Practice Free 200-201 Exam Online Questions
Refer to the exhibit.

What is the potential threat identified in this Stealthwatch dashboard?
- A . A policy violation is active for host 10.10.101.24.
- B . A host on the network is sending a DDoS attack to another inside host.
- C . There are two active data exfiltration alerts.
- D . A policy violation is active for host 10.201.3.149.
C
Explanation:
The exhibit shows a Stealthwatch dashboard displaying information on alarming hosts, alarms by type, and today’s alarms. On the left side under “Top Alarming Hosts,” there are five host IP addresses listed with their respective categories indicating different types of alerts including ‘Data Hoarding’ and ‘Exfiltration.’ In “Alarms by Type” section at center top part of image shows bar graphs representing various alarm types including ‘Crypto Violation’ with their respective counts. On right side under “Today’s Alarms,” there’s a table showing the details of each alarm such as the host IP, the alarm type, the severity, and the time. The potential threat identified in this dashboard is that there are two active data exfiltration alerts, one for host 10.201.3.149 and another for host 10.10.101.24. Data exfiltration is the unauthorized transfer of data from a compromised system to an external destination, such as a command and control server or a malicious actor. This can result in data loss, breach of confidentiality, and damage to the organization’s reputation and assets.
Reference: = Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals – Module 7: Network and Host Forensics
What does the Zero Trust security model signify?
- A . Zero Trust security means that no one is trusted by default from inside or outside the network
- B . Zero Trust states that no users should be given enough privileges to misuse the system on their own
- C . Zero Trust addresses access control and states that an individual should have only the minimum access privileges necessary to perform specific tasks
- D . Zero Trust states that unless a subject is given explicit access to an object, it should be denied access to that object
Refer to the exhibit.

An attacker scanned the server using Nmap.
What did the attacker obtain from this scan?
- A . Identified a firewall device preventing the pert state from being returned.
- B . Identified open SMB ports on the server
- C . Gathered information on processes running on the server
- D . Gathered a list of Active Directory users
B
Explanation:
The Nmap scan results show that several ports, including ftp (21/tcp), ssh (22/tcp), telnet (23/tcp), smtp (25/tcp), and http (80/tcp), are listed as “filtered”. This typically indicates that a firewall is filtering the traffic to these ports, making it impossible to determine whether they are open without further investigation. However, the question specifically asks about SMB ports, which are not shown in the provided Nmap scan results. Therefore, based on the information given, we cannot confirm
that the attacker identified open SMB ports on the server. The correct answer would require additional evidence not present in the scan results.
Reference: = Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) course materials and official Cisco documentation provide insights into interpreting Nmap scan results and identifying port states. These resources can be found at the Cisco Learning Network Store and Cisco’s official training and certifications webpage
Which security principle requires more than one person is required to perform a critical task?
- A . least privilege
- B . need to know
- C . separation of duties
- D . due diligence
C
Explanation:
Separation of duties is a security principle that requires more than one person to perform a critical task, such as authorizing a transaction, approving a budget, or granting access to sensitive data. Separation of duties reduces the risk of fraud, error, abuse, or conflict of interest by preventing any single person from having too much power or privilege. Least privilege, need to know, and due diligence are other security principles, but they do not require more than one person to perform a critical task.
Reference: Separation of Duty (SOD) – Glossary | CSRC – NIST Computer Security …, Separation of Duties | Imperva
A security engineer must investigate a recent breach within the organization. An engineer noticed that a breached workstation is trying to connect to the domain "Ranso4730-mware92-647". which is known as malicious.
In which step of the Cyber Kill Chain is this event?
- A . Vaporization
- B . Delivery
- C . reconnaissance
- D . Action on objectives
D
Explanation:
The event where a breached workstation is trying to connect to a known malicious domain suggests that the attacker is moving towards their end goals, which typically involves actions on objectives. In the Cyber Kill Chain framework, "Action on objectives" refers to the steps taken by an attacker to achieve their intended outcomes, such as data exfiltration, destruction, or ransom demands.
This phase involves the attacker executing their final mission within the target environment, leveraging access gained in earlier stages of the attack.
Reference: Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain
Understanding the Stages of Cyber Attacks
Incident Response and the Cyber Kill Chain
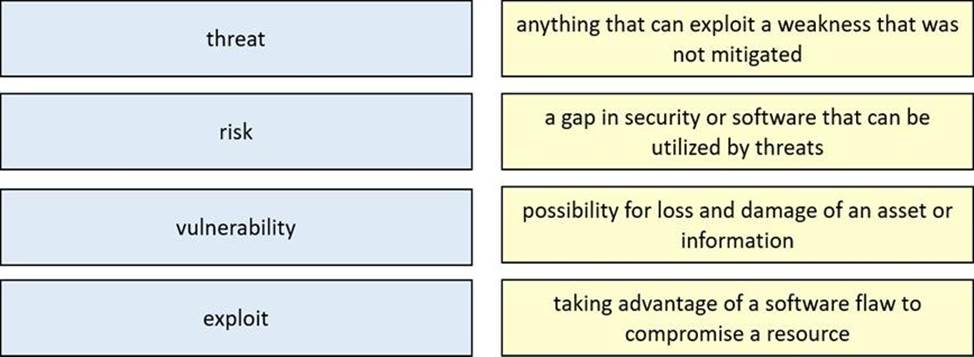
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the security concept from the left onto the example of that concept on the right.
Which type of data must an engineer capture to analyze payload and header information?
- A . frame check sequence
- B . alert data
- C . full packet
- D . session logs
C
Explanation:
To analyze both payload and header information, an engineer must capture the full packet data. This includes all protocol and payload information for the traffic, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of the data being transmitted5678.
Reference: Full packet capture is a common practice in network monitoring and security, as it provides detailed insights into the data transmitted over the network, including both payload and header information
While viewing packet capture data, an analyst sees that one IP is sending and receiving traffic for multiple devices by modifying the IP header.
Which technology makes this behavior possible?
- A . encapsulation
- B . TOR
- C . tunneling
- D . NAT
D
Explanation:
Network Address Translation (NAT) is the technology that allows a single IP address to send and receive traffic for multiple devices by modifying the IP header. NAT remaps one IP address space into another, enabling multiple devices to use a single public IP address to send and receive packets through the Internet2.
Reference: = The concept of NAT and its role in network traffic management is detailed in networking resources and documentation, including those provided by network solution providers2.
A network engineer noticed in the NetFlow report that internal hosts are sending many DNS requests to external DNS servers A SOC analyst checked the endpoints and discovered that they are infected and became part of the botnet Endpoints are sending multiple DNS requests but with spoofed IP addresses of valid external sources.
What kind of attack are infected endpoints involved in1?
- A . DNS hijacking
- B . DNS tunneling
- C . DNS flooding
- D . DNS amplification
D
Explanation:
The attack described is a DNS amplification attack. It involves infected endpoints sending DNS requests with spoofed IP addresses to external DNS servers. The DNS servers then send large responses to the spoofed addresses, which are actually the targets of the attack. This can result in a significant amount of traffic being directed at the target, overwhelming their network resources. DNS amplification is a type of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack that leverages the DNS protocol to amplify the attack traffic.
A company is using several network applications that require high availability and responsiveness, such that milliseconds of latency on network traffic is not acceptable. An engineer needs to analyze the network and identify ways to improve traffic movement to minimize delays.
Which information must the engineer obtain for this analysis?
- A . total throughput on the interface of the router and NetFlow records
- B . output of routing protocol authentication failures and ports used
- C . running processes on the applications and their total network usage
- D . deep packet captures of each application flow and duration
A
Explanation:
For high availability and responsiveness, especially where milliseconds of latency are critical, an engineer must analyze the network’s performance in detail. Total throughput on the interface of the router will provide information on the bandwidth and traffic load, which is essential for understanding if the network can handle the current and projected traffic without delays. NetFlow records are crucial for this analysis as they provide data about the traffic flow across the network, which helps in identifying patterns, peak usage times, and types of traffic. This information is vital for making informed decisions to optimize traffic movement and minimize latency123.
Reference: = Cisco’s guide on Network Traffic Analysis1.
Cisco’s white paper on Network Security Policy: Best Practices2.
Cisco’s documentation on Implementation of High Availability
