Practice Free 200-201 Exam Online Questions
Which technology on a host is used to isolate a running application from other applications?
- A . sandbox
- B . application allow list
- C . application block list
- D . host-based firewall
A
Explanation:
A sandbox is a technology on a host that is used to isolate a running application from other applications. A sandbox creates a controlled and restricted environment for the application to execute, limiting its access to system resources and data. A sandbox can prevent the application from spreading malware, stealing information, or causing damage to the host or the network. A sandbox can also be used to test and analyze the behavior of unknown or suspicious applications without risking the security of the host. Application allow list, application block list, and host-based firewall are other technologies on a host that can be used to control or restrict the execution of applications, but they do not isolate them from other applications.
Reference: How can I best isolate a particular program (game)
App isolation in Windows 10
Types of Endpoint Application Isolation and Containment Technology
An offline audit log contains the source IP address of a session suspected to have exploited a vulnerability resulting in system compromise.
Which kind of evidence is this IP address?
- A . best evidence
- B . corroborative evidence
- C . indirect evidence
- D . forensic evidence
B
Explanation:
The source IP address from an audit log that indicates a session which may have exploited a vulnerability is considered corroborative evidence. This type of evidence supports other evidence that suggests a security breach occurred. In the context of cybersecurity, corroborative evidence can help establish that an attack was carried out and can be used in conjunction with other data points to build a case during an investigation.
Reference: = The Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) training material discusses the types of data needed to investigate security incidents, which includes understanding the role of different types of evidence in building a security incident case1.
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the security concept on the left onto the example of that concept on the right.


Refer to the exhibit.
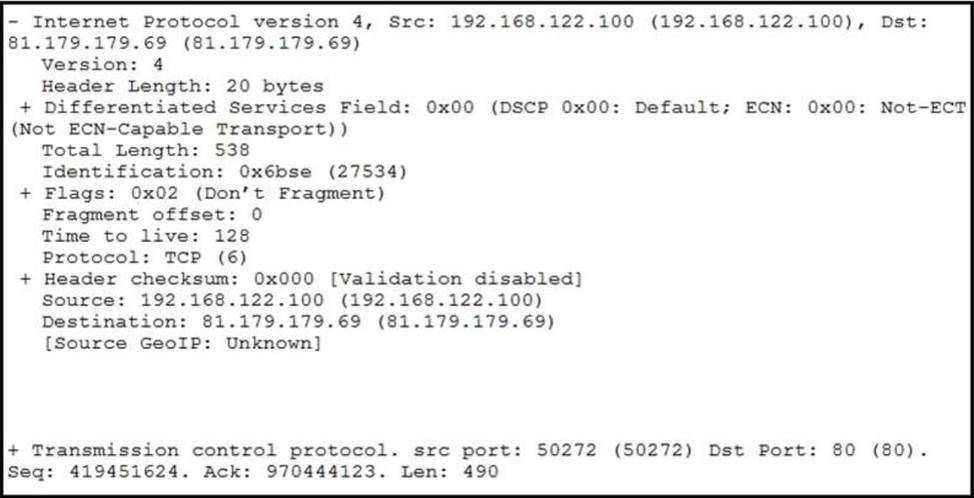
What should be interpreted from this packet capture?
- A . 81.179.179.69 is sending a packet from port 80 to port 50272 of IP address 192.168.122.100 using UDP protocol.
- B . 192.168.122.100 is sending a packet from port 50272 to port 80 of IP address 81.179.179.69 using TCP protocol.
- C . 192.168.122.100 is sending a packet from port 80 to port 50272 of IP address 81.179.179.69 using UDP protocol.
- D . 81.179.179.69 is sending a packet from port 50272 to port 80 of IP address 192.168.122.100 using TCP UDP protocol.
B
Explanation:
The packet capture exhibit shows that the source IP address is 192.168.122.100 and it is sending a packet from source port 50272 to destination port 80 of destination IP address 81.179.179.69 using TCP protocol. The TCP protocol is indicated by the Protocol field which has the value 6. The source and destination ports are indicated by the SrcPort and DstPort fields respectively. The source and destination IP addresses are indicated by the SrcAddr and DstAddr fields respectively.
Reference: = Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals – Module 3: Network Data and Event Analysis
A SOC analyst is investigating an incident that involves a Linux system that is identifying specific sessions.
Which identifier tracks an active program?
- A . application identification number
- B . active process identification number
- C . runtime identification number
- D . process identification number
D
Explanation:
In the context of Linux systems, each active program is tracked using a process identification number (PID). The PID is a unique number that the system uses to refer to a specific process, which is an instance of an executed program. This allows the system and the SOC analyst to monitor and manage different processes, including those initiated by users, the system itself, or by applications.
Reference: = Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) training material provides insights into how a Security Operations Center (SOC) operates and the tools and data used by analysts to monitor and investigate security incidents, including the tracking of active programs on system
Refer to the exhibit.
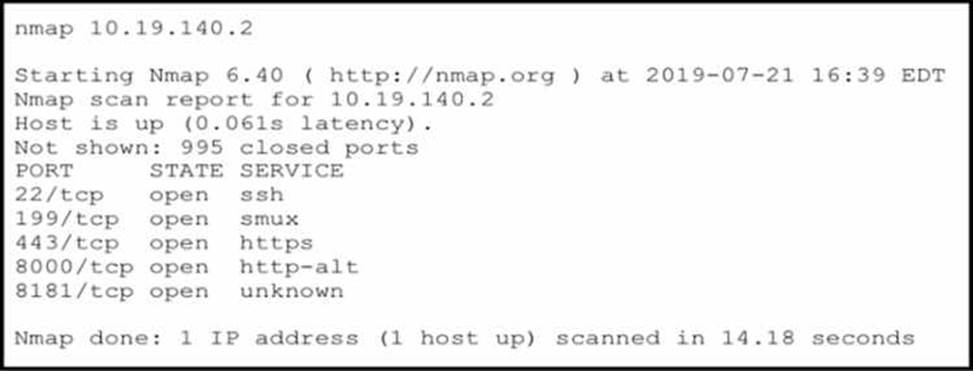
An attacker gained initial access to the company s network and ran an Nmap scan to advance with the lateral movement technique and to search the sensitive data.
Which two elements can an attacker identify from the scan? (Choose two.)
- A . workload and the configuration details
- B . user accounts and SID
- C . number of users and requests that the server is handling
- D . functionality and purpose of the server
- E . running services
D, E
Explanation:
An Nmap scan can provide detailed information about a network including the functionality and purpose of servers on that network as well as any services that are currently running on those servers. This information can be used by an attacker to identify potential vulnerabilities or targets for exploitation during a cyber attack.
Reference: = Cisco Cybersecurity Training
Refer to exhibit.

An engineer is Investigating an Intrusion and Is analyzing the pcap file.
Which two key elements must an engineer consider? (Choose two.)
- A . Variable "info" field and unchanging sequence number
- B . High volume oi SYN packets with very little variance in lime
- C . identical length of 120 and window size (64)
- D . SYN packets acknowledged from several source IP addresses
- E . same source IP address with a destination port 80
B, D
Explanation:
The exhibit shows a pcap file capturing multiple TCP SYN packets directed at the same destination IP address.
High volume of SYN packets with very little variance in time: This pattern is indicative of a SYN flood attack, a type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack where numerous SYN requests are sent to overwhelm the target system.
SYN packets acknowledged from several source IP addresses: This can be indicative of a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack where multiple compromised hosts (botnet) are used to generate traffic.
These characteristics suggest that the network is under a SYN flood or DDoS attack, aiming to exhaust the target’s resources and disrupt service availability.
Reference: Understanding SYN Flood Attacks
Analysis of DDoS Attack Patterns
Wireshark Analysis Techniques for Intrusion Detection
How does an attack surface differ from an attack vector?
- A . An attack vector recognizes the potential outcomes of an attack, and the attack surface is choosing
a method of an attack. - B . An attack surface identifies vulnerable parts for an attack, and an attack vector specifies which attacks are feasible to those parts.
- C . An attack surface mitigates external vulnerabilities, and an attack vector identifies mitigation techniques and possible workarounds.
- D . An attack vector matches components that can be exploited, and an attack surface classifies the potential path for exploitation
B
Explanation:
An attack surface is the sum of all the points where an attacker can try to enter or extract data from an environment. It includes all the hardware, software, network, and human components that are exposed to potential threats. An attack vector is the path or means by which an attacker can exploit a vulnerability in the attack surface. It describes the type, source, and technique of an attack, such as phishing, malware, denial-of-service, etc.
Reference: = Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) v1.0, Module 1: Security Concepts, Lesson 1.1: The CIA Triad and Security Concepts, Topic 1.1.3: Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Exploits
What is personally identifiable information that must be safeguarded from unauthorized access?
- A . date of birth
- B . driver’s license number
- C . gender
- D . zip code
B
Explanation:
Personally Identifiable Information (PII) refers to any data that can be used to identify a specific individual. Safeguarding PII is critical to protect individuals’ privacy and prevent identity theft. A driver’s license number (B) is considered PII because it is unique to an individual and can be used to confirm their identity. Other examples of PII include social security numbers, passport numbers, and financial account numbers. It is important to protect such information from unauthorized access to maintain personal privacy and security.
Reference: Identifying and Safeguarding Personally Identifiable Information (PII)2.
What makes HTTPS traffic difficult to monitor?
- A . SSL interception
- B . packet header size
- C . signature detection time
- D . encryption
D
Explanation:
HTTPS uses SSL/TLS encryption to secure data transmission over the internet. This encryption makes it difficult to monitor HTTPS traffic because the data packets are encrypted making them unreadable to anyone trying to intercept or monitor the data without proper decryption keys.
Reference: = Cisco CyberOps Associate
