Practice Free 200-201 Exam Online Questions
Which technique is a low-bandwidth attack?
- A . social engineering
- B . session hijacking
- C . evasion
- D . phishing
D
Explanation:
Phishing is considered a low-bandwidth attack because it does not require the use of significant network resources. Instead, it relies on social engineering to deceive individuals into providing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links, often through email or other communication methods1.
Refer to the exhibit.

An attacker scanned the server using Nmap.
What did the attacker obtain from this scan?
- A . Identified a firewall device preventing the port state from being returned
- B . Identified open SMB ports on the server
- C . Gathered information on processes running on the server
- D . Gathered a list of Active Directory users.
Which of these describes SOC metrics in relation to security incidents?
- A . time it takes to detect the incident
- B . time it takes to assess the risks of the incident
- C . probability of outage caused by the incident
- D . probability of compromise and impact caused by the incident
A
Explanation:
SOC metrics in relation to security incidents typically refer to the time it takes to detect the incident. These metrics are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of incident response and remediation efforts by SOC teams. For example, metrics like the Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) enable organizations to assess how quickly they can identify a security incident, which is essential for reducing the impact of the incident on the organization.
Refer to the exhibit.

Which field contains DNS header information if the payload is a query or a response?
- A . Z
- B . ID
- C . TC
- D . QR
D
Explanation:
The QR field in the DNS header specifies whether the message is a query (QR=0) or a response (QR=1). This bit is set to 0 for query messages and is set to 1 for response messages, allowing the recipient to distinguish between the two.
What is a difference between a threat and a risk?
- A . A threat is a sum of risks and a risk itself represents a specific danger toward the asset
- B . A threat can be people property, or information, and risk is a probability by which these threats may bring harm to the business
- C . A risk is a flaw or hole in security, and a threat is what is being used against that flaw
- D . A risk is an intersection between threat and vulnerabilities, and a threat is what a security engineer is trying to protect against
D
Explanation:
In cybersecurity, a threat is any potential malicious attack or event that can harm an organization, while a risk is the potential damage or loss that could occur if a threat exploits a vulnerability. Therefore, risk is considered the intersection of threats and vulnerabilities, representing the likelihood and impact of a threat materializing.
An engineer must configure network systems to detect command-and-control communications by decrypting ingress and egress perimeter traffic and allowing network security devices to detect malicious outbound communications.
Which technology must be used to accomplish this task?
- A . static IP addresses
- B . signatures
- C . digital certificates
- D . cipher suite
C
Explanation:
Digital certificates are essential for decrypting ingress and egress perimeter traffic, as they provide the necessary encryption keys for secure communications. By using digital certificates, network security devices can inspect the decrypted traffic to detect any malicious outbound communications that may indicate command-and-control activity.
Which artifact is used to uniquely identify a detected file?
- A . file timestamp
- B . file extension
- C . file size
- D . file hash
D
Explanation:
A file hash is a unique identifier that is used to detect a specific file. It is generated by running a file through a cryptographic hash function, which produces a string of characters that represents the contents of the file. If even a single bit in the file changes, the resulting hash will be different, making it an effective way to identify files uniquely.
What is a difference between SIEM and SOAR?
- A . SOAR predicts and prevents security alerts, while SIEM checks attack patterns and applies the mitigation.
- B . SlEM’s primary function is to collect and detect anomalies, while SOAR is more focused on security operations automation and response.
- C . SIEM predicts and prevents security alerts, while SOAR checks attack patterns and applies the mitigation.
- D . SOAR’s primary function is to collect and detect anomalies, while SIEM is more focused on security operations automation and response.
B
Explanation:
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems are solutions that provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. They collect, store, analyze, and report on log data for incident response, forensics, and regulatory compliance. On the other hand, SOAR (Security Orchestration Automation and Response) platforms allow organizations to collect data about security threats from multiple sources and respond to low-level security events without human assistance.
Reference: Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/security/what-is-a-security-platform.html
Refer to the exhibit.
Which type of log is displayed?
- A . IDS
- B . proxy
- C . NetFlow
- D . sys
D
Explanation:
The exhibit displays a sys log which is used in computer systems for messaging logs. It provides messaging tracking services from different devices like routers, switches etc., which helps in tracking and identifying potential issues.
Reference: = Cisco Cybersecurity source documents or study guide
DRAG DROP
Refer to the exhibit.

Drag and drop the element name from the left onto the correct piece of the PCAP file on the right.

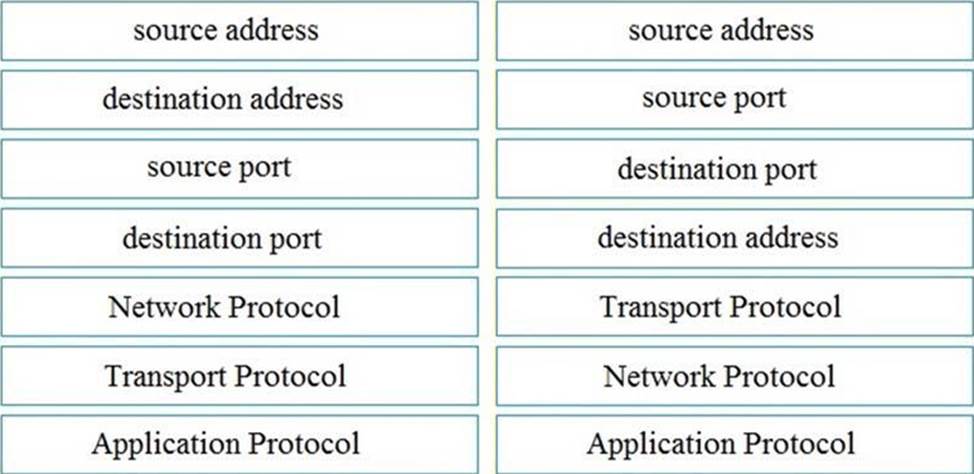
Explanation:
In a PCAP file, which is used to capture network packets, each packet contains various pieces of information that can be analyzed. The source and destination addresses refer to the IP addresses of the sender and receiver of the packets. The source and destination ports refer to the port numbers used for the communication, with common ports like 443 indicating HTTPS traffic. The network protocol here is TCP, which is responsible for establishing a connection and ensuring the delivery of packets. The transport protocol is IPv4, which is the underlying protocol for routing packets across the network. Lastly, the application protocol is TLS v1.2, which is used for secure communication over the internet.
Reference: = The Understanding Cisco Cybersecurity Operations Fundamentals (CBROPS) course material covers the analysis of network traffic and the interpretation of PCAP files, which includes identifying the different elements within a packet capture1.
