Practice Free 200-201 Exam Online Questions
A security incident occurred with the potential of impacting business services.
Who performs the attack?
- A . malware author
- B . threat actor
- C . bug bounty hunter
- D . direct competitor
B
Explanation:
A threat actor is a person or entity that is responsible for an incident that impacts or has the potential to impact an organization’s security. A threat actor can have various motivations, such as financial gain, espionage, sabotage, or activism. A threat actor can use various methods, such as malware, phishing, denial-of-service, or social engineering, to perform an attack. A threat actor is not the same as a malware author, a bug bounty hunter, or a direct competitor, although they may be related or associated. A malware author is someone who creates malicious software that can be used by threat actors. A bug bounty hunter is someone who finds and reports vulnerabilities in software or systems for a reward. A direct competitor is someone who offers similar products or services as the organization and may seek to gain an advantage over it.
Reference: = Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) – Cisco, page 87; CNSSI 4009-2015, page 77
Reference: https://www.paubox.com/blog/what-is-threat-actor/#:~:text=The%20term%20threat%20actor%20refers,CTA)%20when%20referencing%20cyberse curity%20issues
An analyst discovers that a legitimate security alert has been dismissed.
Which signature caused this impact on network traffic?
- A . true negative
- B . false negative
- C . false positive
- D . true positive
B
Explanation:
A false negative occurs when an intrusion detection system (IDS) fails to detect and report actual malicious activity. This means that a legitimate security alert has been dismissed or overlooked, allowing potentially harmful traffic to pass through the network undetected. The impact of false negatives can be significant as they represent missed opportunities to stop or mitigate security threats1.
Reference: = Cisco documentation on security systems, such as IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), discusses the importance of accurately detecting malicious activity and the risks associated with false negatives, which include the failure to trigger alerts for actual attacks1.
Refer to the exhibit.
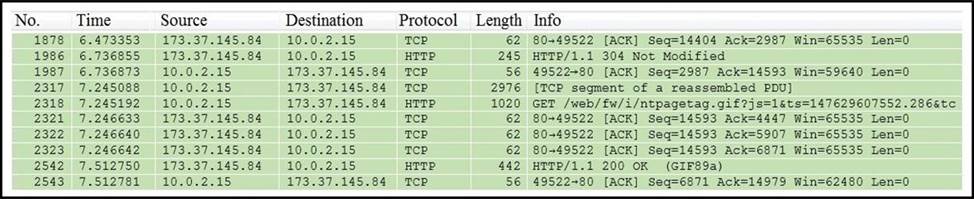
Which packet contains a file that is extractable within Wireshark?
- A . 2317
- B . 1986
- C . 2318
- D . 2542
C
Explanation:
Packet number 2318 is the one that contains a file that is extractable within Wireshark. This can be determined by the information provided in the packet details, which typically includes an HTTP GET request indicating the retrieval of a file, such as an image or document1.
Which piece of information is needed for attribution in an investigation?
- A . proxy logs showing the source RFC 1918 IP addresses
- B . RDP allowed from the Internet
- C . known threat actor behavior
- D . 802.1x RADIUS authentication pass arid fail logs
C
Explanation:
Cyber attribution is the process of identifying the source, motive, and methods of a cyberattack. Cyber attribution can help investigators to determine the responsibility, intent, and capability of the threat actors, as well as to prevent, deter, or respond to future attacks. One of the pieces of information that is needed for cyber attribution is known threat actor behavior, which refers to the patterns, techniques, tools, and tactics that are characteristic of a specific threat actor or group. Known threat actor behavior can help investigators to narrow down the suspects, link different incidents, and understand the objectives and strategies of the attackers.
Reference: = Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) v1.0, Module 5: Security Policies and Procedures, Lesson 5.2: Incident Response, Topic 5.2.3: Cyber Attribution, page 5-14.
A cyberattacker notices a security flaw in a software that a company is using They decide to tailor a specific worm to exploit this flaw and extract saved passwords from the software.
To which category of the Cyber Kill Cham model does this event belong?
- A . reconnaissance
- B . delivery
- C . weaponization
- D . exploitation
C
Explanation:
The category of the Cyber Kill Chain model that this event belongs to is weaponization. This stage occurs after reconnaissance has taken place and the attacker has discovered all necessary information about potential targets, such as vulnerabilities. In the weaponization stage, the attacker’s preparatory work culminates in the creation of malware to be used against an identified target, which in this case is a specific worm tailored to exploit a software flaw and extract saved passwords.
Reference: The Cyber Kill Chain framework, developed by Lockheed Martin, explains the weaponization stage as the process where attackers create or modify cyber weapons based on the intelligence gathered during reconnaissance
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the definition from the left onto the phase on the right to classify intrusion events according to the Cyber Kill Chain model.
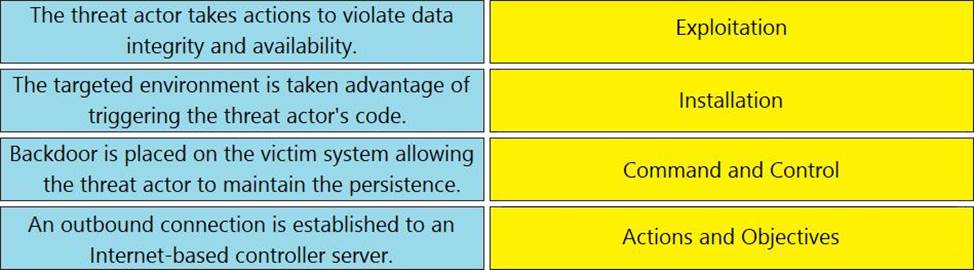
Explanation:
Exploitation – The targeted Environment is taken advantage of triggering the threat actor’s code
Installation – Backdoor is placed on the victim system allowing the threat actor to maintain the persistence.
Command and Control – An outbound connection is established to an Internet-based controller server.
Actions and Objectives – The threat actor takes actions to violate data integrity and availability
Which action should be taken if the system is overwhelmed with alerts when false positives and false negatives are compared?
- A . Modify the settings of the intrusion detection system.
- B . Design criteria for reviewing alerts.
- C . Redefine signature rules.
- D . Adjust the alerts schedule.
B
Explanation:
When a system is overwhelmed with alerts, designing criteria for reviewing alerts can help prioritize and manage them more effectively. This approach allows for a structured review process that can
distinguish between false positives, false negatives, and legitimate alerts, reducing the overall number of alerts that require attention3.
Reference: = The strategy of designing criteria for reviewing alerts is recommended in cybersecurity best practices to manage alert fatigue and improve the efficiency of security operations3.
What is indicated by an increase in IPv4 traffic carrying protocol 41?
- A . additional PPTP traffic due to Windows clients
- B . unauthorized peer-to-peer traffic
- C . deployment of a GRE network on top of an existing Layer 3 network
- D . attempts to tunnel IPv6 traffic through an IPv4 network
D
Explanation:
Protocol 41 is used to encapsulate IPv6 packets in IPv4 headers for transmission over an IPv4 network. This is one of the methods to implement IPv6 transition mechanisms for hosts and routers that are located on IPv4 networks. An increase in IPv4 traffic carrying protocol 41 may indicate that some hosts or routers are trying to tunnel IPv6 traffic through an IPv4 network, which could be a legitimate or malicious activity depending on the network policy.
Reference: = Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) – Cisco, page 177; [IPv6 Transition Mechanisms for IPv4 Domains]
How can TOR impact data visibility inside an organization?
- A . increases data integrity
- B . increases security
- C . decreases visibility
- D . no impact
C
Explanation:
TOR, or The Onion Router, is designed to conceal a user’s location and usage from anyone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis. Using TOR makes it more difficult to trace internet activity, including “visits to Web sites, online posts, instant messages, and other communication forms,” back to the user1. It is intended to protect the personal privacy of users, as well as their freedom and ability to conduct confidential communication by keeping their internet activities unmonitored. Within an organization, the use of TOR can decrease visibility into data traffic because it encrypts the data multiple times and routes it through a series of servers operated by volunteers around the globe. This makes network monitoring and data visibility challenging for cybersecurity professionals within the organization.
Reference: Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS)
What is the difference between the rule-based detection when compared to behavioral detection?
- A . Rule-Based detection is searching for patterns linked to specific types of attacks, while behavioral is identifying per signature.
- B . Rule-Based systems have established patterns that do not change with new data, while behavioral changes.
- C . Behavioral systems are predefined patterns from hundreds of users, while Rule-Based only flags potentially abnormal patterns using signatures.
- D . Behavioral systems find sequences that match a particular attack signature, while Rule-Based identifies potential attacks.
B
Explanation:
Rule-based detection involves identifying malicious activities based on predefined rules or patterns of known attacks; it does not adapt or change with new data. In contrast, behavioral detection adapts over time by learning from new data; it identifies malicious activities based on deviations from established norms or behaviors.
Reference: Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate Overview, Section 1.0: Security Concepts, Subsection 1.1: Compare and contrast the characteristics of data obtained from taps, NetFlow, and packet capture)
