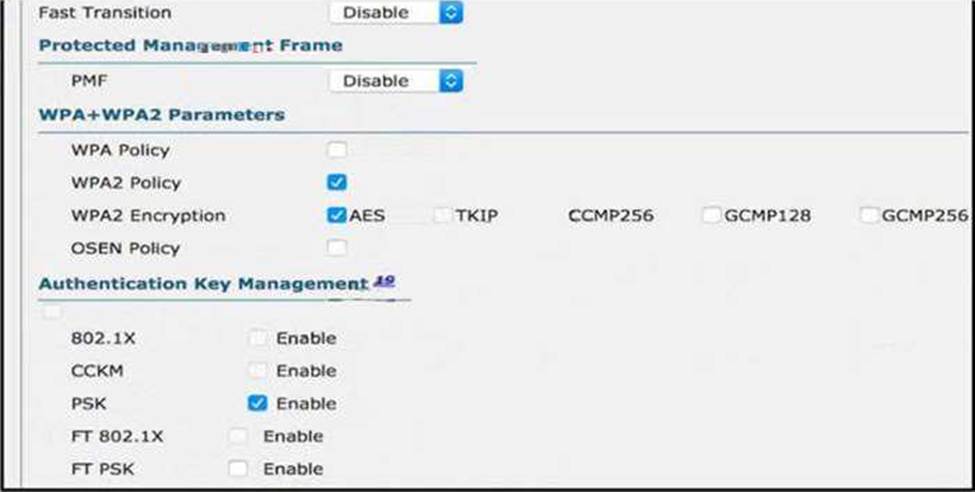
Users need to connect to the wireless network with IEEE 802. 11r-compatible devices. The connection must be maintained as users travel between floors or to other areas in the building.
What must be the configuration of the connection?
- A . Select the WPA Policy option with the CCKM option.
- B . Disable AES encryption.
- C . Enable Fast Transition and select the FT 802.1x option.
- D . Enable Fast Transition and select the FT PSK option.
What is a similarity between OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cable?
- A . Both have a 50 micron core diameter
- B . Both have a 9 micron core diameter
- C . Both have a 62.5 micron core diameter
- D . Both have a 100 micron core diameter
Which type of port is used to connect lo the wired network when an autonomous AP maps two VLANs to its WLANs?
- A . LAG
- B . EtherChannel
- C . trunk
- D . access
Refer to the exhibit.
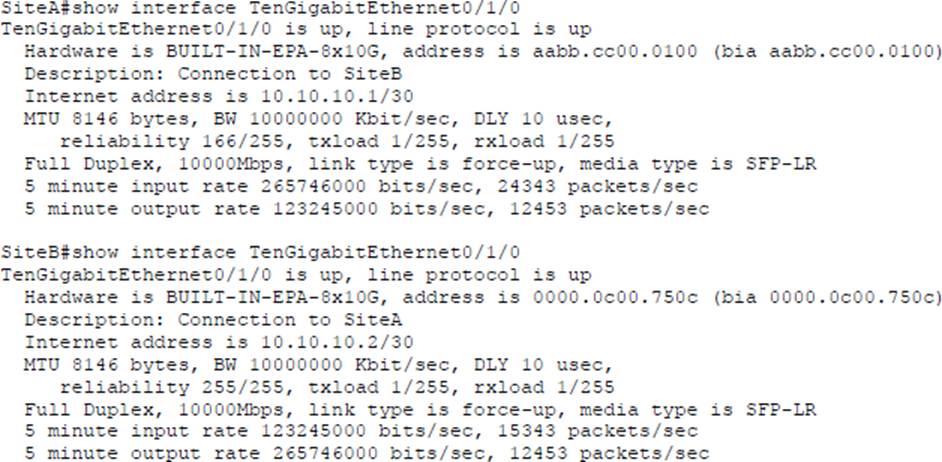
Shortly after SiteA was connected to SiteB over a new single-mode fiber path users at SiteA report intermittent connectivity issues with applications hosted at SiteB.
What is the cause of the intermittent connectivity issue?
- A . Interface errors are incrementing
- B . An incorrect SFP media type was used at SiteA
- C . High usage is causing high latency
- D . The sites were connected with the wrong cable type
What is the purpose of using First Hop Redundancy Protocol in a specific subnet?
- A . Filter traffic based on destination IP addressing
- B . Sends the default route to the hosts on a network
- C . ensures a loop-free physical topology
- D . forwards multicast hello messages between routers
D
Explanation:
FHRP is layer 3 protocol whose purpose is to protect the default gateway by offering redundancy of the gateway in a subnet. This is achieved by allowing two or more routers to provide a backup for the first-hop IP router address. If a failure of an active router occurs, the backup router will take over the address. The routers negotiate their roles (Active/Standby) with each other by multicast hello messages to share the VIP (virtual IP address) between the FHRP routers. The terms Active/Standby vary between the different types of FHRP. The active router will act as the default gateway and the standby router acts as a backup the active router.
Which condition must be met before an NMS handles an SNMP trap from an agent?
- A . The NMS software must be loaded with the MIB associated with the trap.
- B . The NMS must be configured on the same router as the SNMP agent
- C . The NMS must receive a trap and an inform message from the SNMP agent within a configured interval
- D . The NMS must receive the same trap from two different SNMP agents to verify that it is reliable.
Refer to the exhibit.

A packet is being sent across router R1 to host 172.163.3.14.
To which destination does the router send the packet?
- A . 207.165.200.246 via Serial0/1/0
- B . 207.165.200.254 via Serial0/0/1
- C . 207.165.200.254 via Serial0/0/0
- D . 207.165.200.250 via Serial/0/0/0
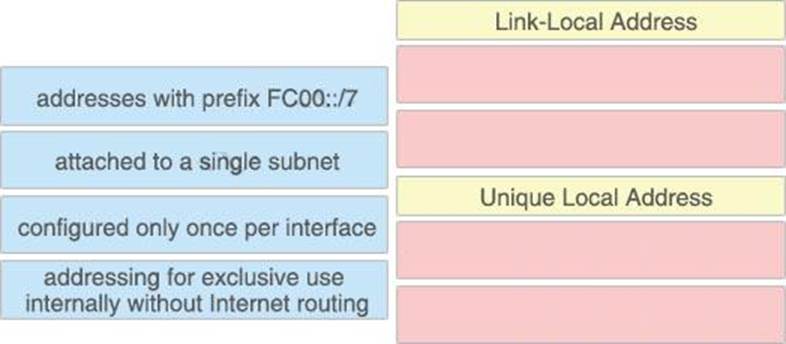
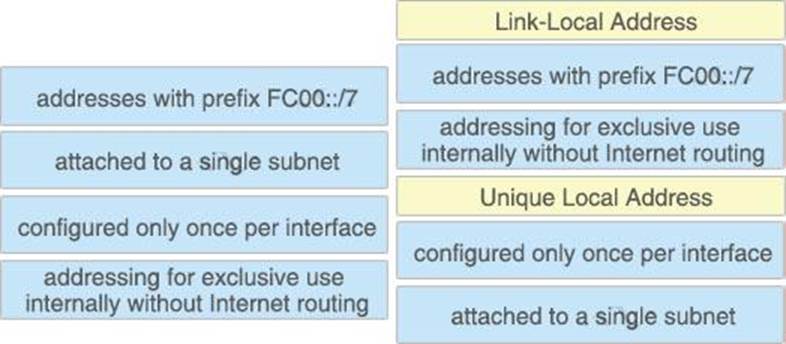
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the IPv6 address type characteristics from the left to the right.
What should a network administrator consider when deciding to implement automation?
- A . Automated systems may have difficulty expanding network changes at scale.
- B . Network automation typically is limited to the configuration and management of virtual devices within a network.
- C . Network automation typically increases enterprise management operating costs.
- D . Manual changes frequently lead to configuration errors and inconsistencies.
D
Explanation:
When deciding to implement automation, a network administrator should consider the benefits and challenges associated with automation. Option D highlights one of the key reasons for implementing automation―manual changes often result in configuration errors and inconsistencies. Automating repetitive and error-prone tasks can help improve the accuracy and reliability of network configurations.
Which two spanning-tree states are bypassed on an interface running PortFast? (Choose two.)
- A . disabled
- B . listening
- C . forwarding
- D . learning
- E . blocking
